Hunting for the elusive tetraneutrons with thermal fission
2024-01-04
(Press-News.org)
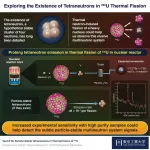
Tetraneutron is an elusive atomic nucleus consisting of four neutrons, whose existence has been highly debated by scientists. This stems primarily from our lack of knowledge about systems consisting of only neutrons, since most atomic nuclei are usually made of a combination of protons and neutrons. Scientists believe that the experimental observation of a tetraneutron could be the key to exploring new properties of atomic nuclei and answering the age-old question: Can a charge-neutral multineutron system ever exist?
Two recent experimental studies reported the presence of tetraneutrons in bound state and resonant state (a state that decays with time but lives long enough to be detected experimentally). However, theoretical studies indicate that tetraneutrons will not exist in a bound state if the interactions between neutrons are governed by our common understanding of two or three-body nuclear forces.
Intrigued, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Hiroyuki Fujioka from Tokyo Institute of Technology set out to investigate the feasibility of bound tetraneutron emission. In their recent study published in Physical Review C, the team explored the possible emission rate of particle-stable tetraneutron via thermal neutron-induced fission of 235U (Uranium-235) in a nuclear reactor. “We are aware from previous literature that the dominant thermal fission process for 235U is binary fission, which leads to the emission of two heavy nuclear fragments together with 2.4 neutrons, on average. But there is a 0.2% probability of ternary fission, in which light nuclear fragments are emitted. We, therefore, chose this route for our experiment under the assumption that the hypothetically bound tetraneutron could be a ternary particle in uranium fission,” explains Dr. Fujioka.
The team adopted the well-known instrumental neutron activation analysis method, where a trace element in a chosen sample is irradiated and activated by the capture of thermal neutrons. For this study, 88SrCO3 was chosen as the target sample and was irradiated for two hours at a thermal power of 5 MW in a nuclear research reactor. The team also performed γ-ray spectroscopy for the irradiated sample to detect signals corresponding to a possible tetraneutron emission.
The 88Sr nuclei were expected to convert into 91Sr with a Q value (change in mass between the initial and final states of a reaction expressed in terms of energy units) of 20 MeV minus the binding energy of the tetraneutron. Since 91Sr is unstable, its radioactive decay followed by the release of γ-rays would indicate the emission of particle-stable tetraneutrons.
The γ-ray spectroscopy results for the irradiated 88Sr sample, however, did not show any photopeak corresponding to the formation of 91Sr. Based on this, the team estimated that if particle-stable tetraneutrons exist, their emission rate might be lower than 8 × 10−7 per fission at the 95% confidence level. They also suggested that improving the purity of samples and increasing the sensitivity of experimentation could help with the detection of subtle signals arising from tetraneutrons.
Dr. Fujioka says, “Our study showed that the instrumental neutron activation method in radiochemistry can be applied to address the open question in nuclear physics. We will improve the sensitivity further to seek for the elusive, charge-neutral system.”
While the team was not able to detect bound tetraneutrons, their work has laid a solid framework for future studies on the elusive tetraneutrons and other such systems.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-04
Over the past decades, scientists have made substantial progress unveiling the underlying mechanisms behind many psychiatric disorders. Every year, new genetic mutations or protein dysregulations are identified as potential culprits for the symptoms, and sometimes even the root causes of complex neurological diseases, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s.
Despite these efforts, the precise roles of several proteins involved in brain function remain obscure. Such is the case for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2), an enzyme expressed in the brain and metabolized by the ...
2024-01-04
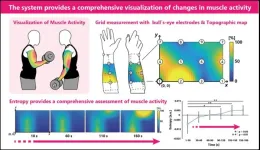
Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a traditional method used to measure the electrical activity of muscles during physical activity. This method has remained unchanged for over 70 years and involves the use of two standard approaches. The first involves a pair of electrodes—metals that conduct electricity through non-metals—to record from a particular muscle, while the second employs a grid of electrodes arranged in a small rectangular layout in order to measure the potential distribution of intra-muscle activity. However, these approaches only provide a measurement of a single muscle at a time. Thus, limiting our understanding of how our muscles coordinate ...
2024-01-04
Weather forecasting is important for various sectors, including agriculture, military operations, and aviation, as well as for predicting natural disasters like tornados and cyclones. It relies on predicting the movement of air in the atmosphere, which is characterized by turbulent flows resulting in chaotic eddies of air. However, accurately predicting this turbulence has remained significantly challenging owing to the lack of data on small-scale turbulent flows, which leads to the introduction of ...
2024-01-04
How deeply someone can be hypnotized — known as hypnotizability — appears to be a stable trait that changes little throughout adulthood, much like personality and IQ. But now, for the first time, Stanford Medicine researchers have demonstrated a way to temporarily heighten hypnotizablity — potentially allowing more people to access the benefits of hypnosis-based therapy.
In the new study, to be published Jan. 4 in Nature Mental Health, the researchers found that less than two minutes of electrical ...
2024-01-04
LA JOLLA (January 4, 2024)—Overwhelming fear, sweaty palms, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate—these are the symptoms of a panic attack, which people with panic disorder have frequently and unexpectedly. Creating a map of the regions, neurons, and connections in the brain that mediate these panic attacks can provide guidance for developing more effective panic disorder therapeutics.
Now, Salk researchers have begun to construct that map by discovering a brain circuit that mediates panic ...
2024-01-04
New study reveals striking similarities in synaptic abnormalities and behavioral patterns between male and female mouse models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study challenges the traditional focus on male subjects in ASD research and highlights the critical importance of including both sexes in investigations. This finding urges a pivotal shift in the scientific community's approach to understanding and addressing ASD, emphasizing the necessity of considering both males and females to comprehensively ...
2024-01-04
Researchers from Amsterdam UMC and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VU) have discovered that the persistent fatigue in patients with long-COVID has a biological cause, namely mitochondria in muscle cells that produce less energy than in healthy patients. The results of the study were published today in Nature Communications.
"We're seeing clear changes in the muscles in these patients," says Michèle van Vugt, Professor of Internal Medicine at Amsterdam UMC.
25 long-COVID patients and 21 healthy ...
2024-01-04
Autophagy, which declines with age, may hold more mysteries than researchers previously suspected. In the January 4th issue of Nature Aging, it was noted that scientists from the Buck Institute, Sanford Burnham Prebys and Rutgers University have uncovered possible novel functions for various autophagy genes, which may control different forms of disposal including misfolded proteins—and ultimately affect aging.
“While this is very basic research, this work is a reminder that it is critical for us to understand whether we have the whole story about the different genes that have been related to aging or age-related diseases,” said Professor ...
2024-01-04
The gut microbiome is so useful to human digestion and health that it is often called an extra digestive organ. This vast collection of bacteria and other microorganisms in the intestine helps us break down foods and produce nutrients or other metabolites that impact human health in a myriad of ways. New research from the University of Chicago shows that some groups of these microbial helpers are amazingly resourceful too, with a large repertoire of genes that help them generate energy for themselves and potentially influence human health as well.
The paper, published January 4, 2024, in Nature ...
2024-01-04
In a landmark study recently published in the journal Nature Methods, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have unveiled mEnrich-seq—an innovative method designed to substantially enhance the specificity and efficiency of research into microbiomes, the complex communities of microorganisms that inhabit the human body.
Unlocking the Microbial World with mEnrich-seq
Microbiomes play a crucial role in human health. An imbalance or a decrease in the variety of microbes in our bodies can lead to an increased risk of several diseases. However, in many microbiome applications, the focus is on studying specific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hunting for the elusive tetraneutrons with thermal fission