(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study among women attending a fertility center found that those with more stress before pregnancy had higher blood sugar levels during pregnancy, which is a sign of weaker cardiovascular health.
People’s stress levels have continued to rise over the years, particularly in the last few years due to the COVID-19 pandemic, putting them at risk for serious health issues such as heart disease. Research shows women may experience more stress than men, especially those going through infertility. Maintaining a healthy pregnancy is important for both mothers and their children.
“We found that maternal stress, evaluated before pregnancy, is negatively associated with cardiovascular health, measured as glucose levels during pregnancy,” said study author Lidia Mínguez-Alarcón, Ph.D., of Harvard Medical School, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Mass. “Our results highlight the importance of considering preconception as a sensitive window of stress in relation to cardiovascular health during pregnancy. A few ways women can lower their stress levels include being more active, avoiding alcohol and drugs, eating healthy and avoiding isolation.”
The authors analyzed self-reported stress levels in 400 women at the Massachusetts General Hospital Fertility Center in Boston, Mass., before they became pregnant and measured their blood sugar levels in late pregnancy. They found women with high levels of stress before pregnancy were more likely to have high blood sugar during pregnancy.
Women who conceived through intrauterine insemination (IUI) had higher stress and blood sugar levels than those who conceived through in vitro fertilization (IVF). During IUI, sperm is injected directly into the uterus. IVF is a multi-step reproductive technology that involves egg stimulation, retrieval, lab fertilization and transfer.
“This may be explained by the fact that IUI treatment has shown less effectiveness as an infertility treatment compared to IVF, so women undergoing IUI may experience more distress compared to those going through IVF,” Mínguez-Alarcón said.
The researchers also found stress and blood sugar levels were higher among women with high socioeconomic status. Mínguez-Alarcón explained the possible reason for this finding could be women with higher incomes and education levels may be employed in demanding, time-intensive jobs.
“It has previously been shown that those with a higher education level experience greater levels of job stress, with stronger associations found in women than in men,” Mínguez-Alarcón said. “Given that education level is positively associated with salary, it is possible that this explanation applies to women with higher incomes as well. Professional women are often also responsible for balancing demands in the workplace with household duties and childcare."
The other authors of this study are Olivia Chagnon, Aya Tanaka, Paige Williams, Tamarra James Todd and Jennifer Ford of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health; Irene Souter of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, Mass.; Kathryn Rexrode of Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School; and Russ Hauser of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
The manuscript, “Preconception Stress and Pregnancy Serum Glucose Levels Among Women Attending a Fertility Center,” was published online.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Women undergoing fertility treatment who are stressed may have heart health issues during pregnancy
Study links high blood sugar during pregnancy with weak heart health
2024-01-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds preconception stress may affect health of women undergoing fertility treatment
2024-01-04
Stress during pregnancy is known to influence health outcomes, but a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers suggests that stress levels before pregnancy are also important to evaluate. Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed the link between self-reported stress immediately before conception among women seeking fertility care and blood glucose levels, a marker of heart health. The team found that maternal stress during preconception ...
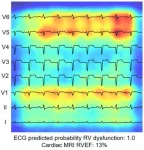
AI-driven study redefines right heart health assessment with novel predictive model
2024-01-04
New York, NY [January 4, 2023]—In a milestone study, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the assessment of the heart’s right ventricle, which sends blood to the lungs.
Conducted by a team using AI-enabled electrocardiogram (AI-ECG) analysis, the research demonstrates that electrocardiograms can effectively predict right-side heart issues, offering a simpler alternative to complex imaging technologies and potentially enhancing patient outcomes.
The findings were described in the December 29 online ...
Better mental, physical health in older people tied to living near nature
2024-01-04
SPOKANE, Wash. – Even small differences in the availability of urban green and blue spaces may be associated with better mental and physical health in older adults, according to a Washington State University study.
The study’s findings showed that having just 10% more forest space in a person’s residential ZIP code was associated with reduced serious psychological distress, which covers mental health problems that require treatment and interfere with people’s social lives, work or school. Similarly, a 10% increase in green space, tree cover, water bodies ...
100 years of Science Changing Life: Scripps Research celebrates a century of transforming human health
2024-01-04
100 years of Science Changing Life: Scripps Research celebrates a century of transforming human health
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research, a nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation, will celebrate its 100-year history throughout 2024. This significant milestone marks a century of seminal discoveries in immunology, infectious diseases (such as COVID-19, flu, HIV), neuroscience, heart disease, cancer, and more. The institute has also made strides in groundbreaking chemistry advances, drug development and educational ...
JAMA names seven academic physicians and nurses to new Editorial Fellowship Program
2024-01-04
Chicago, January 4, 2024 — The JAMA Network today announces a new class of seven academic physicians and nurses selected for a new program to provide junior faculty and current research fellows opportunities to learn about biomedical journals and scientific publication. This inaugural group of fellows will spend six months immersed as part of the JAMA editorial team to obtain direct exposure to the editorial review process and enhance their skills in scientific communication.
Fellows will be assigned to a current JAMA editor for mentorship, attend manuscript meetings, participate in discussions about research design, data validity, potential clinical importance, and conduct ...
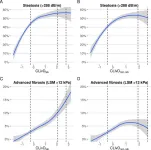
New technique could improve liver fibrosis treatment
2024-01-04
Chronic liver disease, a growing threat to global health, often progresses silently in its early stages. Detecting its precursor, steatotic liver disease (SLD), and advanced liver fibrosis before complications arise is crucial to prevent devastating outcomes. The newly developed Chronic Liver Disease (CLivD) score offers a promising non-invasive approach to this challenge.
In a recent study involving a US general population sample, researchers explored the CLivD score’s ability to identify SLD and advanced fibrosis, assessed using liver stiffness measurement (LSM). The study also evaluated the potential ...
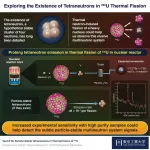
Hunting for the elusive tetraneutrons with thermal fission
2024-01-04
Tetraneutron is an elusive atomic nucleus consisting of four neutrons, whose existence has been highly debated by scientists. This stems primarily from our lack of knowledge about systems consisting of only neutrons, since most atomic nuclei are usually made of a combination of protons and neutrons. Scientists believe that the experimental observation of a tetraneutron could be the key to exploring new properties of atomic nuclei and answering the age-old question: Can a charge-neutral multineutron system ever exist?
Two recent experimental studies reported the presence of tetraneutrons in bound state and resonant state (a state that decays ...
Understanding the role of a new enzyme in the development of autism spectrum disorder
2024-01-04
Over the past decades, scientists have made substantial progress unveiling the underlying mechanisms behind many psychiatric disorders. Every year, new genetic mutations or protein dysregulations are identified as potential culprits for the symptoms, and sometimes even the root causes of complex neurological diseases, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s.
Despite these efforts, the precise roles of several proteins involved in brain function remain obscure. Such is the case for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2), an enzyme expressed in the brain and metabolized by the ...
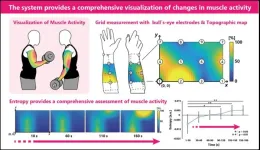
An innovative approach for evaluating muscle coordination and fatigue
2024-01-04
Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a traditional method used to measure the electrical activity of muscles during physical activity. This method has remained unchanged for over 70 years and involves the use of two standard approaches. The first involves a pair of electrodes—metals that conduct electricity through non-metals—to record from a particular muscle, while the second employs a grid of electrodes arranged in a small rectangular layout in order to measure the potential distribution of intra-muscle activity. However, these approaches only provide a measurement of a single muscle at a time. Thus, limiting our understanding of how our muscles coordinate ...
New theoretical framework unlocks mysteries of synchronization in turbulent dynamics
2024-01-04
Weather forecasting is important for various sectors, including agriculture, military operations, and aviation, as well as for predicting natural disasters like tornados and cyclones. It relies on predicting the movement of air in the atmosphere, which is characterized by turbulent flows resulting in chaotic eddies of air. However, accurately predicting this turbulence has remained significantly challenging owing to the lack of data on small-scale turbulent flows, which leads to the introduction of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Women undergoing fertility treatment who are stressed may have heart health issues during pregnancyStudy links high blood sugar during pregnancy with weak heart health