(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from UC San Francisco has found that Paxlovid (Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir) did not reduce the risk of developing long COVID for vaccinated, non-hospitalized individuals during their first COVID-19 infection. They also found a higher proportion of individuals with acute symptoms rebound and test-positivity than previously reported.
The study appears Jan. 4, 2024, in the Journal of Medical Virology.
Paxlovid treatment for acute COVID-19 has been shown to be effective for high-risk unvaccinated individuals. But the effect of the treatment on long COVID risk, including whether it protects vaccinated people from getting long COVID, has been less clear.
The research team selected a group of vaccinated people from the UCSF Covid-19 Citizen Science study who had reported their first positive test for COVID-19 between March and August of 2022 and who were not hospitalized. Some of these participants reported taking oral Paxlovid treatment during the acute phase of their COVID infection, while others did not. In December of 2022, they were invited to answer a follow-up survey with questions about long COVID, COVID rebound symptoms and how long they continued to test positive.
Researchers found the two groups were similar. About 16% of those treated with Paxlovid had long COVID symptoms compared to 14% of those who were not treated with the medication. Commonly reported symptoms included fatigue, shortness of breath, confusion, headache, and altered taste and smell. Those who took Paxlovid and then went on to develop long COVID reported as many long COVID symptoms as those who were not treated with Paxlovid. A small percentage of people developed severe long COVID, and those who had received Paxlovid were just as likely to have severe Long COVID symptoms as those who did not.
Among individuals who experienced symptomatic improvement during Paxlovid treatment, 21% reported rebound symptoms. And among those with rebound symptoms, 10.8% reported one or more Long COVID symptom compared to 8.3% without rebound symptoms. For participants who repeated antigen testing after testing negative and completing treatment, 25.7% reported rebound test positivity. In total, 26.1% reported rebound symptoms or test positivity.
“We found a higher proportion with clinical rebound than previously reported but did not identify an effect of post-treatment rebound on long COVID symptoms,” said study first author Matthew Durstenfeld, MD, MAS, a cardiologist and UCSF assistant professor of Medicine. “Our finding that Paxlovid treatment during acute infection is not associated with lower odds of long COVID surprised us, but it is consistent with two other rigorously conducted studies finding no difference in post-COVID conditions between 4 and 6 months after infection.”
The authors note that the study may have been impacted by limitations arising from its observational nature with researchers relying on patient self-reporting of treatment and Long COVID symptoms.
Authors: Other UCSF authors include Michael J. Peluso, Feng Lin, Noah D. Peyser, Carmen Isasi, Thomas W. Carton, Timothy J. Henrich, Steven G. Deeks, Jeffrey E. Olgin, Mark J. Pletcher, Alexis L. Beatty, Gregory M. Marcus, Priscilla Y. Hsue
Funding: This work (Eureka Research Platform) was supported by NIH/NIBIB 3U2CEB021881-05S1. The COVID-19 Citizen Science Study is supported by Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) contract COVID-2020C2-10761 and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation contract INV-017206. Dr. Durstenfeld is supported by NIH/NHLBI grant K12HL143961.
About UCSF Health: UCSF Health is recognized worldwide for its innovative patient care, reflecting the latest medical knowledge, advanced technologies and pioneering research. It includes the flagship UCSF Medical Center, which is a top-ranked specialty hospital, as well as UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals, with campuses in San Francisco and Oakland, Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital and Clinics, UCSF Benioff Children’s Physicians and the UCSF Faculty Practice. These hospitals serve as the academic medical center of the University of California, San Francisco, which is world-renowned for its graduate-level health sciences education and biomedical research. UCSF Health has affiliations with hospitals and health organizations throughout the Bay Area. Visit https://ucsfhealth.org. Follow UCSF Health on Facebook or on Twitter.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | Twitter.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
● KAT6 is an emerging target in hormone sensitive breast tumors and other cancers. Overexpression of KAT6A/B correlates with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ER+/HER2- breast cancer – the most common subtype.
● The molecule has demonstrated strong preclinical activity. Insilico Medicine presented data on the novel molecule at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in early December.
● This agreement includes upfront and milestone payments with a combined potential value of over $500m and sales royalties.
FLORENCE, Italy and NEW YORK: The Menarini Group ("Menarini"), a leading international pharmaceutical and diagnostics company, and Stemline Therapeutics, ...
INDIANAPOLIS – A significant obstacle to improving care and outcomes for intensive care unit (ICU) patients is the unexpected nature of becoming seriously ill. Which groups of patients are likely to become severely ill and will they survive their ICU stay?
In a first step in creating infrastructure for further studies to identify and follow cohorts of patients who may become critically ill, researchers including Sikandar Khan, D.O, M.S., of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine, have developed and conducted ...
Firms worldwide are increasingly adopting electronic voting, enabling shareholders to cast their votes online, instead of attending shareholder meetings in-person. Shareholders can enjoy superior accessibility to the meetings with electronic voting, compared to those with traditional and in-person setups. Despite the emerging popularity of electronic voting in recent years, however, there is limited evidence of its impact on governance.
To address this gap in research, Associate Professor Wonsuk Ha from the School of Business Administration, Chung-Ang University, along ...
WASHINGTON—A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study among women attending a fertility center found that those with more stress before pregnancy had higher blood sugar levels during pregnancy, which is a sign of weaker cardiovascular health.
People’s stress levels have continued to rise over the years, particularly in the last few years due to the COVID-19 pandemic, putting them at risk for serious health issues such as heart disease. Research shows women may experience more stress than men, especially those going through infertility. Maintaining a healthy pregnancy ...
Stress during pregnancy is known to influence health outcomes, but a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers suggests that stress levels before pregnancy are also important to evaluate. Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed the link between self-reported stress immediately before conception among women seeking fertility care and blood glucose levels, a marker of heart health. The team found that maternal stress during preconception ...
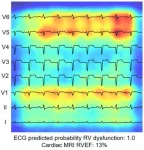
New York, NY [January 4, 2023]—In a milestone study, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the assessment of the heart’s right ventricle, which sends blood to the lungs.
Conducted by a team using AI-enabled electrocardiogram (AI-ECG) analysis, the research demonstrates that electrocardiograms can effectively predict right-side heart issues, offering a simpler alternative to complex imaging technologies and potentially enhancing patient outcomes.
The findings were described in the December 29 online ...
SPOKANE, Wash. – Even small differences in the availability of urban green and blue spaces may be associated with better mental and physical health in older adults, according to a Washington State University study.
The study’s findings showed that having just 10% more forest space in a person’s residential ZIP code was associated with reduced serious psychological distress, which covers mental health problems that require treatment and interfere with people’s social lives, work or school. Similarly, a 10% increase in green space, tree cover, water bodies ...
100 years of Science Changing Life: Scripps Research celebrates a century of transforming human health
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research, a nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation, will celebrate its 100-year history throughout 2024. This significant milestone marks a century of seminal discoveries in immunology, infectious diseases (such as COVID-19, flu, HIV), neuroscience, heart disease, cancer, and more. The institute has also made strides in groundbreaking chemistry advances, drug development and educational ...
Chicago, January 4, 2024 — The JAMA Network today announces a new class of seven academic physicians and nurses selected for a new program to provide junior faculty and current research fellows opportunities to learn about biomedical journals and scientific publication. This inaugural group of fellows will spend six months immersed as part of the JAMA editorial team to obtain direct exposure to the editorial review process and enhance their skills in scientific communication.
Fellows will be assigned to a current JAMA editor for mentorship, attend manuscript meetings, participate in discussions about research design, data validity, potential clinical importance, and conduct ...
Chronic liver disease, a growing threat to global health, often progresses silently in its early stages. Detecting its precursor, steatotic liver disease (SLD), and advanced liver fibrosis before complications arise is crucial to prevent devastating outcomes. The newly developed Chronic Liver Disease (CLivD) score offers a promising non-invasive approach to this challenge.
In a recent study involving a US general population sample, researchers explored the CLivD score’s ability to identify SLD and advanced fibrosis, assessed using liver stiffness measurement (LSM). The study also evaluated the potential ...