(Press-News.org) A study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability has found that green ammonia could be used to fulfil the fuel demands of over 60% of global shipping by targeting just the top 10 regional fuel ports. Researchers at the University of Oxford looked at the production costs of ammonia which are similar to very low sulphur fuels, and concluded that the fuel could be a viable option to help decarbonise international shipping by 2050.
Around USD 2 trillion will be needed to transition to a green ammonia fuel supply chain by 2050, primarily to finance supply infrastructure. The study shows that the greatest investment need is in Australia, to supply the Asian markets, with large production clusters also predicted in Chile (to supply South America), California (to supply Western U.S.A.), North-West Africa (to meet European demand), and the southern Arabian Peninsula (to meet local demand and parts of south Asia).
90% of world’s physical goods trade is transported by ships which burn heavy fuel oil and emit toxic pollutants. This accounts for nearly 3% of the global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. As a result of this, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) committed to decarbonising international shipping in 2018, aiming to halve GHG emissions by 2050. These targets have been recently revised to net zero emissions by 2050.
After investigating the viability of diesel vessel exhaust scrubbers, green ammonia, made by electrolysing water with renewable electricity, was proposed as an alternative fuel source to quickly decarbonise the shipping industry. However, historically there has been great uncertainty as to how and where to invest to create the necessary infrastructure to deliver an efficient, viable fuel supply chain.
René Bañares-Alcántara, Professor of Chemical Engineering in the Department of Engineering Science at the University of Oxford, says: “Shipping is one of the most challenging sectors to decarbonize because of the need for fuel with high energy density and the difficulty of coordinating different groups to produce, utilize and finance alternative (green) fuel supplies.”
To guide investors, the team at the University of Oxford developed a modelling framework to create viable scenarios for how to establish a global green ammonia fuel supply chain. The framework combines a fuel demand model, future trade scenarios and a spatial optimisation model for green ammonia production, storage, and transport, to find the best locations to meet future demand for shipping fuel.
Professor Bañares-Alcántara continues: “The implications of this work are striking. Under the proposed model, current dependence upon oil-producing nations would be replaced by a more regionalised industry; green ammonia will be produced near the equator in countries with abundant land and high solar potential then transported to regional centres of shipping fuel demand.”
END
Green ammonia could decarbonize 60% of global shipping when offered at just 10 regional fuel ports
2024-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Samsung leads again in U.S. patents while Qualcomm leaps into second place; overall grants dip 3.4%
2024-01-09
New Haven, Conn., Jan. 9, 2024—U.S. patent grants declined 3.4% from 2022, the lowest level since 2019, and Samsung held onto the top spot for the second year in a row according to IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, world leader in tracking patent application and grant data.
IFI CLAIMS Patent Services is a Digital Science company that compiles and tracks data from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and other patent-issuing agencies around the globe. IFI translates its world-leading data into an annual U.S. Top 50 and IFI Global 250 patent rankings, providing valuable insights into companies’ R&D activity.
Other findings in IFI’s latest rankings include patent powerhouse ...
Severe MS predicted using machine learning
2024-01-09
A combination of only 11 proteins can predict long-term disability outcomes in multiple sclerosis (MS) for different individuals. The identified proteins could be used to tailor treatments to the individual based on the expected severity of the disease. The study, led by researchers at Linköping University in Sweden, has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
“A combination of 11 proteins predicted both short and long-term disease activity and disability outcomes. We also concluded that it’s important to measure ...
Combining anti-tumor drugs with chemo may improve rare children’s cancer outcomes
2024-01-09
Children who develop neuroblastomas, a rare form of cancer which develops in nerve cells, may benefit from receiving certain anti-tumour drugs as well as chemotherapy, a new trial has found.
The results of the BEACON trial conducted by the Cancer Research UK Clinical Trials Unit at the University of Birmingham found that combining anti-angiogenic drugs, which block tumours from forming blood vessels, alongside various chemotherapy drugs led to more young people seeing their tumours shrinking, from 18% in the control group to 26% among those on Bevacizumab.
The findings are published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology today. The trial saw 160 young ...
EBRAINS research infrastructure secures €38 million in funding for new phase of digital neuroscience
2024-01-09
The European Commission has accepted the EBRAINS 2.0 proposal submitted in response to the INFRASERV call, granting €38 million for the further development of services of the EBRAINS research infrastructure.
The European Commission has signed a grant agreement to fund EBRAINS with €38 million until 2026. Over the next three years, the infrastructure will continue to develop tools and services to widely serve research communities in neurosciences, brain medicine, and brain-inspired technologies.
EBRAINS (European Brain Research Infrastructures) is an EU co-funded collaborative research platform designed to advance neuroscience and brain ...
Train your brain to overcome tinnitus
2024-01-09
An international research team has shown that the debilitating impact of tinnitus can be effectively reduced in just weeks by a training course and sound therapy delivered via a smartphone app.
The team from Australian, New Zealand, French and Belgian universities report these findings today in Frontiers in Audiology and Otology.
It offers some hope for millions affected by tinnitus who:
have been told that there is nothing they can do about it
face long queues waiting for treatment, or
can’t afford the costs of specialist support.
The initial trial worked with 30 sufferers, of whom almost two thirds experienced a ‘clinically ...
A chemical reaction key to various industries just got greener
2024-01-09
Osaka, Japan – From alleviating your allergy symptoms to optimizing herbicide performance, alkylamines are molecules that have many uses. Unfortunately, common methods of producing alkylamines result in harmful waste byproducts. A method of synthesizing alkylamines in a sustainable yet cost-effective way has thus been highly sought after.
Now, in a study recently published in Green Chemistry, a research team led by Osaka University has found a way. The team has developed a method of alkylamine synthesis that works under mild conditions and produces ...
Spanish butterflies better at regulating their body temperature than their British cousins
2024-01-09
Butterfly populations in Catalonia in northern Spain are better than their UK counterparts at regulating their body temperature by basking in the sunshine, but rising global temperatures due to climate change may put Spanish butterflies at greater risk of extinction.
An international study, led by the University of Cambridge and the Institut de Biologia Evolutiva (IBE) in Barcelona, found that butterflies use different methods to regulate their body temperature. In Catalonia, butterflies tend to angle ...
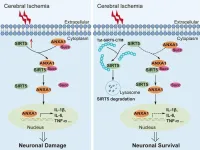
A novel cell-penetrating peptide exerts therapeutic effects against ischemic stroke
2024-01-09
This study is led by Dr. Xing Li and Dr. Yilin Zhao (Department of Anesthesiology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Geriatric Anesthesia and Perioperative Brain Health, and Wuhan Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Anesthesia, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology). The team's previous research found that the increase in SIRT5 in microglia induced by ischemic stroke causes annexin-A1 (ANXA1) desuccinylation, which decreases ANXA1 membrane recruitment and secretion but promotes ANXA1 nuclear translocation, resulting in the production of proinflammatory ...
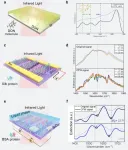
Ultrasensitive molecular sensing with synthesize complex-frequencey waves
2024-01-09
Sensors are essential tools for detecting and analyzing trace molecules in a variety of fields, including environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health. However, developing sensors with high enough sensitivity to detect these tiny amounts of molecules remains a challenge.
One promising approach is surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), which uses plasmonic nanostructures to amplify the infrared signals of molecules adsorbed on their surface. Graphene is a particularly promising material for SEIRA because of its high ...
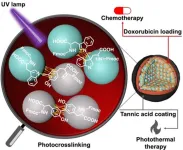
Creating novel amino acid nanoparticles with enhanced anticancer activity
2024-01-09
Ishikawa, Japan -- Amino acids, such as tyrosine and tryptophan, are the fundamental building blocks that make up proteins. These biomolecules have different chemical groups on each end and side chain, and so, have the natural ability to form a chain through the formation of an amide (peptide) bond. However, such linkages are weak and easily degraded under physiological conditions. This is where the Fmoc-protected amino acids come into the picture.
In a new study now, a research team led by Dr. Eijiro Miyako, Associate ...