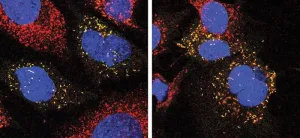
(Press-News.org) Dutch scientists have discovered five biological variants of Alzheimer's disease, which may require different treatment. As a result, previously tested drugs may incorrectly appear to be ineffective or only minimally effective. This is the conclusion of researcher Betty Tijms and colleagues from Alzheimer Center Amsterdam, Amsterdam UMC and Maastricht University. The research results will be published on 9 January in Nature Aging.
In those with Alzheimer's disease, the amyloid and tau protein clump in the brain. In addition to these clumps, other biological processes such as inflammation and nerve cells growth are also involved. Using new techniques, the researchers have been able to measure these other processes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyloid and tau clumps.
Betty Tijms and Pieter Jelle Visser examined 1058 proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of 419 people with Alzheimer's disease. They found that there are five biological variants within this group. The first variant is characterized by increased amyloid production. In a second type, the blood-brain barrier is disrupted and there is a reduced amyloid production and less nerve cells growth. Furthermore, the variants differ in the degree of protein synthesis, the functioning of the immune system, and the functioning of the organ that produces cerebrospinal fluid. Patients with different Alzheimer's variants also showed differences in other aspects of the disease. For example, the researchers found a faster course of the disease in certain subgroups.
The findings are of great importance for drug research. It means that a drug could only work in one variant of Alzheimer's disease. For example, medication that inhibits amyloid production may work in the variant with increased amyloid production but may be harmful in the variant with decreased amyloid production. It is also possible that patients with one variant have a higher risk of side effects, while that risk is much lower with other variants. The next step for the research team is to show that the Alzheimer's variants do indeed react differently to medicines, so that we can treat everyone with appropriate medicines in the future.
END
Different biological variants discovered in Alzheimer's disease
Research from Amsterdam UMC could be essential in the evaluation of future medication
2024-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alzheimer Europe adopts position on anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer’s disease, issuing a call to action for timely, safe and equitable access
2024-01-09
Luxembourg, 9 January 2024 – In a new position paper, and following engagement with its national members and the European Working Group of People with Dementia (EWGPWD), Alzheimer Europe calls for concrete actions to enable timely, safe and equitable access to anti-amyloid drugs, for patients who are most likely to benefit from these innovative new treatments for Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
The growing prevalence and impact of AD has catalysed huge investments in research on its causes, diagnosis, treatment and care. After many high-profile ...
Improved cellular recycling could benefit patients with neurodegenerative conditions
2024-01-09
For the first time, a research team at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) has uncovered a way to potentially reduce the amount of toxic cellular waste accumulating in patients with Zellweger Spectrum Disorder (ZSD).
ZSD is a group of rare, neurodegenerative genetic conditions caused by genetic variations that reduce the number of peroxisomes – the parts of cells that are responsible for, among other tasks, breaking down fats. ZSD varies in severity and is characterized by progressive neurodegeneration as well as symptoms that range from visual impairments, such as cataracts, to liver and kidney disfunction.
Like all living ...
Green ammonia could decarbonize 60% of global shipping when offered at just 10 regional fuel ports
2024-01-09
A study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability has found that green ammonia could be used to fulfil the fuel demands of over 60% of global shipping by targeting just the top 10 regional fuel ports. Researchers at the University of Oxford looked at the production costs of ammonia which are similar to very low sulphur fuels, and concluded that the fuel could be a viable option to help decarbonise international shipping by 2050.
Around USD 2 trillion will be needed to transition to a green ammonia fuel supply chain by 2050, primarily to finance ...
Samsung leads again in U.S. patents while Qualcomm leaps into second place; overall grants dip 3.4%
2024-01-09
New Haven, Conn., Jan. 9, 2024—U.S. patent grants declined 3.4% from 2022, the lowest level since 2019, and Samsung held onto the top spot for the second year in a row according to IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, world leader in tracking patent application and grant data.
IFI CLAIMS Patent Services is a Digital Science company that compiles and tracks data from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and other patent-issuing agencies around the globe. IFI translates its world-leading data into an annual U.S. Top 50 and IFI Global 250 patent rankings, providing valuable insights into companies’ R&D activity.
Other findings in IFI’s latest rankings include patent powerhouse ...
Severe MS predicted using machine learning
2024-01-09
A combination of only 11 proteins can predict long-term disability outcomes in multiple sclerosis (MS) for different individuals. The identified proteins could be used to tailor treatments to the individual based on the expected severity of the disease. The study, led by researchers at Linköping University in Sweden, has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
“A combination of 11 proteins predicted both short and long-term disease activity and disability outcomes. We also concluded that it’s important to measure ...
Combining anti-tumor drugs with chemo may improve rare children’s cancer outcomes
2024-01-09
Children who develop neuroblastomas, a rare form of cancer which develops in nerve cells, may benefit from receiving certain anti-tumour drugs as well as chemotherapy, a new trial has found.
The results of the BEACON trial conducted by the Cancer Research UK Clinical Trials Unit at the University of Birmingham found that combining anti-angiogenic drugs, which block tumours from forming blood vessels, alongside various chemotherapy drugs led to more young people seeing their tumours shrinking, from 18% in the control group to 26% among those on Bevacizumab.
The findings are published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology today. The trial saw 160 young ...
EBRAINS research infrastructure secures €38 million in funding for new phase of digital neuroscience
2024-01-09
The European Commission has accepted the EBRAINS 2.0 proposal submitted in response to the INFRASERV call, granting €38 million for the further development of services of the EBRAINS research infrastructure.
The European Commission has signed a grant agreement to fund EBRAINS with €38 million until 2026. Over the next three years, the infrastructure will continue to develop tools and services to widely serve research communities in neurosciences, brain medicine, and brain-inspired technologies.
EBRAINS (European Brain Research Infrastructures) is an EU co-funded collaborative research platform designed to advance neuroscience and brain ...
Train your brain to overcome tinnitus
2024-01-09
An international research team has shown that the debilitating impact of tinnitus can be effectively reduced in just weeks by a training course and sound therapy delivered via a smartphone app.
The team from Australian, New Zealand, French and Belgian universities report these findings today in Frontiers in Audiology and Otology.
It offers some hope for millions affected by tinnitus who:
have been told that there is nothing they can do about it
face long queues waiting for treatment, or
can’t afford the costs of specialist support.
The initial trial worked with 30 sufferers, of whom almost two thirds experienced a ‘clinically ...
A chemical reaction key to various industries just got greener
2024-01-09
Osaka, Japan – From alleviating your allergy symptoms to optimizing herbicide performance, alkylamines are molecules that have many uses. Unfortunately, common methods of producing alkylamines result in harmful waste byproducts. A method of synthesizing alkylamines in a sustainable yet cost-effective way has thus been highly sought after.
Now, in a study recently published in Green Chemistry, a research team led by Osaka University has found a way. The team has developed a method of alkylamine synthesis that works under mild conditions and produces ...
Spanish butterflies better at regulating their body temperature than their British cousins
2024-01-09
Butterfly populations in Catalonia in northern Spain are better than their UK counterparts at regulating their body temperature by basking in the sunshine, but rising global temperatures due to climate change may put Spanish butterflies at greater risk of extinction.
An international study, led by the University of Cambridge and the Institut de Biologia Evolutiva (IBE) in Barcelona, found that butterflies use different methods to regulate their body temperature. In Catalonia, butterflies tend to angle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Different biological variants discovered in Alzheimer's diseaseResearch from Amsterdam UMC could be essential in the evaluation of future medication