(Press-News.org)
In a new study, environmentally benign inverse-perovskites with high energy conversion efficiency have been reported by Tokyo Tech scientists with potential for practical application as thermoelectric materials (TEMs). Addressing the limitations typically faced with TEMs, such as insufficient energy conversion efficiency and environmental toxicity due to heavy elements, the new TEMs provide a suitable alternative to TEMs based on toxic elements with better thermoelectric properties than conventional eco-friendly TEMs.
Thermoelectric materials (TEMs) capable of converting thermal energy to electrical energy and vice versa have become an essential part of our world, which needs better waste-energy harvesting systems and cooling systems for electronic gadgets.
The energy conversion efficiency of TEMs depends on a dimensionless figure of merit (ZT), which is a product of two different factors: the inverse of thermal conductivity (k) and the power factor (PF).
A high-performance TEM exhibits a high ZT if it possesses low k and high PF. Over the years, scientists developed several high-performance heavy metal chalcogenide-based TEMs, such as Bi2Te3 and PbTe, that fulfill these criteria. While these materials were ideal for energy conversion, they were toxic to the environment and the health of living organisms—they contained toxic heavy elements, such as lead (Pb) and tellurium (Te), which limited their practical applications. On the other hand, although oxide-based TEMs, such as SrTiO3, have several advantages of non-toxicity and abundant natural resources, their ZT has been limited due to their high k.
To address this, a research team led by Associate Professor Takayoshi Katase from Tokyo Institute of Technology explored efficient yet environmentally benign toxic-element-free TEMs. In their recent study published in Advanced Science, the researchers presented “inverse”-perovskite-based high ZT TEMs with the chemical formula Ba3BO, where B refers to silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge).
“Unlike normal perovskites, such as SrTiO3, the positions of cation and anion sites are inverted in inverse-perovskites Ba3BO. So, they contain a large amount of the heavy element, Ba, and their crystal structure is formed by a soft flamework made up of weak O-Ba bonds. These characteristics realize the low k in inverse-perovskites,” says Dr. Katase, elaborating on the standout properties of the materials.
The research team clarified the synthesized bulk polycrystals of Ba3BO possess extremely low k of 1.0–0.4 W/mK at a T of 300-600 K, which is lower than those of Bi2Te3 and PbTe bulks. As a result, the Ba3BO bulks exhibit rather high ZT of 0.16-0.84 at T = 300-623 K. Additionally to the promising experimental results, the team carried out theoretical calculations which predicted a potential maximum ZT of 2.14 for Ba3SiO and 1.21 for Ba3GeO at T = 600 K by optimizing hole concentration. The maximum ZT of these non-toxic TEMs is much higher than that of other eco-friendly TEMs and comparable to the toxic heavy element ones in the same temperature range.
In addition, the team clarified that the high ZT of Ba3BO is due not only to its low k but also its high PF: B ion, which usually behaves as a positively charged cation but as a negatively charged anion in Ba3BO. The B anions are responsible for the carrier transport, which achieves high PF.
In summary, this study validates the potential of the newly designed Ba3BO as a high-performing and eco-friendly alternative to conventional toxic, heavy element-based TEMs. The results establish inverse-perovskites as a promising option for developing advanced environmentally benign TEMs. In this regard, Dr. Katase concludes, “We believe that our unique insight into designing high ZT materials without using toxic elements would have a strong impact on the materials science and chemistry communities as well as among innovators looking to expand the horizon of thermoelectric material applications beyond laboratories into our everyday life.”
END
Humans learn which behaviors pay off and which don’t from watching others. Based on this, we may draw conclusions about how to act – or eat. In the case of the latter, people may use each other as guides to determine what and how much to eat. This is called social modelling and is one of the most powerful social influences on eating behavior.
In a new study, researchers in the UK investigated whether observing others’ facial expressions while eating raw broccoli influenced young women’s liking and desire to ...
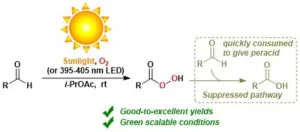
Osaka, Japan – Approximately 5% of global carbon emissions are attributable to producing the chemicals that are essential to modern life. Creating a sustainable solution to one chemical reaction in particular – the autoxidation of aldehydes – has challenged researchers for decades.
Now, in a study recently published in Green Chemistry, researchers from Osaka University, Shizuoka Institute of Science & Technology, and collaborating partners have solved this problem. Through reaction kinetics and mathematical ...
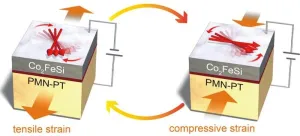
Controlling the direction of magnetization using low electric field is necessary for developing efficient spintronic devices. In spintronics, properties of an electron’s spin or magnetic moment are used to store information. The electron spins can be manipulated by straining orbital magnetic moments to create a high-performance magnetoelectric effect.
Japanese researchers, including Jun Okabayashi from the University of Tokyo, revealed a strain-induced orbital control mechanism in interfacial multiferroics. In multiferroic material, the magnetic property ...
Study Finds Hospital Surfaces Can Harbor Harmful Microbes Even After Routine Disinfection
Microbial contamination, including harmful pathogens, was found on bed rails, workstations, and other frequently-touched surfaces
Arlington, Va. — January 11, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports microbial contamination — including pathogenic and potentially pathogenic bacteria — on high-touch hospital surfaces despite compliance with recommended disinfection protocols. The findings shed light on the persistent challenge of reducing healthcare-associated infections ...
In a study published in Nature Biotechnology, GAO Caixia's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a series of new prime editors based on the Cas12a protein, further expanding the targeting scope and applications of precision genome editing.
Prime editing (PE) enables precise, targeted DNA insertions, deletions, and replacements. To date, all efficient prime editors have been based on Cas9. However, the Cas9 has certain disadvantages that limit the broad application of prime editors. For example, it is too large, experiences higher levels of off-target editing, and has limited effectiveness ...
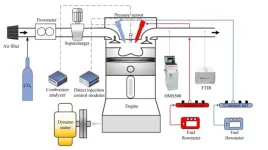
Exploring advanced combustion mode with high efficiency and low emissions has been the dream of successive generations of researchers. Conventional diesel engines have high compression ratios thus with thermal efficiencies of 35%–45%, but the diffusion combustion
characteristics of diesel make NOx and soot emissions high. Gasoline compression ignition (GCI) is an advanced combustion mode in the field of internal combustion engines, which combines the advantages of the high efficiency of diesel engines and the low emissions of gasoline engines. Although the GCI mode ...
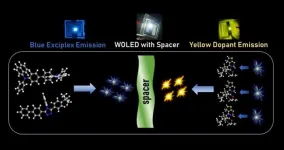
Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) have matured to commercial level. Yet, their widespread market adoption is hindered due to high costs and complicated device architecture. Researchers are actively exploring innovative device engineering strategies to circumvent these issues.
Narayanan Unni and co-workers have tried to address the above challenges by exploiting a concept called exciplex. Exciplex emission is possible at the interface of two different materials which may not be luminescent themselves. This provides an opportunity to use relatively cheaper materials instead of costly fluorescent or phosphorescent emitter materials. They ...
OAKLAND, CA – The California Energy Commission (CEC) has selected PSE Healthy Energy to support their development of social cost and non-energy benefit metrics for the deployment of clean energy resources. These metrics will be used to evaluate scenarios for achieving California’s clean energy goals, including through California’s 100 percent clean energy target, as defined in Senate Bill 100 (SB100).
“Transitioning to 100 percent renewable and zero-carbon electricity resources by 2045 will reshape California’s energy systems,” ...
People taking medical cannabis for chronic pain have a slightly increased risk of arrhythmia, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday). Arrhythmia is when the heart beats too slowly, too quickly or irregularly. It includes conditions like atrial fibrillation.
Recreational use of cannabis has been linked to cardiovascular disease but there has been very little research on the side effects of medical cannabis.
Researchers say the new study is important as a growing number of countries now permit medical cannabis as a treatment for chronic pain.
The study was ...
Researchers from The University of Queensland have launched the world’s biggest drug survey, to gain insight into drug use around the globe.
The Global Drug Survey was founded by Professor Adam Winstock from University College London and has been running annually since 2012.
This year the survey is led by Dr Cheneal Puljevic from UQ’s School of Public Health.
“The aim of the Global Drug Survey is to make drug use safer for people, regardless of the drug’s legality,” Dr Puljevic said.
“We hope to gain insight ...