(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—The popular TikTok trend of ‘hormone balancing’ has taken over the internet with claims to balance your hormones with holistic approaches alone, but medical experts question its legitimacy.
Endocrine Society expert Deena Adimoolam, M.D., will discuss ‘hormone balancing’ during the Society’s Virtual Science Writers Conference on January 24.
What: The Virtual Science Writers Conference will examine:
How hormones function and stay in balance
Common endocrine disorders associated with hormone imbalances
The benefits and risks of using TikTok for hormone health advice
Best ways to take care of your hormone health
Who: Deena Adimoolam, M.D., a privately practicing endocrinologist in New Jersey.
Adimoolam is a physician and endocrinologist with a passion for public health education and nutrition. She diagnoses and treats a wide range of weight-related conditions, including obesity, diabetes, thyroid disease, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and women’s hormonal health issues. She has published research and written chapters for textbooks dedicated to diabetes and obesity.
When: Wednesday, January 24 at 1 PM Eastern
Register to attend the virtual Science Writers Conference by emailing media@endocrine.org. Registered reporters will receive log-in details.
Priority will be given to journalists seeking to register. The recording of this event will be made available on the Society’s YouTube channel for other audiences.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Virtual Science Writers Conference will uncover the truth behind ‘hormone balancing’
2024-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Toxic algae blooms: Study assesses potential health hazards to humans
2024-01-11
Florida’s 156-mile-long Indian River Lagoon (IRL) borders five different counties and has five inlets that connect the lagoon with the Atlantic Ocean. In recent years, this estuary has experienced numerous phytoplankton bloom events due to increased seasonal temperatures coupled with environmental impacts.
Algal blooms produce a myriad of small organic molecules, many of which can be toxic to humans and animals. Among these phycotoxin producers is Microcystis aeruginosa, a freshwater cyanobacterium, which can be found in the Southern IRL. Measurable amounts of microcystins have been found in nasal swabs ...
Researchers discover potential microbiome links to skin aging
2024-01-11
The effects of aging and external factors like UV exposure on skin are well documented. As people age or spend more time in the sun, their skin tends to become drier and more wrinkled,
Recent findings have identified an exciting potential new link to signs of skin aging—the skin microbiome, the collection of microorganisms that inhabits our skin. The results come from a collaborative study carried out by researchers at the Center for Microbiome Innovation (CMI) at the University of California San Diego (UC San Diego) and L'Oréal ...
Join us in sunny San Diego for the ATS 2024 International Conference May 19-22
2024-01-11
What’s New: Register now to learn about the latest in pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine. Join us for scientific sessions and expert interviews. Thirteen sessions will be livestreamed.
Why it matters: Stay up-to-date on subjects like COVID-19, asthma, COPD, and air pollution. We’ll assist you with conducting interviews, whether in-person or from your home office.
Contact Kevin Tuerff, ATS Communications & Marketing for more information, at ktuerff@thoracic.org END ...
Chemical Insights Research Institute commits to public health research with the opening of new laboratories
2024-01-11
ATLANTA – Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes confirmed its commitment to protecting environmental and human health when it opened its new research laboratories supporting scientific studies of environmental exposure and its societal health impact. At a ribbon cutting today, CIRI introduced the Center for Exposure Science; the Center for Toxicology and Human Health; and the Center for Advanced Measurements, each with a designated, cutting-edge laboratory.
Using the latest tools for measuring nanosized particles and parts per billion levels of chemicals and developing high-throughput cellular techniques for measuring human toxicity, ...
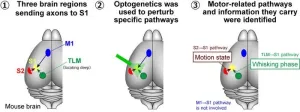
Challenging the traditional views on how the brain processes movement and sensation
2024-01-11
The brain is widely considered the most complex organ in the human body. The intricate mechanisms through which it processes sensory information and how this information affects and is affected by motor control have captivated neuroscientists for more than a century. Today, thanks to advanced laboratory tools and techniques, researchers can use animal models to solve this puzzle, especially in the mouse brain.
During the 20th century, experiments with anesthetized mice proved that sensory inputs primarily define neuronal activity in the primary ...
Understanding healthy and happy expectancy in former soviet countries
2024-01-11
The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked the start of a period ripe with political, economic, and societal changes. In many former Soviet countries, these abrupt and turbulent transformations posed massive challenges to healthcare systems. Together with spikes in job losses and economic hardships, this led to a steep increase in mortality rates that would later come to be known as the “post-Soviet mortality crisis.”
However, this crisis did not affect all former Soviet countries equally. In particular, former Soviet countries in Central Asia, which include Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, saw a ...
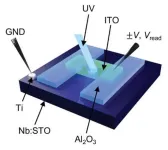
Revolutionizing real-time data processing with edge computing and reservoir technology
2024-01-11
Every day, a significant amount of data related to weather, traffic, and social media undergo real-time processing. In traditional cloud computing, this processing occurs on the cloud, raising concerns about issues such as leaks, communication delays, slow speeds, and higher power consumption. Against this backdrop, “edge computing” presents a promising alternative solution. Located near users, it aims to distribute computations, thereby reducing the load and speeding up data processing. Specifically, edge AI, which involves AI processing at the edge, is expected to find applications in, for example, self-driving ...
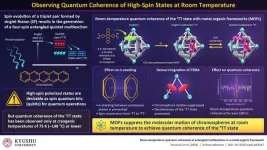
Generating stable qubits at room temperature
2024-01-11
Fukuoka, Japan—In a study published in Science Advances, a group of researchers led by Associate Professor Nobuhiro Yanai from Kyushu University's Faculty of Engineering, in collaboration with Associate Professor Kiyoshi Miyata from Kyushu University and Professor Yasuhiro Kobori of Kobe University, reports that they have achieved quantum coherence at room temperature: the ability of a quantum system to maintain a well-defined state over time without getting affected by surrounding disturbances
This breakthrough was made possible by embedding a chromophore, ...
Potential solvents identified for building on moon and Mars
2024-01-11
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Researchers have taken the first steps toward finding liquid solvents that may someday help extract critical building materials from lunar and Martian-rock dust, an important piece in making long-term space travel possible.
Using machine learning and computational modeling, Washington State University researchers have found about half a dozen good candidates for solvents that can extract materials on the moon and Mars usable in 3D printing. The work, reported in the Journal of Physical Chemistry B, is led by Soumik Banerjee, associate professor in WSU’s School of Mechanical ...
Generative artificial intelligence models effectively highlight social determinants of health in doctors’ notes
2024-01-11
Where we live and work, our age, and the conditions we grew up in can influence our health and lead to disparities, but these factors can be difficult for clinicians and researchers to capture and address. A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham demonstrates that large language models (LLMs), a type of generative artificial intelligence (AI), can be trained to automatically extract information on social determinants of health (SDoH) from clinicians’ notes which could augment efforts to identify patients who may benefit from ...