Activity of pazopanib in EWSR1-NFATC2 translocation-associated bone sarcoma
2024-01-12
(Press-News.org)
“Pazopanib is a multi-kinase inhibitor that is currently approved for treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma and chemotherapy-refractory soft tissue sarcoma.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 12, 2024 – A new case report was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on September 20, 2023, entitled, “Activity of pazopanib in EWSR1-NFATC2 translocation-associated bone sarcoma.”
Pazopanib, a multi-kinase VEGF inhibitor, is currently FDA approved for advanced renal cell carcinoma and advanced soft tissue sarcoma; but limited evidence exists on its efficacy in bone sarcomas.
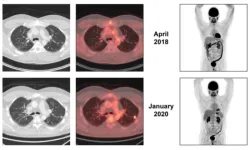
In this case report, researchers Mohamed A. Gouda, Maria A. Zarzour, Ara A. Vaporciyan, Kalevi Kairemo, Hubert H. Chuang, and Vivek Subbiah from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Sarah Cannon Research Institute discuss the case of a patient with a EWSR1-NFATC2 fusion positive bone sarcoma who had exceptional tumor control through using pazopanib and surgery for an overall duration exceeding 5 years. The report also reviews the literature on EWSR1-NFATC2 translocation-associated sarcomas and use of pazopanib in bone sarcomas.
“In brief, this case, in accordance with previously reported evidence, provides proof of activity of pazopanib in EWSR1-NFATC2 positive sarcoma. The report shows that pazopanib when administered in an adjuvant capacity demonstrated its effectiveness in preventing or delaying the progression of additional metastasis. Nevertheless, due to the adjuvant nature of the treatment, it remains uncertain whether this approach would have resulted in tumor shrinkage. Further pre-clinical studies and clinical studies using pazopanib in EWSR1-NFATC2 sarcomas are warranted.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncoscience.587
Correspondence to: Vivek Subbiah
Email: vivek.subbiah@scri.com
Keywords: pazopanib, precision oncology, sarcoma
About Oncoscience:
Oncoscience is a peer-reviewed, open-access, traditional journal covering the rapidly growing field of cancer research, especially emergent topics not currently covered by other journals. This journal has a special mission: Freeing oncology from publication cost. It is free for the readers and the authors.
To learn more about Oncoscience, visit Oncoscience.us and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Instagram
Facebook
YouTube
LinkedIn
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncoscience Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1D
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 4
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-12
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – A groundbreaking 3D, three-layer nanomatrix vascular sheet that possesses multiple features of atherosclerosis has been applied for developing a high-throughput functional assay of drug candidates to treat this disease, University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers report in the journal Biomaterials.
“Current in vitro atherosclerosis models have significant limitations, including the lack of three-layer vascular architecture and limited atherosclerotic features,” said Ho-Wook Jun, Ph.D., a professor ...
2024-01-12
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Size does not matter. Certainly not when it comes to tiny worms securing the attention of biologists. One such biologist, Morris F. Maduro at the University of California, Riverside, has just been awarded a grant of nearly $1.3 million from the National Science Foundation, or NSF, to study a worm (or nematode) about a millimeter in length.
The research project will focus on the gut of Pristionchus pacificus. Like most nematodes, P. pacificus develops quickly, its growth from embryo to adult taking just four days. It is a complete ...
2024-01-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By one estimate, as many as 30% of people in the U.S. are in romantic relationships with partners who do not share their political views. In today’s hyperpartisan climate, where Democrats and Republicans have difficulty talking to each other and their views are polarized about media outlets’ credibility, how do couples with differing political perspectives decide which media to follow? And how do these decisions affect their discussions on political issues and their relationship ...
2024-01-12
MADISON — A team of astronomers have discovered a planet closer and younger than any other Earth-sized world yet identified. It’s a remarkably hot world whose proximity to our own planet and to a star like our sun mark it as a unique opportunity to study how planets evolve.
The new planet was described in a new study published this week by The Astronomical Journal. Melinda Soares-Furtado, a NASA Hubble Fellow at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who will begin work as an astronomy professor at the university in the fall, and recent UW–Madison graduate Benjamin Capistrant, now a graduate student at the University of Florida, co-led the study with co-authors from ...
2024-01-12
Earth’s average surface temperature in 2023 was the warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. Global temperatures last year were around 2.1 degrees Fahrenheit (1.2 degrees Celsius) above the average for NASA’s baseline period (1951-1980), scientists from NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York reported.
“NASA and NOAA’s global temperature report confirms what billions of people around the world experienced last year; we are facing a climate ...
2024-01-12
If you are one of the 30% to 50% of women experiencing urinary incontinence, new research suggests that it could turn into a bigger health issue.
Having more frequent urinary incontinence and leakage amounts is associated with higher odds of disability, according to RUSH researchers in a study published in the January issue of Menopause.
“Often symptoms from urinary incontinence are ignored until they become bothersome or limit physical or social activities,” said Sheila Dugan, MD, chair of the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at RUSH. “Because this study suggests that urinary incontinence is associated with disability, ...
2024-01-12
Ethylene is sometimes called the most important chemical in the petrochemical industry because it serves as the feedstock for a huge range of everyday products. It’s used in the production of antifreeze, vinyl, synthetic rubber, foam insulation, and plastics of all kinds.
Currently, ethylene is produced through an energy- and resource-intensive process called steam cracking, where extremes of temperature and pressure produce ethylene from crude oil in the presence of steam—and in the process, emit tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Another way ...
2024-01-12
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is pleased to announce its 11th World Congress, Targeting Microbiota 2024. This congress is scheduled to take place on October 17-18 in Malta, and will convene international leading experts, researchers, and professionals to explore and discuss the latest advancements in the field of microbiota. Under the new presidency of Maria Cecilia Giron, University of Padova, we anticipate a transformative era, propelling the ISM to new heights in microbiota research.
Thorough Investigation through Specialized Tracks
Recent Advances & Challenges in Microbiota
Microbiota-Host Cross-Talk and Signaling
Metabolomics: Innovations ...
2024-01-12
AUSTIN, Texas — The recent firing and rapid rehiring of Sam Altman, the co-founder and CEO of ChatGPT creator OpenAI, illustrates the delicate dance between visionary CEOs and the boards who oversee them.
Some CEOs — often founders — are fueled by strong convictions about the strategic direction their companies should take. But their boards sometimes don’t share their visions.
When that happens, what is the board’s role in governance? Should it monitor or advise the CEO? Should it back off and approve the CEO’s strategy?
The answer depends on how deeply the CEO is invested in the strategy, says Volker Laux, professor of accounting at Texas ...
2024-01-12
Did smokers do better than non-smokers in a clinical trial for an experimental cancer treatment? That was the intriguing question that led University of Iowa researchers and their colleagues to develop a drinkable, carbon monoxide-infused foam that boosted the effectiveness of the therapy, known as autophagy inhibition, in mice and human cells. The findings were recently published in the journal Advanced Science.
Looking for ways to exploit biological differences between cancer cells and healthy cells ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Activity of pazopanib in EWSR1-NFATC2 translocation-associated bone sarcoma