(Press-News.org) Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Trazadone and CBT no more effective than placebo for improving insomnia among long-term dialysis patients
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1794
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-3448
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A clinical trial of more than 120 persons undergoing hemodialysis found that cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or trazodone were no more effective than placebo for improving mild to moderate chronic insomnia. These findings are important given the prevalence of insomnia among long-term dialysis patients. The study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Insomnia affects up to 50 percent of persons undergoing long-term dialysis. Because insomnia is associated with exacerbated fatigue, depression, pain perception, and poor quality of life, patients
place a high priority on finding effective treatments for this condition. CBT-I and trazodone are commonly used interventions to treat insomnia in the general population, but evidence for efficacy and safety of insomnia treatments cannot be extrapolated to persons undergoing long-term dialysis.
A team led by researchers from the University of Washington randomly assigned 126 persons undergoing hemodialysis and experiencing chronic insomnia to 6 weeks of CBT-I, trazadone, or placebo to compare the effectiveness of the interventions. Participants were assessed for severity of insomnia at 7 and 25 weeks using the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) questionnaire. The authors found that the change in ISI scores were the same for patients regardless of the intervention used, but serious adverse events occurred more frequently in participants using trazodone. According to the authors, given the high burden of insomnia in dialysis patients and high priority placed by patients for symptom relief, more trials are needed to investigate additional therapies for this condition.
An accompanying editorial by Ronald B. Postuma, MD, MSc highlights how the different causes of insomnia impact its treatment. The author notes that lack of efficacy observed with CBT-I in this study is remarkable, given the extremely strong evidence base for its utility in primary insomnia, suggesting that the typical psychophysiological drivers of insomnia in the general population may be simply less pertinent in hemodialysis patients. The authors also highlights that future studies should explore medications specifically designed for insomnia and treatments that target restless legs and neuropathic pain.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author, Rajnish Mehrotra, MD, MS, please email rmehrotr@uw.edu.
----------------------------
2. Gabapentinoids associated with severe exacerbation of COPD
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0849
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A population-based cohort study of more than 10,000 persons using gabapentinoids found that their use was associated with an increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. The study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Gabapentinoid drugs are anticonvulsant drugs indicated for the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Despite limited indications, its prescription has surged across North America and Europe, which may partly stem from excessive off-label prescribing. However, these drugs have been reported to cause central nervous system depression leading to sedation and respiratory depression in animal and human studies. This safety issue may be of particular concern in patients with respiratory disease like COPD.
Researchers from McGill University and Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research studied insurance data for 356 gabapentinoid users with epilepsy, 9,411 with neuropathic pain, and 3,737 with other chronic pain. The gabapentinoid users were matched 1:1 to nonusers on COPD duration, indication for gabapentinoids, age, sex, calendar year, and time-conditional propensity score. The authors found that compared with nonuse, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe COPD exacerbation among users taking these drugs for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and chronic pain and peak increase in risk for severe COPD exacerbation occurred after approximately 6 months of continuous use. Among patients with neuropathic pain and other chronic pain, the risk was observed regardless of age, sex, number of prior COPD exacerbations, prior use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), number of respiratory medications used, or opioid or benzodiazepine use. According to the authors, physicians should consider these potential risks before prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author, Christel Renoux, MD, PhD, please email Pascal Fischer at Pascal.Fischer@ladydavis.ca.
----------------------------
END
Trazadone and CBT no more effective than placebo for improving insomnia among long-term dialysis patients
2024-01-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change threatens global forest carbon sequestration, study finds
2024-01-15
Climate change is reshaping forests differently across the United States, according to a new analysis of U.S. Forest Service data. With rising temperatures, escalating droughts, wildfires, and disease outbreaks taking a toll on trees, researchers warn that forests across the American West are bearing the brunt of the consequences.
The study, led by UF Biology researchers J. Aaron Hogan and Jeremy W. Lichstein was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study reveals a pronounced regional imbalance in forest productivity, a key barometer of ...
Pacific kelp forests are far older that we thought
2024-01-15
The unique underwater kelp forests that line the Pacific Coast support a varied ecosystem that was thought to have evolved along with the kelp over the past 14 million years.
But a new study shows that kelp flourished off the Northwest Coast more than 32 million years ago, long before the appearance of modern groups of marine mammals, sea urchins, birds and bivalves that today call the forests home.
The much greater age of these coastal kelp forests, which today are a rich ecosystem supporting otters, sea lions, seals, and many birds, fish and crustaceans, means that they likely were a ...
Erectile dysfunction medications may increase risk of death when combined with common chest pain medication
2024-01-15
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i)—an erectile dysfunction drug sold under the names Viagra, Levitra, Cialis, and others—are a common medical treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, a new Swedish study published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology suggests that patients are at higher risk for morbidity and mortality over time when PDE5is and nitrate medication are both prescribed.
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition in middle-aged and older men and is a strong predictor of coronary ...
Key moment in the evolution of life on Earth captured in fossils
2024-01-15
Curtin-led research has for the first time precisely dated some of the oldest fossils of complex multicellular life in the world, helping to track a pivotal moment in the history of Earth when the seas began teeming with new lifeforms - after four billion years of containing only single-celled microbes.
Lead author PhD student Anthony Clarke, from the Timescales of Mineral Systems Group within Curtin’s School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, said to determine the age of the fossils, researchers used volcanic ash layers like bookmarks in the geological sequence.
“Located ...
Chasing the light: Sandia study finds new clues about warming in the Arctic
2024-01-15
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Arctic, Earth’s icy crown, is experiencing a climate crisis like no other. It’s heating up at a furious pace — four times faster than the rest of our planet. Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories are pulling back the curtain on the reduction of sunlight reflectivity, or albedo, which is supercharging the Arctic’s warming.
The scientists are not armed with parkas and shovels. Instead, they have tapped into data from GPS satellite radiometers, capturing the sunlight bouncing off the Arctic. This ...
Physicists identify overlooked uncertainty in real-world experiments
2024-01-15
The equations that describe physical systems often assume that measurable features of the system — temperature or chemical potential, for example — can be known exactly. But the real world is messier than that, and uncertainty is unavoidable. Temperatures fluctuate, instruments malfunction, the environment interferes, and systems evolve over time.
The rules of statistical physics address the uncertainty about the state of a system that arises when that system interacts with its environment. But they’ve ...
Kessler Foundation receives grant to investigate impact of combining aerobic exercise and virtual reality for individuals with multiple sclerosis
2024-01-15
East Hanover, NJ – January 15, 2024 – Kessler Foundation received a $39,994 grant from the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers to investigate the impact of a unique combination of a single bout of aerobic cycling and virtual reality (VR) on processing speed in persons with multiple sclerosis (MS) and mobility disability.
Processing speed is the most common cognitive problem in persons with MS and may actually contribute to broader cognitive difficulties, according to the grant recipient, Carly Wender, PhD, research scientist in the Center for Neuropsychology ...
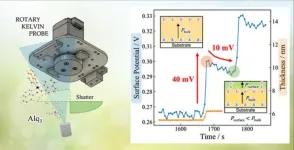
The power of pause: Controlled deposition for effective and long-lasting organic devices
2024-01-15
Organic optoelectronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), use molecules with specific structures arranged on thin films. Additionally, the arrangement of these molecules on any surface is crucial for various processes that occur within these devices. This arrangement is guided by two primary factors: the deposition rate (how fast the molecules are placed) and the surface temperature. Slower deposition rates and higher temperatures facilitate the proper arrangement, resulting in more stable structures. Finding the right time scale for this process is also critical, and ...
Going beyond plastic: Chung-Ang University team explores tara gum as a green polymer
2024-01-15
Synthetic, non-biodegradable plastics are major sources of environmental pollution and have prompted a rising interest in sustainable, biodegradable alternatives derived from natural polymers. “Tara gum,” derived from the seeds of the tara tree (Caesalpinia spinosa), stands out as a promising solution. This natural, water-soluble substance contains polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates), including the widely used “galactomannan,” which is employed in coatings, edible films, and as a stabilizer and thickener. The biocompatibility, biodegradability, and safety of tara gum also make it valuable in industries like food and drug delivery. ...
Sahmyook University researchers open doors to next-generation memristive devices
2024-01-15
Memristive devices constitute a category of devices capable of retaining their internal resistance, thus offering superior performance compared to conventional devices that use integrated circuits. Several materials have been explored to manufacture these devices. In recent years, transition metal oxides have gradually become widely popular for this purpose.
Due to their increasing application in diverse domains like artificial intelligence systems, memristive devices must now overcome several issues related to data retention, endurance, and a large number of conductance states. Moreover, the individual fabrication ...