Thermoelectric permanent magnet opens new possibilities in thermal management technologies
Magnetically enhanced transverse thermoelectric conversion
2024-01-16
(Press-News.org)
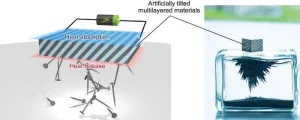
1. A NIMS research team has demonstrated that the transverse thermoelectric conversion (i.e., energy conversion between charge and heat currents that flow orthogonally to each other) can be greatly enhanced by applying magnetic fields or utilizing magnetism. In addition, the team developed a thermoelectric permanent magnet—a new functional material capable of thermoelectric cooling and power generation—by combining permanent magnets and thermoelectric materials into a hybrid structure. These results may guide in achieving thermal management and energy harvesting using common magnets.
2. The Seebeck effect and the Peltier effect have been extensively researched for their application to thermoelectric conversion (TEC) technologies. These effects are classified as longitudinal TEC phenomena—conversion between charge and heat currents that flow in parallel to each other. Although longitudinal TEC devices have higher energy conversion efficiency than their transverse counterparts, their structures are more complex. By contrast, structurally simpler transverse TEC devices can have low energy losses, low manufacturing cost, and excellent durability. To achieve the practical use of transverse TEC devices, however, their conversion efficiency needs to be improved. Transverse TEC is driven by different types of physical phenomena: magnetically induced phenomena (i.e., the magneto-thermoelectric effect) and phenomena attributed to anisotropic crystalline or electronic structures. These phenomena had previously only been researched independently of one another.
3. This NIMS research team recently fabricated an artificially tilted multilayered material—a hybrid material capable of simultaneously exhibiting three different types of TEC phenomena, including the magneto-thermoelectric effects. The team then demonstrated the enhanced cooling performance of this material due to the transverse TEC. The hybrid material was created by alternately stacking and bonding Bi88Sb12 alloy slabs, which exhibit large magneto-thermoelectric effects, and Bi0.2Sb1.8Te3 alloy slabs, which exhibit a large Peltier effect. This stack was then cut diagonally to form the artificially tiled multilayered material. When magnetic fields were applied to this material, its transverse TEC efficiency increased, which was found to be attributed to the combined effects of the three types of TEC phenomena. The team then replaced the Bi0.2Sb1.8Te3 alloy slabs with permanent magnets (see the figure below) and found that the transverse TEC performance can be improved by the magneto-thermoelectric effects even without external magnetic fields.
4. This research demonstrated ways in which magnetic materials can be designed to increase their thermoelectric cooling and power generation capabilities. In future research, the team will develop materials/devices with better thermal management and energy harvesting capabilities for a sustainable society and improved IoT systems.
5. This project was carried out by Ken-ichi Uchida (Distinguished Group Leader, Research Center for Magnetic and Spintronic Materials (CMSM), NIMS), Takamasa Hirai (Researcher, CMSM, NIMS), Fuyuki Ando (Special Researcher, CMSM, NIMS), and Hossein Sepehri-Amin (Group Leader, CMSM, NIMS). This work was conducted as part of the Uchida Magnetic Thermal Management Materials Project (Research Director: Ken-ichi Uchida; grant number: JPMJER2201) under JST’s ERATO Strategic Basic Research Program.
6. This research was published in the online version of Advanced Energy Materials on November 29, 2023.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-16
To prevent aircraft stalls, engineers have long studied the flow of air over airfoils such as airplane wings to detect the angles when flow separation occurs. Recently, a team of researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University including Xi-Jun Yuan and Zi-Qiao Chen investigated the use of quantum computing in connection with machine learning as a more accurate way of solving such problems. Their research was published Nov. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The use of a quantum support vector machine rather than a classical support vector machine increased the accuracy of classification of flow separation from 81.8% ...
2024-01-16
The scientific community has long been enamored of the potential for soft bioelectronic devices, but has faced hurdles in identifying materials that are biocompatible and have all of the necessary characteristics to operate effectively. Researchers have now taken a step in the right direction, modifying an existing biocompatible material so that it conducts electricity efficiently in wet environments and can send and receive ionic signals from biological media.
“We’re talking about ...
2024-01-16
Key takeaways
Decreasing trend in opioid prescriptions: There was a notable nationwide reduction in opioid prescriptions after surgery from 2013 to 2017, reflecting a shift in the medical community's approach to pain management.
Social determinants affect opioid prescription rates: At the county level, lower median population age, higher education levels, insufficient sleep, higher health care costs, fewer mental health providers, and higher uninsured rates are linked to higher opioid prescription rates.
No ...
2024-01-16
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is an extremely common bacterial infection; about 30% of people have colonies of SA living in their nose. SA is often harmless, but it is also a leading cause of hospital-acquired and community-associated infections. A vaccine for SA would be a game-changer for public health, but for decades, all vaccine candidates for SA have failed in clinical trials despite successful preclinical studies in mice. Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have finally explained why.
In a new study, published January ...
2024-01-16
About The Study: Based on four simulation models, breast cancer screening, treatment of stage I to III breast cancer, and treatment of metastatic breast cancer were each associated with reduced breast cancer mortality between 1975 and 2019 in the U.S.
Authors: Sylvia K. Plevritis, Ph.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.25881)
Editor’s ...
2024-01-16
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 eligible studies, including 17 among children (n = 45,851) and 25 among adults (n = 268,095), found a positive association between intake of 100% fruit juice and weight gain in children. Analysis of cohort studies in adults found a significant positive association among studies unadjusted for total energy, suggesting potential mediation by calories; an analysis of trials in adults found no significant association between 100% fruit juice consumption and body weight. The findings ...
2024-01-16
About The Study: The findings of this study of U.S. families receiving employer-sponsored health insurance suggest that three decades of increasing health care premiums were likely associated with reduced annual earnings and increased earnings inequality by race and ethnicity and wage level and were meaningfully associated with wage stagnation.
Authors: Kurt Hager, Ph.D., M.S., of the UMass Chan Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
2024-01-16
About The Study: The results of this survey study involving 4,119 currently competing U.S. college athletes suggest that interpersonal violence is associated with marked changes in the psychosocial health and emotional well-being of college athletes, particularly those who identify as female and with non-heterosexual sexual orientations. Variations in coaching style have the potential to alter these associations. Ongoing efforts are needed to leverage the unique position that coaches hold to help reduce interpersonal violence and create safe places where all college athletes can thrive.
Authors: Yetsa A. Tuakli-Wosornu, M.D., ...
2024-01-16
PHILADELPHIA – Ordering a palliative care consultation by “default” – via an automatic order programmed into the electronic medical record that doctors may cancel if they choose – is an effective strategy to give more hospitalized patients the opportunity to benefit from palliative care, and sooner, according to a new study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Palliative care is specialized medical care focused on relieving the symptoms and stress of a serious illness and improving quality of life, in alignment with a patient’s ...
2024-01-16
The rising cost of health insurance is an ongoing concern in the United States. New research shows that increasing health insurance costs are eating up a growing proportion of worker’s compensation, and have been a major factor in both flattening wages and increasing income inequality over the past 30 years.
In a study from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, researchers found that the cost of employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) health care benefits increased much faster than workers’ wages since the late 1980s, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Thermoelectric permanent magnet opens new possibilities in thermal management technologies
Magnetically enhanced transverse thermoelectric conversion