(Press-News.org)
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for indirect semantic associativity analysis, leveraging existing semantic relations without the need for additional data.
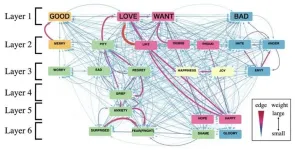
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers from Japan have identified emotional hubs that exist across languages. Their work, published online in Scientific Reports on December 09, 2023, analyzed word associations by employing a "colexification network" and revealed that the emotion-related concepts "GOOD," "WANT," "BAD," and "LOVE" have the highest number of associations with all other words that represent emotions.
The researchers, including Dr. Tohru Ikeguchi, Ms. Mitsuki Fukuya, and Dr. Tomoko Matsumoto from the Tokyo University of Science, and Dr. Yutaka Shimada from Saitama University, built a network by connecting concepts in several languages. In doing so, they ensured that the connection between two words represented the strength of colexification. "Colexification is the phenomenon of a single word with multiple concepts. For example, the Spanish word “malo” has two meanings “BAD” and “SEVERE.” It means that the two concepts of “BAD” and “SEVERE” are colexified in Spanish. In this paper, by focusing on colexification, we succeeded in detecting central emotions that share semantic commonality with many other emotions," explains Dr. Ikeguchi, the lead author of the study.
In a discovery that affirms the universality of their findings, the team discovered that three of the four emotions they identified are identical to core emotions discovered through traditional semantic methods and the natural semantic metalanguage (NSM), which corresponds with their previous study findings. In this context, Dr. Ikeguchi notes, "To identify the semantic primes, NSM researchers studied numerous languages using traditional semantic methods. Intriguingly, the set of semantic primes includes three of our four central emotion-related concepts: ‘GOOD,’ ‘BAD,’ and ‘WANT.’ This agreement supports our conclusion that the central concepts identified by colexification analysis could be shared by many languages rather than specific to English".
The findings of this study may offer novel insights into the evolution of languages and cross-cultural communication since words are considered to be intricately connected to emotions. The outcomes gain significance amid the increasing importance of comprehending natural language processing. As Dr. Ikeguchi explains, "Concepts associated with sentiments or emotions play an important role in the field of natural language processing, particularly sentiment analyses. The analysis methods enable us to identify semantically positive and negative orientations of written texts and have various applications in the real world."
A better understanding of natural language processing will also aid in the development of language processing algorithms and large language models (LLMs). LLMs are now used extensively for information processing and content generation. Globally, there is a trend of increasing investments aimed at enhancing and refining these models. Therefore, the findings of this study may have useful implications for the future of online communication.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-48922-8
About The Tokyo University of Science
Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of “Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society," TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
Website: https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/mediarelations/
About Professor Tohru Ikeguchi from Tokyo University of Science
Dr. Tohru Ikeguchi is a professor at the Department of Information and Computer Technology at the Tokyo University of Science. Professor Ikegachi has published nearly 178 scientific articles in areas such as Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos, Nonlinear Time Series Analysis, Network Science, Computational NeuroScience, Application of Chaotic Neurodynamics for Solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems, . He has previously worked at Universite de Louis Pasteur and Saitama University, and has been cited multiple times.
END
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
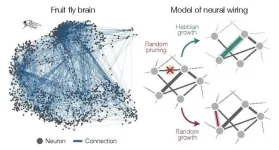
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
Large-scale genetic analysis has helped researchers uncover the interplay between cancer-driving genetic mutations and inherited genetic variants in a rare type of blood cancer.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, combined various comprehensive data sets to understand the impact of both cancer-driving spontaneous mutations and inherited genetic variation on the risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN).
The study, published today (17 January) in Nature Genetics, describes how inherited genetic variants can influence whether a spontaneous mutation in a particular ...
When a person has one or more blocked arteries, providers may choose to conduct a minimally invasive procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention, or PCI.
By inflating a balloon and potentially placing a stent, blood can flow more freely from the heart.
Despite carrying less risk than open surgery, stenting and balloon angioplasty can result in complications like bleeding and kidney injury.
Researchers at Michigan Medicine developed an AI-driven algorithm that accurately predicts death and complications after PCI — which could emerge as a tool ...
A new analysis of trial data on pregnant smokers, led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London, finds that the regular use of nicotine replacement products during pregnancy is not associated with adverse pregnancy events or poor pregnancy outcomes.
The PREP 2 study used data collected from over 1100 pregnant smokers attending 23 hospitals in England and 1 stop-smoking service in Scotland to compare pregnancy outcomes in women who did or did not use nicotine in the form of e-cigarettes (EC) or nicotine patches ...
The pioneering research of Dr Yiliang Ding investigating the structure and function of RNA in living cells has been recognised with a major award.
Yiliang a group leader at the John Innes Centre, is among nine recipients of the 2024 Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists in the UK, announced today by the Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences.
The awards recognise research that is transforming medicine, technology, and our understanding of the world across three categories: Chemical Sciences, Physical Sciences & Engineering, and ...
Researchers at the University of Basel have built a quantum memory element based on atoms in a tiny glass cell. In the future, such quantum memories could be mass-produced on a wafer.
It is hard to imagine our lives without networks such as the internet or mobile phone networks. In the future, similar networks are planned for quantum technologies that will enable the tap-proof transmission of messages using quantum cryptography and make it possible to connect quantum computers to each other.
Like their conventional counterparts, such quantum networks require memory elements in which information can be temporarily stored ...