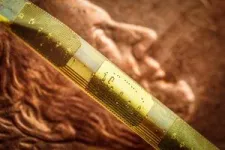
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Basel have built a quantum memory element based on atoms in a tiny glass cell. In the future, such quantum memories could be mass-produced on a wafer.
It is hard to imagine our lives without networks such as the internet or mobile phone networks. In the future, similar networks are planned for quantum technologies that will enable the tap-proof transmission of messages using quantum cryptography and make it possible to connect quantum computers to each other.
Like their conventional counterparts, such quantum networks require memory elements in which information can be temporarily stored and routed as needed. A team of researchers at the University of Basel led by Professor Philipp Treutlein has now developed such a memory element, which can be micro-fabricated and is, therefore, suitable for mass production. Their results were recently published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters.
Photon storage in glass cells
Light particles are particularly suited to transmitting quantum information. Photons can be used to send quantum information through fiber optic cables, to satellites or into a quantum memory element. There, the quantum mechanical state of the photons has to be stored as precisely as possible and, after a certain time, converted back into photons.
Two years ago, the Basel researchers demonstrated this works well using rubidium atoms in a glass cell. “However, that glass cell was handmade and several centimeters in size,” says postdoc Dr. Roberto Mottola: “To be suitable for everyday use, such cells need to be smaller and amenable to being produced in large numbers.”
That is precisely what Treutlein and his collaborators have now achieved. To use a much smaller cell measuring only a few millimeters, which they obtained from the mass production of atomic clocks, they needed to develop a few tricks. In order to have a sufficient number of rubidium atoms for quantum storage despite the small size of the cell, they had to heat up the cell to 100 degrees centigrade to increase the vapor pressure.
Moreover, they exposed the atoms to a magnetic field of 1 tesla, more than ten thousand times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field. This shifted the atomic energy levels in a way that facilitated the quantum storage of photons using an additional laser beam. This method allowed the researchers to store photons for around 100 nanoseconds. Free photons would have traveled 30 meters in that time.
A thousand quantum memories on a single wafer
“In this way, we have built, for the first time, a miniature quantum memory for photons of which around 1000 copies can be produced in parallel on a single wafer”, says Treutlein. In the current experiment, storage was demonstrated using strongly attenuated laser pulses, but in the near future, Treutlein, in collaboration with the CSEM in Neuchatel, also wants to store single photons in the miniature cells. Moreover, the format of the glass cells still needs to be optimized, such as to store the photons for as long as possible while preserving their quantum states.
END
Mass-producible miniature quantum memory
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new targeted treatment calms the cytokine storm
2024-01-17
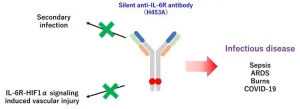
Osaka, Japan – Cytokines are chemical messengers that help the body get rid of invading bacteria and viruses, and control inflammation. The body carefully balances cytokines because they help keep the immune system healthy. However, this balance is upset if the immune system overreacts. A serious infection or a severe burn can unleash a cytokine storm in the body. During the storm—also called cytokine release syndrome (CRS)—the body produces too many cytokines, leading to life-threatening inflammation.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a key cytokine in the storm because it helps to drive the inflammation that damages ...
Tiny AI-based bio-loggers revealing the interesting bits of a bird’s day
2024-01-17
Osaka, Japan – Have you ever wondered what wildlife animals do all day? Documentaries offer a glimpse into their lives, but animals under the watchful eye do not do anything interesting. The true essence of their behaviors remains elusive. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a camera that allows us to capture these behaviors.
In a study recently published in PNAS Nexus, researchers from Osaka University have created a small sensor-based data logger (called a bio-logger) that automatically detects and records video of infrequent behaviors in wild seabirds without supervision by researchers.
Infrequent behaviors, such as diving into the water for food, can ...
SDG-washing found among Canada's top companies
2024-01-17
Canada's biggest companies often speak of their plans to be more sustainable, but a new study found corporations aren't fully backing up those commitments.
A team of University of Waterloo researchers concluded that corporate investing in communities fell despite an increase in companies committing to the United Nation's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) over the last decade.
Researchers investigated the community investment of Canada's 58 leading private-sector companies as a percentage of their net profit after tax to determine whether introducing SDGs created ...
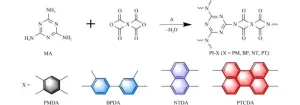
Enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting with a donor-acceptor polyimide
2024-01-17
Polyimide (PI) has emerged as a promising organic photocatalyst owing to its distinct advantages of high visible-light response, facile synthesis, molecularly tunable donor-acceptor structure, and excellent physicochemical stability. However, the synthesis of high-quality PI photoelectrode remains a challenge, and photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting for PI has been less studied.
A research group of Huiyan Zhang and Sheng Chu from Southeast University prepared PI films by a ...
Spider venom heart drug a step closer
2024-01-17
A spider venom molecule being investigated by a University of Queensland team has met critical benchmarks towards becoming a treatment for heart attack and stroke.
Associate Professor Nathan Palpant and Professor Glenn King from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience have previously shown that the drug candidate Hi1a protects cells from the damage caused by heart attack and stroke.
Dr Palpant said a subsequent study has put the drug through a series of preclinical tests designed to mimic real-life treatment scenarios.
“These tests are a major step towards helping us understand how Hi1a would work ...
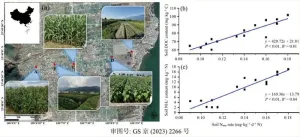
Is soil nitrogen mineralization important in agricultural intensive areas?
2024-01-17
Soil nitrogen mineralization (Nmin) is a key process that converts organic N into mineral N that controls soil N availability to plants. However, regional assessments of soil Nmin in cropland and its affecting factors are lacking, especially in relation to variation in elevation. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for crops but mineral N in soil, the only form that can be absorbed and used by crops, represents only about 1% of total soil N. Although N fertilization is commonly a necessary method for supplying N to crops, N release due to excess N fertilizer in the environment ...
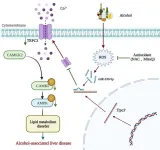
Hepatic TRPC3: an emerging regulator of alcohol-associated liver disease
2024-01-17
Excessive alcohol intake is strongly associated with alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) which accounts for 25% and 30% of deaths from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Impairment of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+-mediated signaling in ALD suggests that Ca2+ channels are important in ALD pathological progression.
TRPC (transient receptor potential cation channel protein C) is an evolutionarily conserved non-selective cation channel protein primarily located in the cell membrane with six transmembrane segments. So far four TRPC subfamilies have been identified, categorized into TRPC1, TRPC2, TRPC4/5, and TRPC3/6/7. Among them, TRPC3 is the most well-studied ...
USC Stem Cell study throws our understanding of gene regulation for a loop
2024-01-17
The blueprint for human life lies within the DNA in the nucleus of each of our cells. In human cells, around six and a half feet of this genetic material must be condensed to fit inside the nucleus. DNA condensation is not random. To function properly, the genetic material is highly organized into loop structures that often bring together widely separated sections of the genome critical to the regulation of gene activity. In a new paper published in Nature Communications, USC Stem Cell scientists from the laboratory ...
A manned submersible found a fault scarp of the 2011 Tohoku-oki megaquake in the Japan Trench
2024-01-17
Niigata, Japan – On September 4, 2022, a geologist Hayato Ueda in Niigata University boarded a submarine vehicle with a pilot Chris May and had a dive into the Japan Trench within the epicenter area of the 2011 Tohoku-oki megaquake, which caused the devastating tsunami disaster. On the 7,500 m deep trench bottom, they found a 26 m high nearly vertical cliff on the eastern slope of a 60 m high ridge. Previous bathymetric surveys from the sea surface have revealed that the ridge did not exist before, and appeared just after the megaquake ...
Video gamers worldwide may be risking irreversible hearing loss and/or tinnitus
2024-01-17
Video gamers worldwide may be risking irreversible hearing loss and/or tinnitus—persistent ringing/buzzing in the ears—finds a systematic review of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Public Health.
What evidence there is suggests that the sound levels reported in studies of more than 50,000 people often near, or exceed, permissible safe limits, conclude the researchers.
And given the popularity of these games, greater public health efforts are needed to raise awareness of the potential ...