(Press-News.org) A spider venom molecule being investigated by a University of Queensland team has met critical benchmarks towards becoming a treatment for heart attack and stroke.
Associate Professor Nathan Palpant and Professor Glenn King from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience have previously shown that the drug candidate Hi1a protects cells from the damage caused by heart attack and stroke.
Dr Palpant said a subsequent study has put the drug through a series of preclinical tests designed to mimic real-life treatment scenarios.
“These tests are a major step towards helping us understand how Hi1a would work as a therapeutic – at what stage of a heart attack it could be used and what the doses should be,” Dr Palpant said.
“We established that Hi1a is as effective at protecting the heart as the only cardioprotective drug to reach Phase 3 clinical trials, a drug that was ultimately shelved due to side effects.
“Importantly, we found that Hi1a only interacts with cells in the injured zone of the heart during an attack and doesn’t bind to healthy regions of the heart – reducing the chance of side effects.”
Professor King, who recently won the Prime Minister’s Prize for Innovation for developing the world’s first insecticides from spider venom, discovered Hi1a in the venom of the K’gari funnel web spider.
“Hi1a could reduce damage to the heart and brain during heart attacks and strokes by preventing cell death caused by lack of oxygen,” Professor King said.
“Our testing and safety studies from independent contract research organisations has provided evidence that Hi1a could be an effective and safe therapeutic.”
Infensa Bioscience, a company co-founded by the researchers, raised $23 million in 2022 to develop Hi1a for commercial purposes.
Infensa CEO and UQ researcher, Associate Professor Mark Smythe, said cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death globally.
“Most deaths from cardiovascular disease are caused by heart attacks and strokes, yet there are no drugs on the market that prevent the damage they cause,” Dr Smythe said.
“An effective drug to treat heart attacks would have worldwide impact, providing a breakthrough to improve the lives of millions of individuals living with heart disease.”
The research team included Dr Meredith Redd from IMB as well as Dr Melissa Reichelt and Dr Yusuke Yoshikawa from UQ’s School of Biomedical Sciences.
The study was published in the world’s leading cardiac journal The European Heart Journal.
Video: https://youtu.be/73zFDfeuTv8
END
Spider venom heart drug a step closer
A spider venom molecule being investigated by a University of Queensland team has met critical benchmarks towards becoming a treatment for heart attack and stroke.
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
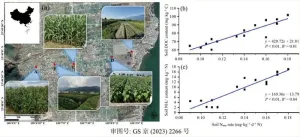
Is soil nitrogen mineralization important in agricultural intensive areas?
2024-01-17
Soil nitrogen mineralization (Nmin) is a key process that converts organic N into mineral N that controls soil N availability to plants. However, regional assessments of soil Nmin in cropland and its affecting factors are lacking, especially in relation to variation in elevation. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for crops but mineral N in soil, the only form that can be absorbed and used by crops, represents only about 1% of total soil N. Although N fertilization is commonly a necessary method for supplying N to crops, N release due to excess N fertilizer in the environment ...
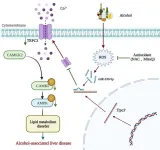
Hepatic TRPC3: an emerging regulator of alcohol-associated liver disease
2024-01-17
Excessive alcohol intake is strongly associated with alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) which accounts for 25% and 30% of deaths from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Impairment of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+-mediated signaling in ALD suggests that Ca2+ channels are important in ALD pathological progression.
TRPC (transient receptor potential cation channel protein C) is an evolutionarily conserved non-selective cation channel protein primarily located in the cell membrane with six transmembrane segments. So far four TRPC subfamilies have been identified, categorized into TRPC1, TRPC2, TRPC4/5, and TRPC3/6/7. Among them, TRPC3 is the most well-studied ...
USC Stem Cell study throws our understanding of gene regulation for a loop
2024-01-17
The blueprint for human life lies within the DNA in the nucleus of each of our cells. In human cells, around six and a half feet of this genetic material must be condensed to fit inside the nucleus. DNA condensation is not random. To function properly, the genetic material is highly organized into loop structures that often bring together widely separated sections of the genome critical to the regulation of gene activity. In a new paper published in Nature Communications, USC Stem Cell scientists from the laboratory ...
A manned submersible found a fault scarp of the 2011 Tohoku-oki megaquake in the Japan Trench
2024-01-17
Niigata, Japan – On September 4, 2022, a geologist Hayato Ueda in Niigata University boarded a submarine vehicle with a pilot Chris May and had a dive into the Japan Trench within the epicenter area of the 2011 Tohoku-oki megaquake, which caused the devastating tsunami disaster. On the 7,500 m deep trench bottom, they found a 26 m high nearly vertical cliff on the eastern slope of a 60 m high ridge. Previous bathymetric surveys from the sea surface have revealed that the ridge did not exist before, and appeared just after the megaquake ...
Video gamers worldwide may be risking irreversible hearing loss and/or tinnitus
2024-01-17
Video gamers worldwide may be risking irreversible hearing loss and/or tinnitus—persistent ringing/buzzing in the ears—finds a systematic review of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Public Health.
What evidence there is suggests that the sound levels reported in studies of more than 50,000 people often near, or exceed, permissible safe limits, conclude the researchers.
And given the popularity of these games, greater public health efforts are needed to raise awareness of the potential ...
Enlarged breast tissue in men (gynaecomastia) linked to heightened risk of death
2024-01-17
Men with enlarged breast tissue, not caused by excess weight—a condition formally known as gynaecomastia—may be at heightened risk of an early death before the age of 75, suggests the first study of its kind, published online in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Those with a pre-existing risk factor, such as cancer or circulatory, lung, and gut diseases before diagnosis seem to be most vulnerable, the findings indicate.
Enlarged breast tissue in men is usually caused by a hormone imbalance and affects around a third to around two thirds of men, depending on age. It is distinct from what is often dubbed ...
Same-level workplace falls set to rise amid surge in older female workforce numbers
2024-01-17
Same-level falls in the workplace are set to rise amid rapid growth in the numbers of older female employees in the workforce, suggests Australian research published online first in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Although workplace falls, overall, are more common among male employees, particularly falls from height, same-level falls are more common in older women, the findings indicate.
The prevalence and relative severity of workplace falls mean that better prevention strategies are needed to mitigate these sex-specific risk factors, conclude the researchers.
In 2016, an estimated 1.53 million deaths and 76.1 million years of ...
Silkmoths: Different olfactory worlds of females and males
2024-01-17
The world smells different for female silkmoths than for males
In humans, the sense of smell is similarly developed in men and women, although women have slightly more olfactory neurons and therefore a slightly more sensitive nose. On the whole, however, they perceive the same odors. Male moths, on the other hand, live in a completely different olfactory world to their female counterparts. For example, the antennae of male silkmoths - their "nose" - are highly specialized to detect female sex pheromones, ...
Wrongly-enforced rules over “digital surrogates” by museums censors research and creative use, study warns
2024-01-17
Cultural institutions are censoring research, learning and creativity because of the way they police the reuse of digital copies of out-of-copyright artworks and artefacts, a new study warns.
Cultural institutions have created a “mess” by claiming and enforcing new rights over the reproduction images of works in their collections.
This allows museums and other organisations to refuse requests for the use of the images in education or research or charge high fees. This impedes free and creative expression and amounts to censorship, according to Dr Andrea Wallace from the University of Exeter Law School.
Researchers, educators and others regularly ...
Space solar power project ends first in-space mission with successes and lessons
2024-01-17
One year ago, Caltech’s Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1) launched into space to demonstrate and test three technological innovations that are among those necessary to make space solar power a reality.
The spaceborne testbed demonstrated the ability to beam power wirelessly in space; it measured the efficiency, durability, and function of a variety of different types of solar cells in space; and gave a real-world trial of the design of a lightweight deployable structure to deliver and hold the aforementioned solar cells and power transmitters.
Now, with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Spider venom heart drug a step closerA spider venom molecule being investigated by a University of Queensland team has met critical benchmarks towards becoming a treatment for heart attack and stroke.