(Press-News.org) LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding author of a paper published in the journal Earth and Space Science on an innovative application of AI to permafrost data.
“Current models don’t give the resolution needed to understand how permafrost thaw is changing the environment and affecting infrastructure,” Thaler said. “Our model creates high-resolution maps telling us where permafrost is now and where it is likely to change in the future.”
The AI models also identify the landscape and ecological features driving the predictions, such as vegetative greenness, landscape slope angle and the duration of snow cover.
AI versus field data
Thaler was part of a team with fellow Los Alamos researchers Joel Rowland, Jon Schwenk and Katrina Bennett, plus collaborators from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, that used a form of AI called supervised machine learning. The work tested the accuracy of three different AI approaches against field data collected by Los Alamos researchers from three watersheds with patchy permafrost on the Seward Peninsula in Alaska.
Permafrost, or ground that stays below freezing temperature two years or more, covers about one-sixth of the exposed land in the Northern Hemisphere, Thaler said. Thawing permafrost is already disrupting roads, oil pipelines and other facilities built over it and carries a range of environmental hazards as well.
As air temperatures warm under climate change, the thawing ground releases water. It flows to lower terrain, rivers, lakes and the ocean, causing land-surface subsidence, transporting minerals, altering the direction of groundwater, changing soil chemistry and releasing carbon to the atmosphere.
Useful results
The resolution of the most widely used current pan-arctic model for permafrost is about one-third square mile, far too coarse to predict how changing permafrost will undermine a road or pipeline, for instance. The new Los Alamos AI model determines surface permafrost coverage to a resolution of just under 100 square feet, smaller than a typical parking space and far more practical for assessing risk at a specific location.
Using their AI model trained on data from three sites on the Seward Peninsula, the team generated a map showing large areas without any permafrost around the Seward sites, matching the field data with 83% accuracy. Using the pan-arctic model for comparison, the team generated a map of the same sites with only 50% accuracy.
“It's the highest accuracy pan-arctic product to date, but it obviously isn't good enough for site-specific predictions,” Thaler said. “The pan-arctic product predicts 100% of that site is permafrost, but our model predicts only 68%, which we know is closer to the real percentage based on field data.”
Feeding the AI models
This initial study proved the concept of the Los Alamos model on the Seward data, delivering acceptable accuracy for terrain similar to the location where the field data was collected. To measure each model’s transferability, the team also trained it on data from one site then ran the model using data from a second site with different terrain that the model had not been trained on. None of the models transferred well by creating a map matching actual findings at the second site.
Thaler said the team will do additional work on the AI algorithms to improve the model’s transferability to other areas across the Arctic. “We want to be able to train on one data set and then apply the model to a place it hasn’t seen before. We just need more data from more diverse landscapes to train the models, and we hope to collect that data soon,” he said.
Part of the study involved comparing the accuracy of three different AI approaches — extremely randomized trees, support vector machines and an artificial neural network — to see which model came closest to matching the “ground truth” data gathered in field observations at the Seward Peninsula. Part of that data was used to train the AI models. Each model then generated a map based on unseen data predicting the extent of near-surface permafrost.
While the Los Alamos research demonstrated a marked improvement over the best — and widely used — pan-arctic model, the results from the team’s three AI models were mixed, with the support vector machines showing the most promise for transferability.
The paper: “High-Resolution Maps of Near-Surface Permafrost for Three Watersheds on the Seward Peninsula, Alaska Derived From Machine Learning.” Earth and Space Science. DOI: 10.1029/2023EA003015
The funding: Department of Energy Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research through the Next Generation Ecosystem Experiment (NGEE) Arctic and Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
-30-
LA-UR-24-20349
END
New AI makes better permafrost maps
Improved mapping gives decision makers a new tool for protecting infrastructure as Arctic warms
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
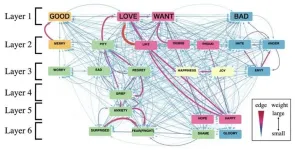
New study unveils emotional hubs that exist across languages
2024-01-17
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
Childhood stress linked to higher risk of high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes in adults
2024-01-17
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
US air pollution rates on the decline but pockets of inequities remain
2024-01-17
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
Fly brain, mouse brain, worm brain: They all network the same
2024-01-17
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
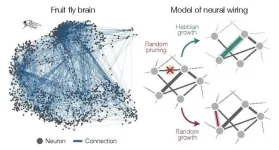
Surprisingly simple model explains how brain cells organize and connect
2024-01-17
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
Transforming clinical recording of deep brain activity with a new take on sensor manufacturing
2024-01-17
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
Role of inherited genetic variants in rare blood cancer uncovered
2024-01-17
Large-scale genetic analysis has helped researchers uncover the interplay between cancer-driving genetic mutations and inherited genetic variants in a rare type of blood cancer.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, combined various comprehensive data sets to understand the impact of both cancer-driving spontaneous mutations and inherited genetic variation on the risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN).
The study, published today (17 January) in Nature Genetics, describes how inherited genetic variants can influence whether a spontaneous mutation in a particular ...
AI model predicts death, complications for patients undergoing angioplasty, stents
2024-01-17
When a person has one or more blocked arteries, providers may choose to conduct a minimally invasive procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention, or PCI.
By inflating a balloon and potentially placing a stent, blood can flow more freely from the heart.
Despite carrying less risk than open surgery, stenting and balloon angioplasty can result in complications like bleeding and kidney injury.
Researchers at Michigan Medicine developed an AI-driven algorithm that accurately predicts death and complications after PCI — which could emerge as a tool ...
E-cigarettes help pregnant smokers quit without risks to pregnancy
2024-01-17
A new analysis of trial data on pregnant smokers, led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London, finds that the regular use of nicotine replacement products during pregnancy is not associated with adverse pregnancy events or poor pregnancy outcomes.
The PREP 2 study used data collected from over 1100 pregnant smokers attending 23 hospitals in England and 1 stop-smoking service in Scotland to compare pregnancy outcomes in women who did or did not use nicotine in the form of e-cigarettes (EC) or nicotine patches ...
John Innes Centre researcher honored with prestigious Blavatnik award
2024-01-17
The pioneering research of Dr Yiliang Ding investigating the structure and function of RNA in living cells has been recognised with a major award.
Yiliang a group leader at the John Innes Centre, is among nine recipients of the 2024 Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists in the UK, announced today by the Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences.
The awards recognise research that is transforming medicine, technology, and our understanding of the world across three categories: Chemical Sciences, Physical Sciences & Engineering, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] New AI makes better permafrost mapsImproved mapping gives decision makers a new tool for protecting infrastructure as Arctic warms