(Press-News.org)
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers at Kyushu University, in collaboration with Osaka University and the Fine Ceramics Center, have developed a framework that uses machine learning to speed up the discovery of materials for green energy technology. Using the new approach, the researchers identified and successfully synthesized two new candidate materials for use in solid oxide fuel cells – devices that can generate energy using fuels like hydrogen, which don’t emit carbon dioxide. Their findings, which were reported in the journal, Advanced Energy Materials, could also be used to accelerate the search for other innovative materials beyond the energy sector.
In response to a warming climate, researchers have been developing new ways to generate energy without using fossil fuels. “One path to carbon neutrality is by creating a hydrogen society. However, as well as optimizing how hydrogen is made, stored and transported, we also need to boost the power-generating efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells,” explains Professor Yoshihiro Yamazaki, of Kyushu University’s Department of Materials Science and Technology, Platform of Inter-/Transdisciplinary Energy Research (Q-PIT).
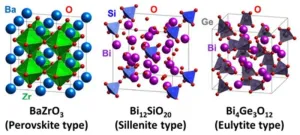
To generate an electric current, solid oxide fuel cells need to be able to efficiently conduct hydrogen ions (or protons) through a solid material, known as an electrolyte. Currently, research into new electrolyte materials has focused on oxides with very specific crystal arrangements of atoms, known as a perovskite structure.
“The first proton-conducting oxide discovered was in a perovskite structure, and new high-performing perovskites are continually being reported,” says Professor Yamazaki. “But we want to expand the discovery of solid electrolytes to non-perovskite oxides, which also have the capability of conducting protons very efficiently.”
However, discovering proton-conducting materials with alternative crystal structures via traditional “trial and error” methods has numerous limitations. For an electrolyte to gain the ability to conduct protons, small traces of another substance, known as a dopant, must be added to the base material. But with many promising base and dopant candidates - each with different atomic and electronic properties – finding the optimal combination that enhances proton conductivity becomes difficult and time-consuming.
Instead, the researchers calculated the properties of different oxides and dopants. They then used machine learning to analyze the data, identify the factors that impact the proton conductivity of a material, and predict potential combinations.
Guided by these factors, the researchers then synthesized two promising materials, each with unique crystal structures, and assessed how well they conducted protons. Remarkably, both materials demonstrated proton conductivity in just a single experiment.
One of the materials, the researchers highlighted, is the first-known proton conductor with a sillenite crystal structure. The other, which has a eulytite structure, has a high-speed proton conduction path that is distinct from the conduction paths seen in perovskites. Currently, the performance of these oxides as electrolytes is low, but with further exploration, the research team believes their conductivity can be improved.
“Our framework has the potential to greatly expand the search space for proton-conducting oxides, and therefore significantly accelerate advancements in solid oxide fuel cells. It’s a promising step forward to realizing a hydrogen society,” concludes Professor Yamazaki. “With minor modifications, this framework could also be adapted to other fields of materials science, and potentially accelerate the development of many innovative materials.”
###
For more information about this research, see "Discovery of Unconventional Proton-Conducting Inorganic Solids via Defect-Chemistry-Trained, Interpretable Machine Learning" Susumu Fujii, Yuta Shimizu, Junji Hyodo, Akihide Kuwabara, Yoshihiro Yamazaki, Advanced Energy Materials, https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202301892
About Kyushu University
Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses—including one of the largest in Japan—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its Vision 2030, Kyushu U will 'Drive Social Change with Integrative Knowledge.' Its synergistic application of knowledge will encompass all of academia and solve issues in society while innovating new systems for a better future.
END
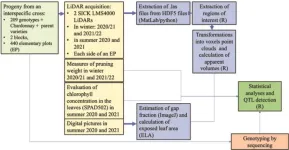
In response to the pressing need to reduce pesticide usage and adapt grapevine varieties to climate change, there's an unprecedented effort to phenotype new genotypes using high-throughput methods. Teams globally are developing advanced systems, employing technologies like multispectral cameras and LiDAR, to assess growth traits, photosynthetic capability, and other architectural parameters. However, traditional methods remain time-consuming and less efficient for large-scale studies. The current research gap lies in effectively employing LiDAR technology ...
Cultivating seed mixtures for local pastures is an age-old method to produce cost-effective and balanced animal feed, enhancing agricultural autonomy and environmental friendliness in line with evolving European regulations and organic consumer demands. Despite its benefits, farmers face adoption challenges due to the asynchronous ripening of cereals and legumes and the difficulty in assessing the nutritional value of heterogeneous seeds. Current practices rely on informal, empirical methods, and a proposed solution is to develop a mobile app or online service, similar to Pl@ntNet, for automated nutritional evaluation of seed mixtures, ...
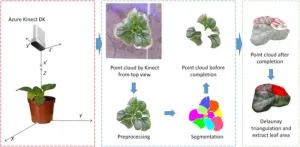
The 3-dimensional point cloud technology revolutionizes non-invasive measurement of plant phenotypic parameters, offering vital data for agriculture and research. Current research focuses on overcoming the limitations of 2.5D imaging and occlusions. Methods such as structure from motion, multi-view stereo, and advanced active 3D reconstruction techniques are being explored for this purpose. However, issues persist with incomplete data acquisition and the inaccuracy of phenotypic parameter extraction due ...
To improve grape yield predictions, automated berry counting has emerged as a crucial yet challenging task due to the dense distribution and occlusion of berries. While grape cultivation is a significant global economic activity, traditional manual counting methods are inaccurate and inefficient. Recent research has shifted towards deep learning and computer vision, employing detection and density estimation techniques for more precise counts. However, these methods grapple with the variability of farmland and high occlusion rates, leading to significant counting errors. Additionally, creating high-performance ...
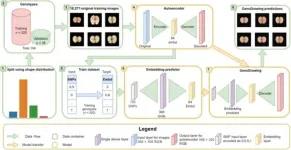
Advancements in whole-genome sequencing have revolutionized plant species characterization, providing a wealth of genotypic data for analysis. The combination of genomic selection and neural networks, especially deep learning and autoencoders, has emerged as a promising method for predicting complex traits from this data. Despite the success in applications like plant phenotyping, challenges remain in accurately translating visual information from images into measurable data for genomic studies.
In November 2023, Plant ...
Erin Overstreet has been selected as the new executive director of the USC Stevens Center for Innovation where she will oversee the university’s commercialization of USC-driven intellectual property.
Overstreet’s expertise and experience embody technology transfer and innovation across the academic, educational, and venture capital sectors; such experience is critical for bridging USC research to a broadened, national technology transfer ecosystem, said Ishwar Puri, senior vice president of the Office of Research and Innovation.
“The university has the utmost confidence in Dr. Overstreet’s ability to ...
In the field of Landscape Architecture, Topography aims to study the complex and ongoing changing relationship between humans and the land through continuously updated and iterative tools and media. It maintains a balance between abstract concepts and concrete perceptions, which can both drive the development of science and technology in this field and hold on to openness to artistic expression. Thus, topographical design may be an effective way to help facilitate refining landscape design methods.
The work entitled “Can Topography ...
Associate Professor Andrew Baker from QUT School of Biology and Environmental Science said antechinuses are carnivorous marsupials well-known for suicidal sex sessions where all males die after the 1 to 3 week breeding period.
“During the breeding season, male and females mate promiscuously in frenzied bouts lasting as long as 14 hours. Certain stress-induced death follows for all males as surging testosterone causes cortisol to flood uncontrolled through the body, reaching pathological levels,” Professor Baker said.
“The males drop dead, which provides an opportunity ...
Protecting the world’s oceans against accelerating damage from human activities could be cheaper and take up less space than previously thought, new research has found.
The University of Queensland’s Professor Anthony Richardson collaborated on the study, which looks to halt the rapid decline of marine biodiversity from expanding industrial activities in marine areas beyond national jurisdictions (ABNJ).
“This ‘blue acceleration’ as we call it, has seen a greater diversity of stakeholders interested in ABNJs, such as the high seas and the international seabed beyond exclusive economic zones,” ...
Frequently using more than three strategies to stay alert while driving could be a sign of excessive sleepiness due to obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
People with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Around one in five people are estimated to have OSA but the majority of sufferers do not realise they have a problem. OSA causes excessive sleepiness and people with untreated OSA are at higher risk of collisions on the road.
Researchers say that asking people ...