New video camera system captures the colored world that animals see, in motion
Open-source camera and software system records natural animal-view videos with over 90% accuracy
2024-01-23
(Press-News.org) A new camera system allows ecologists and filmmakers to produce videos that accurately replicate the colors that different animals see in natural settings, Vera Vasas at the University of Sussex, UK, and colleagues from the Hanley Color Lab at George Mason University, US, report in the open access journal PLOS Biology, publishing January 23rd.
Different animals perceive the world differently because of the capabilities of the photoreceptors in their eyes. For example, animals like honeybees and some birds can see UV light, which are outside the range of human perception. Reconstructing the colors that animals actually see can help scientists better understand how they communicate and navigate the world around them. False color images give us a glimpse into this dynamic world, but traditional methods such as spectrophotometry are often time consuming, require specific lighting conditions, and cannot capture moving images.
To address these limitations, researchers developed a novel camera and software system that captures animal-view videos of moving objects under natural lighting conditions. The camera simultaneously records video in four color channels: blue, green, red and UV. This data can be processed into “perceptual units” to produce an accurate video of how those colors are perceived by animals, based on existing knowledge of the photoreceptors in their eyes. The team tested the system against a traditional method that uses spectrophotometry and found that the new system predicted perceived colors with an accuracy of over 92%.
This novel camera system will open new avenues of research for scientists, and allow filmmakers to produce dynamic, accurate depictions of how animals see the world around them, the authors say. The system is built from commercially available cameras, housed in a modular, 3D-printed casing, and the software is available open-source, allowing other researchers to use and build on the technology in the future.
Senior author Daniel Hanley adds, “We’ve long been fascinated by how animals see the world. Modern techniques in sensory ecology allow us to infer how static scenes might appear to an animal; however, animals often make crucial decisions on moving targets (e.g., detecting food items, evaluating a potential mate’s display, etc.). Here, we introduce hardware and software tools for ecologists and filmmakers that can capture and display animal-perceived colors in motion.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002444
Supplementary Videos URL: https://plos.io/4a9pRxS
Citation: Vasas V, Lowell MC, Villa J, Jamison QD, Siegle AG, Katta PKR, et al. (2024) Recording animal-view videos of the natural world using a novel camera system and software package. PLoS Biol 22(1): e3002444. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002444
Author Countries: United Kingdom, United States, Canada
Funding: see manuscript
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-23
In a new study, two species of bacteria grown in a lab reversed their predator-prey relationship after one species was grown at a lower temperature. Marie Vasse of MIVEGEC, France, and colleagues publish these findings January 23rd in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Prior research has shown that ecological context can influence predator-prey relationships. For instance, similarity or contrast between background color and coloration of a prey species can influence how easily it is detected by predators. In addition, predator-prey relationships can sometimes switch, as is the case for two crustacean species that mutually prey on each other, where a change in surrounding salinity ...
2024-01-23
Author Interview:
Why did you create this reporting guideline?
We created this reporting guideline because consensus methods are widely used to produce recommendations in research and patient care, and so it is important to be able to judge how well they were conducted and how relevant these results might be.
How did you go about this?
We assembled an international steering committee of clinicians, journal editors, guideline and consensus experts, publication professionals and patients to look at how ...
2024-01-23
A new study finds that very few patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are able to achieve normal blood glucose levels through weight loss alone. A team led by Andrea Luk of the Chinese University of Hong Kong, report these findings January 23rd in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
Clinical trials suggest that people with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose levels without medication if they lose weight and keep it off. However, it is unknown how many patients can achieve remission through weight loss alone under real-world conditions. In the new study, researchers looked at 37,326 people in Hong Kong who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes to see ...
2024-01-23
The Louis-Jeantet Foundation honors the Director at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences for discovering a new kind of biological matter that acts as a highly selective barrier to control central transport pathways in the cell. He has made groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of the processes by which macromolecules are transported into and out of the cell nucleus, the foundation said. The prestigious award is endowed with 500,000 Swiss francs (around 537,000 euros).
Görlich studies how cells solve the logistical challenge of getting their ...
2024-01-23
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Ecologists have long known that standing dead trees, commonly referred to as snags, are an important habitat element for forest dwellers and act as a driver of biodiversity.
They’re so important that in some managed forests, snag creation is part of the conservation tool kit – i.e., crews sometimes convert a percentage of live trees into dead ones through techniques ranging from sawing off their tops to wounding their trunks to injecting them with disease-causing fungi.
Until now, however, key questions had remained unanswered: How well do any of those techniques actually work over the long term? ...
2024-01-23
NEW ORLEANS – Ochsner Health has been named the winner of five awards from Press Ganey, a globally recognized analytics company offering healthcare experience solutions and services.
These awards are part of Press Ganey’s annual ranking of the top hospitals and health systems in the country, according to performance in patient experience, employee experience, physician experience, clinical quality performance and consumer experience.
“We’re honored to be recognized by Press Ganey for our excellence and compassion in caring for ...
2024-01-23
Ozempic and other GLP1 agonists are associated with a reduced risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic liver disease, according to a nationwide study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden published in the journal Gut.
GLP1 agonists like Ozempic reduce blood sugar levels and are mainly used to treat type 2 diabetes. However, as the drug also reduces appetite, it is now increasingly used to treat obesity and has become a popular weight-loss drug.
Reduced risk of liver damage
Results from early clinical trials also suggest that GLP1 agonists may reduce the risk of liver damage. Therefore, researchers at ...
2024-01-23
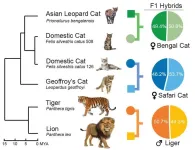
DENVER/Jan. 23, 2024 – Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers have delved into various cat species' entire DNA sequence (genome), uncovering novel perspectives on domestic and wild cat evolution. This new work highlights distinct genetic changes and will be a critical tool for researchers investigating feline diseases and characteristics.
This study, which led to the findings published in Nature Genetics, used cutting-edge genome sequencing and assembly technologies to generate a more comprehensive and complete cat genome assembly, providing fundamental information on the feline blueprint and aiding in advancements in feline medicine.
"This ...
2024-01-23
Emerging research suggests it may be easier to use fusion as a power source if liquid lithium is applied to the internal walls of the device housing the fusion plasma.
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is a hot gas made of electrically charged particles. Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are working on solutions to efficiently harness the power of fusion to offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, often using devices called tokamaks, which confine plasma using magnetic fields.
“The purpose of these devices is to confine the energy,” said Dennis Boyle, a staff research physicist ...
2024-01-23
Concrete is an essential material in the construction industry, where it is fundamental to the foundations and structures of dwellings and office buildings, as well as roads, dams and bridges, among many other infrastructure projects. However, the service life of concrete is limited, and it must be monitored in order to guarantee the safety of these structures. To facilitate fast, low-cost, in-situ analysis that dispenses with the need to take samples to a laboratory, researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Physics Institute (IF-USP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Leuven in Belgium, have developed a luminescent material that reveals the presence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New video camera system captures the colored world that animals see, in motion
Open-source camera and software system records natural animal-view videos with over 90% accuracy