(Press-News.org) Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and IBM have published a strategy for identifying new targets for immunotherapy through artificial intelligence (AI). This is the first peer-reviewed publication from the two organizations’ Discovery Accelerator partnership, designed to advance research in healthcare and life sciences.
The team worked together to develop supervised and unsupervised AI to reveal the molecular characteristics of peptide antigens, small pieces of protein molecules immune cells use to recognize threats. Project members came from diverse groups led by Cleveland Clinic’s Timothy Chan, M.D., Ph.D., as well as IBM’s Jeff Weber, Ph.D., Senior Research Scientist, and Wendy Cornell, Ph.D., Manager and Strategy Lead for Healthcare and Life Sciences Accelerated Discovery .
“In the past, all our data on cancer antigen targets came from trial and error,” says Dr. Chan, chair of Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Immunotherapy and Precision Immuno-Oncology and Sheikha Fatima Bint Mubarak Endowed Chair in Immunotherapy and Precision Immuno-Oncology. “Partnering with IBM allows us to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence and health sciences research to change the way we develop and evaluate targets for cancer therapy.”
For decades, scientists have been researching how to better identify antigens and use them to attack cancer cells or cells infected with viruses. This task has proved challenging because antigen peptides interact with immune cells based on specific features on the surface of the cells, a process which is still not well understood. Research has been limited by the sheer number of variables that affect how immune systems recognize these targets. Identifying these variables is difficult and time intensive with regular computing, so current models are limited and at times inaccurate.
Published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, the study found that AI models that account for changes in molecular shape over time can accurately depict how immune systems recognize a target antigen. Through these models, researchers could home in on what processes are critical to target with immunotherapy treatments such as vaccines and engineered immune cells.
Researchers can incorporate these insights into other AI models moving forward to identify more effective immunotherapy targets.
“These discoveries are an example of what makes this partnership successful – combining IBM’s cutting-edge computational resources with Cleveland Clinic’s medical expertise,” Dr. Weber says. “These findings resulted from a key collaboration between everyone from a world-class expert in cancer immunotherapy to our physics-based simulation and AI experts. Collaboration when combined with innovation has terrific potential.”
Cleveland Clinic and IBM launched their Discovery Accelerator partnership in 2021, which is focused on advancing the pace of biomedical research through the use of high-performance computing, artificial intelligence and quantum computing. The landmark partnership brings together Cleveland Clinic’s world-renowned expertise in healthcare and life sciences, with IBM’s next generation technologies to make scientific discovery faster.
END
Cleveland Clinic and IBM Researchers publish findings on artificial intelligence and immunity
The study, published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, highlights how artificial intelligence can be designed to develop better immunotherapy treatments
2024-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When some adolescent girls internalize rejection, it really is in their head
2024-01-23
Everyone ruminates about the bad things that happen to them. Whether it’s a nasty breakup, an embarrassing failure or simply when someone is mean, it can be hard to stop thinking about what happened and why. For people who ruminate too much, this negative thought pattern can cause lasting problems with mental health.
A research team led from the University of California, Davis, Center for Mind and Brain found that adolescent girls who have a stronger tendency to ruminate show different patterns of brain activity when faced with social rejection. The study was ...
Researchers design new open-source technology for interfacing with living neurons
2024-01-23
Neurons intricately communicate and respond to stimuli within a vast network, orchestrating essential functions from basic bodily processes to complex thoughts. Traditional neuroscience methods, relying on in vivo electrophysiology (within a living organism), often have difficulty addressing the complexity of the brain as a whole. An alternative approach involves extracting cells from the organism and conducting studies on a culture dish instead (in vitro), providing researchers with enhanced control and precision in measuring neural processes. In a new study featured in Advanced Science, researchers unveil a cost-effective, open-source in vitro system ...
Why do young women with multiple sclerosis face health disparities?
2024-01-23
While recent therapies have the potential to stall or delay the progression of multiple sclerosis, a new study shows that young Black and Hispanic women fare worse than young white women.
Minority women were more likely to have more advanced disease and faced greater challenges in pregnancy, the researchers reported in their study, publishing in the journal Neurology on Jan. 23, 2024.
Researchers tracked medical records at nine MS centers throughout the country for 294 women whose pregnancies resulted in live births. Approximately half of the patients ...
Could two drugs be better than one for treating prostate cancer?
2024-01-23
Combining testosterone-blocking drugs in patients with prostate cancer relapse prevents the spread of cancer better than treatment with a single drug, a multi-institution, Phase 3 clinical trial led by UC San Francisco researchers has found.
The approach can extend the time between debilitating drug treatments without prolonging the time it takes to recover from each treatment.
Prostate cancer affects 1 in 8 men and causes 34,000 deaths each year in the United States. It is usually treated with one of several testosterone-lowering drugs for a set period of ...
Predicting and controlling bad-actor AI activity in a year of global elections
2024-01-23
MEDIA CONTACT:
Cate Douglass; cdouglass@gwu.edu
More than 50 countries are set to hold national elections this year and analysts have long sounded the alarm on the threat of bad actors using artificial intelligence (AI) to disseminate and amplify disinformation during the election season across the globe.
Now, a new study led by researchers at the George Washington University predicts that daily, bad-actor AI activity is going to escalate by mid-2024, increasing the threat that it could affect election results. The research, published today in the journal PNAS Nexus, is the first quantitative scientific ...
When lab-trained AI meets the real world, ‘mistakes can happen’
2024-01-23
First study to examine the impact of tissue contamination on AI models
‘If it’s paying attention to the tissue contaminants, it’s paying less attention to the patient’s tissue that is being examined’
‘Pathologists fear — and AI companies hope — that the computers are coming for our jobs. Not yet.’
Human pathologists are extensively trained to detect when tissue samples from one patient mistakenly end up on another patient’s microscope slides ...
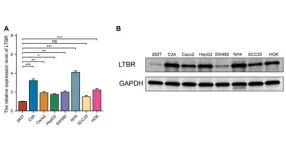
Systematic analysis of the prognostic value and immunological function of LTBR in cancer
2024-01-23
“[...] we identified LTBR as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy and a marker of immune infiltration and poor prognosis.”
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “Systematic analysis of the prognostic value and immunological function of LTBR in human cancer.”
Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTBR) is a positive T cell proliferation regulator gene. It is closely associated with the tumor immune microenvironment. However, its role in cancer and ...
CUNY SPH Foundation expands Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund with endowment
2024-01-23
The CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH) has announced an expansion and endowment of the Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund as a groundbreaking and permanent source of support for students dedicated to advancing health equity in underserved Hispanic and Latino communities.
Established by Dr. Marilyn Aguirre-Molina, CUNY SPH professor emerita and CUNY SPH Foundation Board member, and distinguished academician Dr. Carlos W. Molina, the Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund now becomes the first named and endowed master’s degree scholarship in the school’s ...
Study reveals disparities in use of evidence-based integrative pain management modalities among adults with chronic pain
2024-01-23
A recent study from researchers at University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health examined variables associated with engagement in (1) integrative health and medicine (IHM) and (2) nonpharmacologic modalities rather than opioids among United States adults with chronic pain. The study, published in the Journal of Pain Research, uncovered disparities in access to these modalities, particularly among older adults, Black/African American individuals, and those with higher depressive symptoms and lower education and income levels, who are more likely to have chronic pain.
The researchers used data ...
Ageism, mistaken beliefs complicate acceptance of older adults’ sexuality
2024-01-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — More than 25% of the young adults surveyed in a recent study mistakenly believed that sexual activity increases older adults’ risk of heart attack and that disinterest in sex is a normal and inevitable part of aging. While most of those in the study had permissive views about sexual activity in later life, the findings also shed light on the misconceptions and ageist views that can infringe on older adults’ rights to sexual expression.
More than 270 young adults ages 18-35 participated in the study, which assessed their level of knowledge about sexuality in older adulthood, their general attitudes toward ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Cleveland Clinic and IBM Researchers publish findings on artificial intelligence and immunityThe study, published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, highlights how artificial intelligence can be designed to develop better immunotherapy treatments