(Press-News.org) Chopped carrot pieces are among the most universally enjoyed foods and a snacking staple – a mainstay of school lunchboxes, picnics and party platters year-round.
Now researchers from the University of Bath have uncovered the secret science of prepping the popular root veg and quantified the processes that make them curl up if left uneaten for too long.
Mechanical Engineering student Nguyen Vo-Bui carried out the research as part of his final-year studies, in the limited circumstances of Covid-19 lockdowns of 2021.
Without access to labs, Nguyen aimed to identify the geometrical and environmental factors which have the most influence on carrots’ longevity. Working in his kitchen, he characterised, analytically modelled and verified the ageing of over 100 Lancashire Nantes carrot halves, cut lengthways, using finite-element (FE) models normally used in structural engineering.
The research team concluded that residual stresses and dehydration were the two key factors behind the curling behaviour. The starchy outer layer of the carrot (the cortex) is stiffer than the soft central vein (also known as the vascular cylinder). When cut lengthwise, the two carrot halves curl because the difference in stress becomes unbalanced. Dehydration leads to further loss of stiffness, further driving the curling effect.
Their recommendations to manufacturers include handling carrots in cold, moist, airtight and humidity-controlled environments to protect their natural properties and increase their edible life span.
They say the study provides a methodology to predict the deformation of cut root vegetables, adding that the procedure is likely to apply to other plant structures. The study gives food producers a new mathematical tool that could be applied to the design of packaging and food handling processes, potentially reducing food waste.
One of the world’s top crops by market value, carrots are known for their high production efficiency – but despite this, wastage is high. Around 25-30% of this occurs prior to processing and packaging – due to deformities, mechanical damage or infected sections. Fresh cut and minimally processed carrots are a convenient ready-to-use ingredient that make possible the use of carrots that might otherwise be discarded, reducing food waste.
Dr Elise Pegg, a senior lecturer in Bath’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, is one of the research paper authors and oversaw the study. She said: “We have mathematically represented the curl of a cut carrot over time, and showed the factors that contribute to curling.
“Our motivation was to look for ways to improve the sustainability of carrot processing and make them as long-lasting as possible. We have produced a methodology that a food producer could use to change their processes, reducing food waste and making packaging and transportation more efficient. Understanding the bending behaviour in such systems can help us to design and manufacture products with higher durability.
“A question like this would normally be investigated from a biological perspective, but we have done this work using purely mechanical principles. I'm so pleased for Nguyen – it’s a measure of his resourcefulness and dedication to produce such interesting research in a challenging situation.”
Over the course of a week, the curl of the carrot halves increased – with the average radius of each carrot’s curvature falling from 1.61m to 1.1m. A 1.32-times reduction in stiffness was also seen, correlating with the carrots drying out – on average, their weight fell by 22%.
Nguyen added: “This was interesting research – to apply mechanical principles to vegetables was surprising and fun.
“One of the big challenges was to devise an experiment that could be done in a lockdown setting, without access to normal labs and equipment. To now be in a position to have this work published in an academic journal and potentially be used by the food industry is really rewarding.
“This project has inspired me to continue my studies at the University of Bath and I now study residual stresses in porous ferroelectric ceramics for my PhD.”
As well as having to use a suitcase to collect the 30kg of carrots the experiment demanded from a farmers market, a further challenge was finding ways to use them afterward. Carrot cake, the Indian carrot dessert Gajar Ka Halwa, carrot pesto and many other dishes kept Nguyen and his flatmates fed for several days.
The research paper, Modelling of longitudinally cut carrot curling induced by the vascular cylinder-cortex interference pressure, is published in The Royal Society Open Science (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.230420)
END
Why do carrots curl? Research reveals the mechanics behind root vegetable ageing
Undergraduate research conducted in a kitchen during lockdown could reduce food waste and help keep veg in prime condition for longer
2024-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
FDG PET/CT imaging after just one week may predict treatment response in patients with advanced melanoma
2024-01-24
Bottom Line: Imaging the tumors of patients with advanced melanoma receiving pembrolizumab (Keytruda) after only one week—rather than the standard of around three months—identified metabolic changes that corresponded with treatment response and progression-free survival (PFS).
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Michael D. Farwell, MD, an associate professor of radiology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
Background: Cancer immunotherapy has helped ...
Centralized social networks potentially hinder innovation by making decision-making too similar
2024-01-24
Social systems where influence is focused around one or a few individuals may create environments where new ideas are ignored, and innovation is hindered.
This is according to a study published today in People and Nature by researchers at the University of Sydney and Stockholm University. It looked at the social networks and fertiliser use of 30 rural, cocoa-producing villages in Sulawesi, to examine how innovative and sustainable farming practices are adopted among communities.
It found that when one or two farmers hold a disproportionate level of influence (often due to their roles as "model farmers" in official sustainability programs) ...
Tunnelling of electrons via the neighboring atom
2024-01-24
Tunnelling is one of most fundamental processes in quantum mechanics, where the wave packet could traverse a classically insurmountable energy barrier with a certain probability. Within the atomic scale, tunnelling effects play an important role in molecular biology, such as accelerating enzyme catalysis, prompting spontaneous mutations in DNA and triggering olfactory signaling cascades. Photoelectron tunnelling is a key process in light-induced chemical reactions, charge and energy transfer and radiation emission. The size of optoelectronic chips ...
Space-based landscape site perception: Teaching principles and methods for the basic course of landscape architecture
2024-01-24
Replacing abstract form-making training with the perception of landscape site has been an important trend in the basic course of landscape architecture. Based on theoretical research and the authors’ teaching practice, this article aims to explore the significance, objects, and methods of site perception training. The authors argue that because landscape design is stemmed from the perception and interpretation of site characteristics, experiencing landscape sites must precede form-making training to become the foundation of design learning. Human-scale spaces that concern elements, structure, processes, and feelings for perception, representation, ...
Suppression of deep-level traps for lead-free perovskite solar cells
2024-01-24
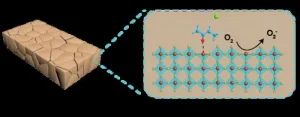
Tin perovskites have gained tremendous attention in lead-free perovskite solar cells. However, Sn vacancies and undercoordinated Sn ions on the tin perovskite surfaces can create deep-level traps, leading to non-radiative recombination and absorption nucleophilic O2 molecules, impeding further device efficiency and stability.
Researchers led by Prof. Ligang Xu at Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, China, are interested in lead-free perovskite solar cells, where the deep-level traps lead to inferior efficiency and stability. The work first introduced semicarbazide hydrochloride (SEM-HCl) into ...
Color liquid crystal grating based color holographic 3D display system with large viewing angle
2024-01-24
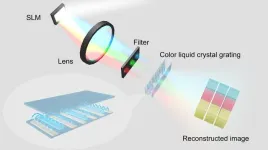
Holographic display technology provides an ultimate solution for real 3D display and has great potential in augmented reality and virtual reality. However, the color and viewing angle of holographic 3D display mainly depend on the wavelength of the laser and the pixel size of the current spatial light modulator. Inevitable color differences and narrow viewing angle in conventional systems seriously affect the holographic display effect and hinder the application of holographic 3D display in many fields.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Qiong-Hua Wang from Beihang ...
Walking fitness can predict fracture risk in older adults
2024-01-24
The ability to walk one kilometre comfortably can help predict fracture risk, according to researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, suggest that simply asking a patient about walking limitation could allow clinicians to identify those in need of further bone health screening and prescribe interventions that could prevent fractures from occurring.
“We’ve discovered that trouble walking even short distances appears closely tied to higher fracture risk over the following five years,” says lead author of the study, Professor ...
Genome assembly and resequencing analyses provide new insights into the evolution, domestication and ornamental traits of crape myrtle
2024-01-24
Crape myrtle (Lagerstroemia indica), a widely cherished ornamental plant, boasts a rich history, originating in Southeast Asia to Oceania and flourishing in cultivation centers like China for over 1600 years. Renowned for its unique blooming during the summer peak, it has evolved through extensive hybridization, and now includes more than 200 species. Current research has made strides in understanding the determinants of plant architecture, flower, leaf color, and dwarfism traits through transcriptomics and QTL mapping. However, the absence of a reference genome for L. indica severely limits comprehensive ...
Learning for life: The higher the level of education, the lower the risk of dying
2024-01-24
Education saves lives regardless of age, sex, location, and social and demographic backgrounds. That’s according to the latest and largest study of its kind published today in The Lancet Public Health.
Researchers have known that those who reach higher levels of schooling live longer than others, but they didn’t know to what extent until now. What they found was that the risk of death drops by two per cent with every additional year of education. That means those who completed six years of primary school had a lower risk of death by an average of 13 per cent. After graduating from secondary school, the risk ...
Community perinatal mental health teams reduce risk of mental health relapse after childbirth
2024-01-24
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London, and in partnership with the University of Exeter and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, has found that women with a history of severe mental illness face a lower risk of relapse after giving birth in regions where they have access to a community perinatal mental health team (CPMHT).
The research, published in Lancet Psychiatry, is the first of its kind to evaluate the effectiveness of CPMHTs, and suggests that women with access to specialist support have a reduced risk of acute relapse after birth, but also highlights the importance of the need for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Why do carrots curl? Research reveals the mechanics behind root vegetable ageingUndergraduate research conducted in a kitchen during lockdown could reduce food waste and help keep veg in prime condition for longer