(Press-News.org) Obesity among primary school children in the UK spiked during the COVID-19 lockdown, with a 45% increase between 2019/20 and 2020/21 among 4-5-year-olds, according to a study published on January 24, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Iván Ochoa-Moreno from the University of Southampton, UK, and colleagues. The authors estimated that without reversals, increased obesity rates in Year 6 children alone will cost society an additional £800 million in healthcare.
During the first year of the pandemic, school closures dramatically altered the routines of young children. Cancellation of organized sports, disrupted sleep schedules, more screen time, and deterioration of healthy eating habits likely contributed to the largest single-year increase in overweight and obesity prevalence seen in children in decades. To better understand the long-term health and economic costs of rising obesity rates in young children, the authors of the study compared Body Mass Index (BMI) data from England’s National Childhood Measurement Programme (NCMP) before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic among children in their first and last years of primary school (aged 4-5 and 10-11 years old). Using data from two additional longitudinal cohorts in the UK, they modeled the impact of these BMI trends on adult health outcomes and costs.
The researchers observed a 45% increase in obesity prevalence during 2020-2021 in children between 4-5 years old, and a similar effect in Year 6 children. This increase was twice as high in the most deprived areas of England. While the number of overweight and obese 4-5 year olds returned to pre-pandemic levels the following year, the increases seen in older children persisted into 2022. The study estimated that this group of children will cost society an additional £800 million in healthcare, for conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease, over their lifetimes.
The researchers state that the persistence of weight gain in older children suggests that reversing obesity is very challenging in older age groups, while the quick reversal to pre-pandemic levels in young children highlights the promise of policies targeting children under five as a strategy to tackle obesity.
One of the study’s authors, Professor Keith Godfrey, adds: “The sharp increase in childhood obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic illustrates the profound impacts on children’s development. Alongside the escalating costs of the ongoing epidemic of childhood obesity, it is clear that more radical new policy measures are required to reduce obesity and secure wellbeing and prosperity for the country as a whole.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296013
Citation: Ochoa-Moreno I, Taheem R, Woods-Townsend K, Chase D, Godfrey KM, Modi N, et al. (2024) Projected health and economic effects of the increase in childhood obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic in England: The potential cost of inaction. PLoS ONE 19(1): e0296013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0296013
Author Countries: UK
Funding: MH is supported by European Union Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme under grant agreement No. 733206. KMG is supported by the UK Medical Research Council (MC_UU_12011/4), the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR Senior Investigator (NF-SI-0515-10042) and NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre (IS-BRC-1215-20004)), the European Union (Erasmus+ Programme ImpENSA 598488-EPP-1-2018-1-DE-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP), British Heart Foundation (RG/15/17/3174, SP/F/21/150013) and the US National Institute On Aging of the National Institutes of Health (Award No. U24AG047867). For the purpose of Open Access, the author has applied a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) licence to any Author Accepted Manuscript version arising from this submission. KWT is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) through the Southampton Biomedical Research Centre (BRC). RT is funded by NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Studentship.
END
Obesity spiked in children during COVID-19 lockdowns—only the youngest bounced back
BMI data from over 1 million children in England indicates high lifetime costs to society of post-pandemic obesity rates
2024-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Risk of death during heatwaves in Brazil linked to socioeconomic factors
2024-01-24
A new study suggests that heatwaves are exacerbating socioeconomic inequalities in Brazil, with people who are female, elderly, Black, Brown, or who have lower educational levels potentially facing greater risk of death during heatwaves. Djacinto Monteiro dos Santos of Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 24, 2024.
As climate change progresses, heatwaves are becoming hotter, longer, and more frequent in many regions ...
DNA from preserved feces reveals ancient Japanese gut environment
2024-01-24
DNA from ancient feces can offer archaeologists new clues about the life and health of Japanese people who lived thousands of years ago, according to a study published January 24, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Luca Nishimura and Ituro Inoue from the National Institute of Genetics, Japan, Hiroki Oota from The University of Tokyo, Mayumi Ajimoto from Wakasa History Museum, and colleagues.
Fossilized feces, also known as coprolites, can preserve an array of genetic material from the digestive tracts ...
A virus that infected the first animals hundreds of millions of years ago has become essential for the development of the embryo
2024-01-24
At least 8% of the human genome is genetic material from viruses. It was considered ‘junk DNA’ until recently, but its role in human development is now known to be essential
Researchers at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) describe for the first time the role of these viruses in a key process in development, when cells become pluripotent few hours after fertilization
The finding, published in Science Advances, is relevant for regenerative medicine and for the creation of artificial ...
City of Hope, TGen researchers develop machine-learning tool to detect cancer earlier via liquid biopsy
2024-01-24
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), a precision medicine research organization that is part of City of Hope, have developed and tested an innovative machine-learning approach that could one day enable the earlier detection of cancer in patients by using smaller blood draws. The study was published today in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“A huge body of evidence shows that cancer caught at later stages kills people. This new technology gets us closer to a world ...
Gene behind heart defects in Down syndrome identified
2024-01-24
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 19:00hrs GMT 24 January 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Gene behind heart defects in Down syndrome identified
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have identified a gene that causes heart defects in Down syndrome, a condition that results from an additional copy of chromosome 21.
Reducing the overactivity of this gene partially reversed these defects in mice, setting the scene for potential future therapies for heart conditions in people with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome ...
Moving humanoid robots outside research labs: the evolution of the iCub3 avatar system
2024-01-24
Genova (Italy), 24 January 2024 - Over the past four years, the research team at the Artificial and Mechanical Intelligence (AMI) lab at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) in Genova (Italy) has developed advanced avatar technologies, known as the iCub3 system, in continuous testing with real-world scenarios. The system was utilized to enable a human operator to remotely visit locations 300 km away, to entertain the public at events and television appearances, and ...
Retinal imaging and genetics data used to predict future disease risk
2024-01-24
Mass Eye and Ear physician-researchers show that retinal imaging can help predict a person’s risk of developing ocular, neuropsychiatric, cardiac, metabolic, and pulmonary diseases.
The team also identified genetic loci associated with retinal thinning, which could help develop personalized treatment plans and future therapies for eye diseases such as glaucoma and macular degeneration.
The retina is said to provide a window into a person’s systemic health. In a new study published January 24th in Science Translational Medicine, physician-researchers from Mass ...
North China fossils show eukaryotes first acquired multicellularity 1.63 billion years ago
2024-01-24
In a study published in Science Advances on Jan. 24, researchers led by Prof. ZHU Maoyan from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported their recent discovery of 1.63-billion-year-old multicellular fossils from North China.
These exquisitely preserved microfossils are currently considered the oldest record of multicellular eukaryotes. This study is another breakthrough after the researchers’ earlier discovery of decimeter-sized eukaryotic fossils in the Yanshan area ...
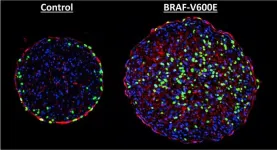
Harnessing skin cancer genes to heal hearts
2024-01-24
DURHAM, N.C. – Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that one of the most dangerous mutations found in skin cancers might moonlight as a pathway to mending a broken heart.
The genetic mutation in the protein BRAF, a part of the MAPK signaling pathway that can promote cell division, is one of the most common and most aggressive found in melanoma patients. In a new study, researchers show that introducing this mutation to rat heart tissue grown in a laboratory can induce growth.
Repairing ...
Special Feature calls attention to biological invasion research in China
2024-01-24
This month, the Ecological Society of America spotlights the challenge posed by invasive alien species in China with the release of a Special Feature, “Management of Biological Invasions in China,” in the latest issue of its journal Ecological Applications.
Accelerating rates of biological invasion have led to growing concerns about the destructive impacts of invasive alien species, or IAS, on the environment and human societies. This is especially true in China, which has witnessed a surge in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Obesity spiked in children during COVID-19 lockdowns—only the youngest bounced backBMI data from over 1 million children in England indicates high lifetime costs to society of post-pandemic obesity rates