(Press-News.org) A newly published review of the CABI-led Pest Risk Information Service (PRISE) project shows that smallholder farmers in four African countries who received pest alerts created using earth observation data benefitted from reduced crop losses and higher incomes compared to farmers who did not.
Crop pests are the major cause of loss of smallholder productivity resulting in negative impacts on livelihoods – the estimated the economic impact of invasive alien pests alone on Africa’s agricultural sector is USD $65.58 billion a year (CABI, 2021, CABI Agriculture and Bioscience).
This review is a keystone paper that brings together six years of work on PRISE. The highlight of the review, published in the Journal of Integrated Pest Management, shows that smallholder farmers in four African countries really benefit from the service.
For instance, in respect of 2,000 smallholder maize farmers in Kenya surveyed in 2021 who received pest alerts for fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda), a harvest of 2,089 kg/ha was achieved with an income of 18,020 Ksh/ha. This is compared to smallholder farmers who did not receive these alerts where only a harvest of 1,988 kg/ha was gained with a lower income of 15,733 Ksh/ha.
In recent decades, significant progress has been made that allows farmers to access important information to improve crop health, including how to manage crop pests.
PRISE alerts augment the advice (the what) already being serviced to farmers with their bespoke optimum ‘time to action window’ (the when) allowing farmers to prepare for pest threats in advance so increasing the efficiency and efficacy of interventions.
This in turn reduces the reliance on ‘in case’ action, which is time-consuming, costly, and often ineffective, the scientists say.
PRISE, which began in 2017, was carried out by a team of scientists from Africa and Europe for farmers in sub-Sharan Africa. In Europe, the partners include CABI and Assimila Ltd, who work with four in-country lead partners from government agencies in Africa.
These include the Kenyan Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO); the Plant Protection and Regulatory Services Directorate (PPRSD) and Crop Research Institute (CRI) in Ghana; the Department of Agriculture Extension Services in Malawi; and the Zambia Agricultural Research Institute (ZARI).
In the early part of PRISE, technical help was also provided by the Science and Technology Facilities Council/Centre for Environmental Data Analysis (2017-2022), and King's College London (2017-2020).
Data from a variety of sources
PRISE works by gathering data from a variety of sources including satellite observation, weather data, geographic data, and details about the seasonal occurrence, abundance and biology of pests that include the tomato leafminer (Phthorimaea absoluta).
This information is then combined in a ‘data cube’ to run algorithms, which ultimately produce pest time to act information. The information generated is used to give farmers timely alerts and advice to help manage local pest outbreaks as part of their Integrated Pest Management (IPM) plans.
Forecast time to act
Using downscaled and processed Earth Observation data to drive the models, PRISE partnered with African national agencies to communicate pre and in-season pest alerts that forecast the time to act against key insect pests.
Alerts were designed to be integrated into country-specific Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) recommendations to provide a complementary package to agricultural stakeholders.
For example, by converting time-to-act information into maps coupled with PlantwisePlus GAP information, bulletins (PDF documents) were developed twice a month, combining the PRISE action alert with relevant diagnostic and management advice from Pest Management Decision Guides.
Benefits more pronounced for male-headed households
Dr Bryony Taylor, Digital Development Coordinator, Modelling and Data Science at CABI and an author of the review, said, “Results varied across countries and crops, as was expected. Nevertheless, overall positive impact was noted for some but not all farmers who had received the PRISE forecasts – either with or without other GAP information, especially in relation to a reduction in crop losses.
“The differences were more pronounced for male-headed households as compared to those headed by women, with significant reductions in crop losses for men for all crops and all countries apart from bean and tomato crops in Malawi.
“However, for women, the only significant reduction in crop losses were observed in Kenya for all crops, and in Zambia for maize. No significant changes in levels of crop losses were seen for any crops in female-headed households in Malawi.”
The scientists stress that time for monitoring pests is limited as smallholder farmers, especially women who frequently do most of the work, are already heavily burdened by agriculture and household workloads.
Further work needed to target female farmers
They add that further work will be needed with dissemination partners to target women to sign up to extension messaging services to ensure they receive the time to act upon messages directly.
Furthermore, to enable women farmers to benefit from the messaging, it will be necessary to work with partners to address the social norms that constrain women’s access to land, credit, and farming inputs, so that they are able to respond to the time to act on the messaging in full.
Additional information
Main image: A farmer uses the Pest Risk Information Service to access information on how to mitigate fall armyworm on maize in Malawi (Credit: CABI).
Full paper reference
Charlotte Day, Sean T Murphy, Jon Styles, Bryony Taylor, Tim Beale, William Holland, Frances Williams, Andy Shaw, Cambria Finegold, MaryLucy Oronje, Birgitta Oppong-Mensah, Noah Phiri, Alyssa Lowry, Elizabeth A. Finch, Josephine Mahony, Suzy Wood, Léna Durocher-Granger, Duncan Chacha, Norbert Maczey, Pablo Gonzalez-Moreno, Sarah E. Thomas, Joe Beeken, Jane Lewis, Gerado Lopez Saldana, Solomon Duah, Mary Bundi, Lusike Wasilwa, Ruth Amata, Ruth Musila, Daniel Mutisya (the late),Christine Kaari, Patrick Kalama, Johnson O. Nyasani, Matthews Matimelo, Henry Mgomba, Christopher Gaitu, Christopher Ocloo, Isaac Adjei, Mensah, Godfried Ohene-Mensah, Jerry Asalma Nboyine, Blessings Susuwele, ‘Forecasting the population development of within-season insect crop pests in sub-Saharan Africa: The Pest Risk Information Service,’ Journal of Integrated Pest Management, Volume 15, Issue 1, 2024, DOI: 10.1093/jipm/pmad026
The paper can be read in full open access here: https://academic.oup.com/jipm/article/15/1/7/7585279?searchresult=1
END
African smallholder farmers benefit from reduced crop losses and higher incomes from a novel pest alert service
A review of the CABI-led Pest Risk Information Service shows that smallholder farmers in four African countries benefited from reduced crop losses and higher incomes after pest alerts received using earth observation data
2024-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cervical cancer rates rising in low-income U.S. counties
2024-01-25
HOUSTON ― Women in low-income areas of the U.S. face a stark rise in cervical cancer incidence and mortality, according to a new study led by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The results, published in the International Journal of Cancer, demonstrate that the incidence rate for distant-stage cervical cancer has increased most among white women living in low-income counties, at 4.4% annually since 2007. The largest increase in cervical cancer mortality rates occurred ...
Press registration opens for ACS Spring 2024
2024-01-25
Journalists who register for the American Chemical Society’s (ACS’) upcoming hybrid meeting and exposition — ACS Spring 2024 — will have access to nearly 12,000 presentations on topics including agriculture and food, energy and fuels, health and medicine, sustainability, and more. ACS Spring 2024 is being held virtually and in person in New Orleans on March 17-21, with the theme “Many Flavors of Chemistry.”
ACS considers requests for press credentials and complimentary meeting registration from reporters ...
UTSA to establish new college in AI, cyber, computing and data science
2024-01-25
UTSA announced a pioneering initiative to reshape its academic landscape with the creation of a new college dedicated to artificial intelligence (AI), cybersecurity, computing, data science and related disciplines. This initiative aligns with the university's commitment to innovation and academic excellence while also positioning UTSA to lead in the rapidly evolving landscape of advanced technologies.
Nearly 6,000 students are enrolled in AI, cyber, computing and data science-related degree programs at UTSA, reflecting ...
New satellite capable of measuring Earth precipitation from space
2024-01-25
Measuring the amount of precipitation that falls in a specific location is simple if that location has a device designed to accurately record and transmit precipitation data. In contrast, measuring the amount and type of precipitation that falls to Earth in every location is logistically quite difficult. Importantly, this information could provide a wealth of data for characterizing and predicting Earth’s water, energy and biogeochemical cycles. Researchers from China recently deployed a satellite, FengYun 3G (FY-3G), that is successfully collecting Earth precipitation data from space.
Scientists from the China Meteorological Administration developed and launched ...
Women exposed to toxic metals may experience earlier aging of their ovaries
2024-01-25
WASHINGTON—Middle-aged women who are exposed to toxic metals may have fewer eggs in their ovaries as they approach menopause, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diminished ovarian reserve is when women have fewer eggs compared to others their age. The condition may be linked to health problems such as hot flashes, weak bones and a higher chance of heart disease.
Menopause is a normal part of the aging process a woman goes through that causes her monthly periods to end. The menopausal transition includes the years leading up to that point, when women may experience symptoms such as changes in ...
The moon is shrinking, causing landslides and instability in lunar south pole
2024-01-25
Earth’s moon shrank more than 150 feet in circumference as its core gradually cooled over the last few hundred million years. In much the same way a grape wrinkles when it shrinks down to a raisin, the moon also develops creases as it shrinks. But unlike the flexible skin on a grape, the moon’s surface is brittle, causing faults to form where sections of crust push against one another.
A team of scientists discovered evidence that this continuing shrinkage of the moon led to notable surface warping in its south polar ...
Icahn Mount Sinai School of Medicine receives Helmsley Charitable Trust grant for Crohn's disease research
2024-01-25
New York, NY [January 25, 2024]—The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has been awarded a grant of more than $4 million from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust to support an innovative research project aimed at understanding the early stages of Crohn’s disease before noticeable symptoms develop.
Led by the Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences along with the Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology in the Department of Medicine at the Icahn School of ...
Sika deer overpopulation endangers beech forests in Southern Kyushu, Japan
2024-01-25
Fukuoka, Japan—Kyushu University researchers have found that Japanese beech (Fagus crenata) in the forests of southern Kyushu have seen reduced growth, due to soil erosion caused by the overpopulation of sika deer (Cervus nippon). Their findings, which were published in the journal Catena, could help in the development of new strategies for forest conservation.
Conservation is more than just preserving forests; it's about protecting the diverse web of life. One area where conservation has become critical is a beech forest in Shiiba Village, in the remote mountains of Southern Kyushu. The Japanese beech is a prominent and iconic species in ...
UTSA researchers reveal faint features in galaxy NGC 5728 though JWST image techniques
2024-01-25
(SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS) — Mason Leist is working remotely—127 million light-years from Earth—on images of a supermassive black hole in his office at the UTSA Department of Physics and Astronomy.
The UTSA Graduate Research Assistant led a study, published in The Astronomical Journal, on the best method to improve images obtained by the James Webb Science Telescope (JWST) using a mathematical approach called deconvolution. He was tasked by the Galactic Activity, Torus, and Outflow Survey (GATOS), an international team of scientists, to enhance JWST observations of the galaxy NGC 5728.
The GATOS team, co-led by UTSA Professor and Leist’s doctoral ...
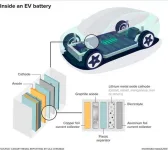
Polymer power: Incheon National University researchers enhance the safety of lithium batteries
2024-01-25
Lithium-ion batteries are a widely used class of rechargeable batteries in today’s world. One of the processes that can hamper the functioning of these batteries is an internal short circuit caused by direct contact between the cathode and anode (the conductors that complete the circuit within a battery). To avoid this, separators composed of polyolefins—a type of polymer— can be employed to maintain separation. However, these separators can melt at higher temperatures, and the inadequate absorption of electrolytes (essential for conveying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
[Press-News.org] African smallholder farmers benefit from reduced crop losses and higher incomes from a novel pest alert serviceA review of the CABI-led Pest Risk Information Service shows that smallholder farmers in four African countries benefited from reduced crop losses and higher incomes after pest alerts received using earth observation data