(Press-News.org) UTSA announced a pioneering initiative to reshape its academic landscape with the creation of a new college dedicated to artificial intelligence (AI), cybersecurity, computing, data science and related disciplines. This initiative aligns with the university's commitment to innovation and academic excellence while also positioning UTSA to lead in the rapidly evolving landscape of advanced technologies.
Nearly 6,000 students are enrolled in AI, cyber, computing and data science-related degree programs at UTSA, reflecting a 31% increase since 2019. UTSA graduated more than 1,000 students in these programs, currently distributed across four colleges, in 2022-2023.
"The convergence of AI, data science, computing, and cybersecurity signifies a very forward-looking endeavor as we embrace the fifth industrial revolution, now especially propelled by AI advancements," said UTSA President Taylor Eighmy. "These disciplines will remain intertwined for the foreseeable future. With an escalating demand for emerging technologies, their applications, and the demand for a skilled workforce, this new college will greatly accelerate UTSA's economic and workforce impact here in San Antonio, across Texas, and nationally."
The proliferation of artificial intelligence applications, in particular, in recent years has contributed to unprecedented advancements across industries including health care, finance, manufacturing and more, as organizations harness the power of AI and machine learning to streamline processes and drive innovation. Amidst the dynamic expansion of AI, as well as data science and cybersecurity, the demand for skilled professionals is reaching unprecedented heights.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, there are approximately 3.5 million open positions in cybersecurity and data science globally, highlighting the critical need for expertise in safeguarding digital assets and extracting meaningful insights from vast datasets. In Texas alone, there are over 46,000 job opportunities in these fields, as reported by Cyberseek.
Computerworld's analysis indicates a significant surge in job creation, with an estimated five million roles emerging in 2022, spanning data science, AI/machine learning, cloud computing, cybersecurity, product management, and digital social media. Looking ahead, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 36% increase in data scientist jobs and a 35% increase in cybersecurity jobs nationally over the next decade.
In Texas, the growth trajectory is impressive, with a forecasted 26.5% increase in AI and data science jobs, underscoring the state's pivotal role in shaping the future workforce in these transformative fields.
In an email to UTSA faculty and staff, Interim Provost and Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs Heather Shipley announced the formation of the AI, Cyber, Computing, and Data Science Planning Advisory Task Force to lead a planning exercise to establish the new college. The task force is charged with surveying student interests, regional workforce needs and partnering opportunities; exploring multidisciplinary research opportunities; and recommending a college organizational structure that aligns these programs to enhance student success, career readiness and transdisciplinary research.
Jonathon Halbesleben, dean of the Carlos Alvarez College of Business, and Jianwei Niu, interim dean of University College, will serve as task force chairs. School of Data Science Founding Director David Mongeau will guide the external benchmarking and outreach through community charettes with San Antonio stakeholders and the surveying of best practices at peer and aspiring institutions.
Shipley noted that similar initiatives led to the creation of the College for Health, Community and Policy in 2019 and the Margie and Bill Klesse College of Engineering and Integrated Design in 2021.
“Ensuring UTSA students are well-prepared for their chosen careers in the dynamic transdisciplinary workforce is our most important responsibility,” Shipley said. “This initiative is driven by our commitment to fostering innovation, advancing research, and delivering educational excellence across related disciplines. More specifically, it seeks to amplify synergies among academic and research domains, fostering the transdisciplinary collaboration that is critical to developing our students’ ability to tackle complex, multifaceted challenges as the future leaders in these fields.”
UTSA has been a trailblazer in the fields of AI, cyber, computing and data science. The School of Data Science, established in 2018, is only school of its kind at a Carnegie R1 U.S. Hispanic Serving Institution. Ithas achieved significant milestones, including being awarded $1.2 million for student training and research programs, hosting the national Academic Data Science Alliance annual meeting in 2023, and designing a new certificate program in data engineering, which will be offered beginning this summer. San Pedro I, the downtown San Antonio home for the School of Data Science, now is a hub for more than 1,000 students and researchers.
Veronica Salazar, UTSA chief enterprise development officer and senior vice president for business affairs, emphasized the strategic alignment of this initiative with UTSA's investment in downtown San Antonio and the city’s tech corridor.
“Through this initiative, we are not only investing in the intellectual capital of our students but also contributing to the growth and vibrancy of downtown San Antonio,” Salazar said. “This initiative is a testament to UTSA’s dedication to providing a dynamic hub in our city’s core for education, research and engagement, further solidifying our role as a key player in the San Antonio's development."
Task force membership will be announced later this month. The task force is expected to deliver its final report outlining specific recommendations for a new organizational structure to enhance student success, career readiness and transdisciplinary research in June. Discussions with potentially impacted faculty, as well as other campus and external stakeholders, will follow in Fall 2024.
END
UTSA to establish new college in AI, cyber, computing and data science
2024-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
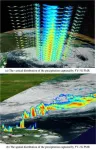
New satellite capable of measuring Earth precipitation from space
2024-01-25
Measuring the amount of precipitation that falls in a specific location is simple if that location has a device designed to accurately record and transmit precipitation data. In contrast, measuring the amount and type of precipitation that falls to Earth in every location is logistically quite difficult. Importantly, this information could provide a wealth of data for characterizing and predicting Earth’s water, energy and biogeochemical cycles. Researchers from China recently deployed a satellite, FengYun 3G (FY-3G), that is successfully collecting Earth precipitation data from space.
Scientists from the China Meteorological Administration developed and launched ...
Women exposed to toxic metals may experience earlier aging of their ovaries
2024-01-25
WASHINGTON—Middle-aged women who are exposed to toxic metals may have fewer eggs in their ovaries as they approach menopause, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diminished ovarian reserve is when women have fewer eggs compared to others their age. The condition may be linked to health problems such as hot flashes, weak bones and a higher chance of heart disease.
Menopause is a normal part of the aging process a woman goes through that causes her monthly periods to end. The menopausal transition includes the years leading up to that point, when women may experience symptoms such as changes in ...
The moon is shrinking, causing landslides and instability in lunar south pole
2024-01-25
Earth’s moon shrank more than 150 feet in circumference as its core gradually cooled over the last few hundred million years. In much the same way a grape wrinkles when it shrinks down to a raisin, the moon also develops creases as it shrinks. But unlike the flexible skin on a grape, the moon’s surface is brittle, causing faults to form where sections of crust push against one another.
A team of scientists discovered evidence that this continuing shrinkage of the moon led to notable surface warping in its south polar ...
Icahn Mount Sinai School of Medicine receives Helmsley Charitable Trust grant for Crohn's disease research
2024-01-25
New York, NY [January 25, 2024]—The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has been awarded a grant of more than $4 million from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust to support an innovative research project aimed at understanding the early stages of Crohn’s disease before noticeable symptoms develop.
Led by the Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences along with the Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology in the Department of Medicine at the Icahn School of ...
Sika deer overpopulation endangers beech forests in Southern Kyushu, Japan
2024-01-25
Fukuoka, Japan—Kyushu University researchers have found that Japanese beech (Fagus crenata) in the forests of southern Kyushu have seen reduced growth, due to soil erosion caused by the overpopulation of sika deer (Cervus nippon). Their findings, which were published in the journal Catena, could help in the development of new strategies for forest conservation.
Conservation is more than just preserving forests; it's about protecting the diverse web of life. One area where conservation has become critical is a beech forest in Shiiba Village, in the remote mountains of Southern Kyushu. The Japanese beech is a prominent and iconic species in ...
UTSA researchers reveal faint features in galaxy NGC 5728 though JWST image techniques
2024-01-25
(SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS) — Mason Leist is working remotely—127 million light-years from Earth—on images of a supermassive black hole in his office at the UTSA Department of Physics and Astronomy.
The UTSA Graduate Research Assistant led a study, published in The Astronomical Journal, on the best method to improve images obtained by the James Webb Science Telescope (JWST) using a mathematical approach called deconvolution. He was tasked by the Galactic Activity, Torus, and Outflow Survey (GATOS), an international team of scientists, to enhance JWST observations of the galaxy NGC 5728.
The GATOS team, co-led by UTSA Professor and Leist’s doctoral ...
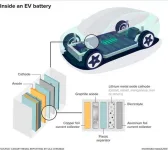
Polymer power: Incheon National University researchers enhance the safety of lithium batteries
2024-01-25
Lithium-ion batteries are a widely used class of rechargeable batteries in today’s world. One of the processes that can hamper the functioning of these batteries is an internal short circuit caused by direct contact between the cathode and anode (the conductors that complete the circuit within a battery). To avoid this, separators composed of polyolefins—a type of polymer— can be employed to maintain separation. However, these separators can melt at higher temperatures, and the inadequate absorption of electrolytes (essential for conveying ...
Suicide and race: Uncovering patterns underlying increasing suicide rates in the USA
2024-01-25
Are there specific communities that bear the brunt of suicide mortality? Certain studies have revealed that historically marginalized and economically deprived indigenous populations are linked with higher rates of cluster suicides—especially in Canada, the United States, and Australia. Public health officials need to consider that the risk of suicide contagion—social transmission due to insufficient interventions and resources—is real and must be countered. Now, a consortium of public health experts from Japan, Australia, and China have analyzed trends in suicide mortality in American Indian or Alaskan Native (AIAN) populations, while exploring ...
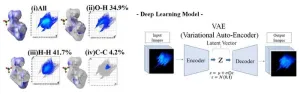
Deep learning reveals molecular secrets of explosive perchlorate salts
2024-01-25
Perchlorates are a class of compounds that are notorious for their explosive nature. This raises safety concerns during experiments involving complex compounds that contain perchlorate ions, since explosions can be triggered even by the slightest shock or heat. It is, therefore, important to study their molecular structure and understand the reason behind their explosive nature.
In this context, a method called the Hirschfield surface analysis has been extensively used for visualizing and quantifying the crystal structure and molecular interactions of crystal compounds. Moreover, a two-dimensional fingerprint plot derived from the Hirschfield ...
National retailers support heart and stroke health through annual Life is Why™ campaign
2024-01-25
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2024 — This February, during American Heart Month and the American Heart Association’s Centennial year, the Association is devoted to a world of healthier lives for all by teaming up with retailers and brands around the country for Life is Why™, a cause marketing campaign supporting the Association’s life-saving heart and brain health mission. Life is Why inspires consumers to celebrate their reasons to live healthier, longer lives and participate personally in the mission of the Association by donating at the point-of-sale or by purchasing a product ...