(Press-News.org)
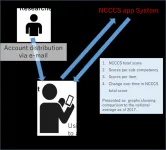
To improve the care coordination competency of nurses involved in the management of critically ill patients on life support, an electronic app—NCCCS—was developed by Associate Professor Chie Takiguchi of Toho University and Professor Tomoko Inoue of International University of Health and Welfare.
The NCCCS app utilizes the scoring system referred to as the Nurses' Care Coordinate Competency Scale (NCCCS), developed by Dr. Takiguchi et al. in 2017, and it is currently being translated into Chinese, Italian, Polish, and Persian. This app offers immediate feedback to nurses caring for critically ill patients on life support based on their self-assessment of the frequency of their care coordination behaviors.
The NCCCS app was tested in the study and found to be highly effective in training when used by individuals who had certain years of critical care management experience but had low care coordination competencies.
While the significance of care coordination for appropriate critical care is recognized, there is a lack of established educational methods for nurses engaged in care coordination. The quality of care, especially concerning the success or failure of multidisciplinary care for critically ill patients on life support, has been demonstrated to be linked not only to survival rates but also to the development of physical, mental, and cognitive dysfunction in post-intensive care patients.
Dr. Takiguchi said, "Our NCCCS app will help nurses enhance their care coordination competencies
in the management of critically ill patients. It offers a new strategy to improve the physical, mental, and cognitive outcomes of critically ill patients."
The research findings were published in the Japan Journal of Nursing Science on January 25, 2024.
Key Highlights
The group that engaged in self-assessment and received feedback through the NCCCS app demonstrated an increase in the frequency of care coordination behaviors after one month, in contrast to the self-assessment group without feedback. Notably, the participants with less experience in managing critically ill patients did not exhibit a corresponding increase in the frequency of these behaviors.
The group, whose NCCCS score was below the national average as of 2017 experienced an increased frequency of care coordination behaviors one month later, following feedback from the NCCCS app, compared to the group without feedback.
The group receiving feedback on their self-assessment scores through the NCCCS app exhibited heightened attention, confidence, and interest in learning about care coordination, in contrast to the group without feedback. Additionally, they reported that the use of the NCCCS app fostered teamwork and enhanced the quality of care.
The findings of this study may provide a new strategy for improving outcomes in critically ill patients on life support.
About Toho University
Toho University, with its focus on natural and life sciences, is dedicated to advancing education and research guided by the brand concept of "Connecting the Future with the Science of Life." The university provides a diverse array of academic fields and fosters an environment conducive to cutting-edge, up-to-date research spanning various disciplines.
Website: https://global.toho-u.ac.jp/
About Associate Professor Chie Takiguchi
Dr. Takiguchi is an academic researcher with extensive experience in critical care practice. From a nursing perspective, she is passionate about education, research, and building systems that not only save the lives of critically ill patients but also improve their long-term functional prognosis. More recently, her team has been working on the establishment of a continuous multidisciplinary care model for critically ill patients.
END
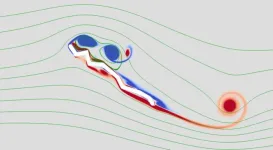
Scientists from Hiroshima University undertook a study of dragonfly wings in order to better understand the relationship between a corrugated wing structure and vortex motions. They discovered that corrugated wings exhibit larger lift than flat wings.
Their work was published in the journal Physical Review Fluids on December 7, 2023.
The researchers set out to determine if the corrugation of a dragonfly's wing is a secret ingredient for boosting lift. While past research has largely zoomed in ...
Amylases are among the most important biotechnological and industrial enzymes that can be applied in various sectors, such as food, pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, paper, and detergents.
The enzymes’ costs come from a range of factors including the quantity produced, the production process, the expense of its recovery, and the degree of purity at which it will be marketed, etc. The use of agro-industrial substrates and microorganisms brings the potential to low-cost enzyme production. Meanwhile, due to the ability to improve physical and chemical resistance to industrial environmental extremes, such as high temperature and pH, as well ...
Staying hydrated and consuming appropriate amounts of salt is essential for the survival of terrestrial animals, including humans. The human brain has several regions constituting neural circuits that regulate thirst and salt appetite, in intriguing ways.
Previous studies suggested that water or salt ingestion quickly suppresses thirst and salt appetite before the digestive system absorbs the ingested substances, indicating the presence of sensing and feedback mechanisms in digestive organs that help real-time thirst and salt appetite modulation in response to drinking ...
Early in the pandemic, clinicians noticed that certain immunocompromised patients were experiencing persistent SARS-CoV-2 infections, some lasting weeks to months at a time.
This raised concerns that one of these cases could be the source of an emerging viral variant that has benefited from an extended battle with the immune system.
A prospective study published in the journal Lancet Microbe provides more clarity on which patient populations are at higher risk for prolonged infections —and hints that this fear is likely unwarranted.
The ...
A new statistical tool developed by researchers at the University of Chicago improves the ability to find genetic variants that cause disease. The tool, described in a new paper published January 26, 2024, in Nature Genetics, combines data from genome wide association studies (GWAS) and predictions of genetic expression to limit the number of false positives and more accurately identify causal genes and variants for a disease.
GWAS is a commonly used approach to try to identify genes associated with a range of human traits, including most common diseases. Researchers compare genome sequences ...
As part of the Ice Memory initiative, PSI researchers, with colleagues from the University of Fribourg and Ca’ Foscari University of Venice as well as the Institute of Polar Sciences of the Italian National Research Council (CNR), analysed ice cores drilled in 2018 and 2020 from the Corbassière glacier at Grand Combin in the canton of Valais. A comparison of the two sets of ice cores published in Nature Geoscience shows: Global warming has made at least this glacier unusable as a climate archive.
Reliable information about the past climate and air pollution can no longer be obtained from ...
A valuable molecule sourced from the soapbark tree and used as a key ingredient in vaccines, has been replicated in an alternative plant host for the first time, opening unprecedented opportunities for the vaccine industry.
A research collaboration led by the John Innes Centre used the recently published genome sequence of the Chilean soapbark tree (Quillaja saponaria) to track down and map the elusive genes and enzymes in the complicated sequence of steps needed to produce the molecule QS-21.
Using transient expression techniques developed at the John Innes Centre, the team reconstituted the ...
As digital devices progressively replace pen and paper, taking notes by hand is becoming increasingly uncommon in schools and universities. Using a keyboard is recommended because it’s often faster than writing by hand. However, the latter has been found to improve spelling accuracy and memory recall.
To find out if the process of forming letters by hand resulted in greater brain connectivity, researchers in Norway now investigated the underlying neural networks involved in both modes of writing.
“We ...
Computers can count seals from aerial photographs with lightning speed and reliability. Based on their spatial patterns, the tiny dots on the aerial images can even be assigned to one of the two major species of seals in the Wadden Sea. That is shown in the thesis that marine biologist Jeroen Hoekendijk will defend on January 26 in Wageningen. "To better understand if and how marine mammals like seals are affected by climate change and the disappearance of sea ice, this help from artificial intelligence (AI) in observations is crucial," Hoekendijk said. Hoekendijk carried out his research at the Royal Netherlands Institute ...
Where freshwater rivers meet seas and oceans lies a scientifically intriguing and ecologically important type of ecosystem. As estuarine ecosystems provide various and diverse services to humanity and the planet at large, including food security and natural buffers and filters in the events of storms and water pollution, there has been an increasing need to facilitate and support the exchange of research findings and ideas related to their conservation and sustainable management by means of new-age technology and novel approaches.
This is how a team of renowned and passionate ...