(Press-News.org) Harvesting energy sources such as heat, vibration, light, and electromagnetic waves from everyday environments such as industrial sites and automobiles and converting them into electrical energy is known as energy harvesting. Energy harvesting makes it easier to power today's popular IoT sensors and wireless devices that are located in environments where battery replacement is difficult.
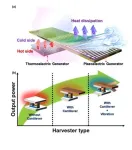
Dr. Hyun-Cheol Song and Dr. Sunghoon Hur of Electronic Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a hybrid energy harvesting system that increases power production by more than 50% by combining thermoelectric and piezoelectric effects.
The thermoelectric effect, which converts thermal energy from both ends of the device into electrical energy, has a low energy conversion efficiency, and the piezoelectric effect, which converts mechanical vibration into electrical energy, has a high impedance, so energy cannot be reliably harvested. To overcome the limitations of single-mode energy harvesters, hybrid energy harvesters have been proposed in the past, but they are mainly based on simply combining the energy generated by each mechanism.
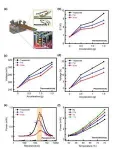
In response, the KIST research team developed a thermoelectric-piezoelectric hybrid energy harvester that complements the shortcomings of thermoelectric and piezoelectric devices to create a synergistic effect in environments with heat sources and vibrations. First, instead of a heat sink, which is a static shape with a large cross-sectional area that is bulky and in contact with air, a cantilever was fabricated to improve the heat dissipation effect in a vibration environment, resulting in a thermoelectric device output that was improved by more than 25%. The researchers also proposed a hybrid energy harvesting structure in which a polymer-type piezoelectric device (MFC) was attached to the cantilever to generate additional power by generating tensile and compressive deformation of the piezoelectric device as the cantilever shakes. The research team successfully applied this hybrid energy harvester to stably drive a commercial IoT sensor (GPS positioning sensor, 3 V, 20 mW), demonstrating the potential for future IoT sensors to run continuously without battery power supply.
"This study confirms that the hybrid energy harvesting system can be reliably applied to our real life," said Dr. Sunghoon Hur of KIST, who led the research. "We have confirmed its effectiveness in places where heat and vibration exist together, such as automobile engines, and are currently planning to build a system that can be applied to factory facilities or construction machinery engines that are difficult to supply power and diagnose their condition wirelessly."
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-ho Lee) as Institutional Program of KIST and was published in the latest issue of Energy Conversion and Management (IF: 10.4, top 1.8% in JCR), an international journal in the energy field.
END
Hybrid energy harvesters that harness heat and vibration simultaneously
Developing a hybrid energy harvester that goes beyond simple coupling of thermoelectric and piezoelectric devices to generate higher power
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Organ donations after MAiD made up 14% of deceased donations in Quebec
2024-01-29
Organ donation after medical assistance in dying (MAiD) represented 14% of Quebec's total deceased donations in 2022, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230883.
To understand the impact of organ donation after MAiD, Quebec researchers analyzed data on all patients referred to Transplant Québec for possible organ donation after MAiD from January 2018 to December 2022. This represented the first 5 full years when organ donation after MAiD was allowed in the province. Over the 5-year period, Transplant Québec received 245 referrals for donation after MAiD, ...
Polycystic ovarian syndrome: new review to help diagnose and manage
2024-01-29
A new review in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) is aimed at helping clinicians diagnose and manage polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), an endocrine disorder that affects about 10% of femaleshttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231251.
This disorder affects females of reproductive age and is associated with infertility, miscarriage and pregnancy complications. Its long-term health consequences include hypertension, cancer risks, and metabolic and psychological impacts. Patients usually present to health care between ages 18 and 39 years complaining of menstrual cycle irregularities, ...
Robot trained to read braille at twice the speed of humans
2024-01-29
Researchers have developed a robotic sensor that incorporates artificial intelligence techniques to read braille at speeds roughly double that of most human readers.
The research team, from the University of Cambridge, used machine learning algorithms to teach a robotic sensor to quickly slide over lines of braille text. The robot was able to read the braille at 315 words per minute at close to 90% accuracy.
Although the robot braille reader was not developed as an assistive technology, the researchers say the high sensitivity required to read braille makes it an ideal test in the development of robot ...
Obesity and alcohol are contributing to increases in bowel cancer rates among young adults
2024-01-29
Overweight and obesity are contributing to rising death rates from bowel cancer among people aged 25-49 years in the European Union (EU) and the UK, although death rates from this type of cancer are decreasing overall across Europe.
These findings are from a new study published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday), which predicts death rates from cancer in the EU and UK for 2024. It is the first time that an increase in bowel cancer death rates among young adults has been predicted for the EU, and it confirms a trend in the UK that the researchers first noted in 2021.
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), ...
Playing an instrument linked to better brain health in older adults
2024-01-29
Engaging in music throughout your life is associated with better brain health in older age, according to a new study published by experts at the University of Exeter.
Scientists working on PROTECT, an online study open to people aged 40 and over, reviewed data from more than a thousand adults over the age of 40 to see the effect of playing a musical instrument – or singing in a choir - on brain health. Over 25000 people have signed up for the PROTECT study, which has been running for 10 years.
The team reviewed participants’ musical experience and lifetime exposure ...
New research finds volume alone does not predict quality outcomes in pediatric cardiac surgery
2024-01-28
A study of pediatric heart surgery centers across the United States has demonstrated that, when it comes to successful surgery, it’s not just the size of the program that matters in determining quality outcomes.
Historically, hospitals with a “low volume” of pediatric heart operations—in this case, those that perform 103 surgeries or fewer a year—have been associated with worse outcomes for patients. However, a team led by D. Chauhan, MD, from WVU Medicine Children’s ...
Almost 50% of patients under 60 years choose TAVR over surgical aortic valve replacement with worse outcomes
2024-01-28
Despite national guidelines recommending surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) for patients under age 65 with severe aortic stenosis, many hospitals are still opting for a nonsurgical approach in patients under 60—possibly with poorer survival rates.
In a study presented at The Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ 2024 Annual Meeting in San Antonio, Texas, researchers from the department of cardiac surgery in the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles and the department of population health science and policy at Mount Sinai New York compared ...
New study reveals the profound impact of forced separation between humans and their pets
2024-01-28
Pet owners forced to be separated from their animals in crisis situations, including those who are victims of domestic violence, are suffering from a lack of support services needed to protect them.
These are the findings of a new review of 27 years of international research, published in the peer-reviewed journal Anthrozoös, which unveils the increased risks to both safety and psychological well-being when people are faced with the threat of forced separation from their pets.
The results provide important insights towards addressing the challenges arising from domestic violence, homelessness or natural disasters that can threaten the bond between humans and ...
Immunotherapy post-surgery improves overall survival for kidney cancer
2024-01-27
Boston – For the first time in fifty years, results from a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled trial have shown an overall survival benefit from an adjuvant therapy in patients with kidney cancer.
Treatment with pembrolizumab, an immunotherapy drug, after surgery significantly prolonged overall survival in patients with clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (ccRCC) at high risk for recurrence, according to an analysis of results from the KEYNOTE-564 study. Pembrolizumab was associated with a 38% reduction in risk of death compared with placebo.
“We can now ...
STS announces late-breaker research to be presented at the 2024 Annual Meeting
2024-01-27
The Society of Thoracic Surgeons has released late-breaking research scheduled for presentation at the 2024 Annual Meeting taking place January 27 - 29 in San Antonio. The conference, healthcare’s leading scientific and educational convening specializing in cardiothoracic surgery, has a rich history of showcasing clinical trials with a strong foundation of detailed methodology and trusted data collection governed by ethical clinical principles.
The event’s late-breaking trial sessions focus on studies anticipated to significantly influence advances in cardiothoracic patient care. In this fast-paced healthcare landscape, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
[Press-News.org] Hybrid energy harvesters that harness heat and vibration simultaneouslyDeveloping a hybrid energy harvester that goes beyond simple coupling of thermoelectric and piezoelectric devices to generate higher power