(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Plant biologists report that a species of tree fern found only in Panama reanimates its own dead leaf fronds, converting them into root structures that feed the mother plant. The fern, Cyathea rojasiana, reconfigures these “zombie leaves,” reversing the flow of water to draw nutrients back into the plant.
Watch a video about the findings.
This weird phenomenon occurs only after the leaves die and droop to the ground, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign plant biology professor James Dalling, who made the discovery with his team while studying a different plant in a Panamanian forest reserve. Dalling noticed that the fronds were strongly embedded in the soil and had sprouted a network of rootlets. Laboratory tests revealed that the zombie leaves were drawing nitrogen out of the soil.
Even after they are converted into roots, the wilted fronds look like decayed plant matter, which is probably why generations of plant biologists failed to notice that they were performing a life-sustaining task, Dalling said.
“This is a truly novel repurposing of tissue. And it’s distinct from what we know other ferns do,” he said.
Other plants, including some ferns, send out leaves or shoots that touch the ground and sprout roots to sustain a new plant, he said. But reconfiguring dead tissue to feed the original plant has never been reported. The new findings are detailed in the journal Ecology.
C. rojasiana belongs to an ancient lineage of tree ferns dating back to the Jurassic period, Dalling said. The zombie leaves are most likely an adaptation to the nutrient-poor volcanic soils.
“Panama is a land bridge between North and South America that coalesced 7 million years ago out of an archipelago of islands, and those islands are the result of volcanic activity in the past,” he said. “In one site we discovered, a layer of volcanic ash several meters deep looks like sand that you would dig up on a sandy beach. The plants that grow there are distinct from those that we find elsewhere in that forest reserve.”
The patchiness of the vegetation means soil nutrients also are unevenly distributed.
“And so the tree ferns seem to be putting out tentacles to sample the surrounding soils,” Dalling said. “They’re able to sample a greater range of nutrient environments for the same amount of investment of rootlets than if they just sent out a single rooting structure all around the fern. I think it’s all about the economics of how they use resources in a patchy environment.”
The tree ferns also grow very slowly.
“They’re probably putting on one or two leaves a year, and so they’re adding on the order of a few centimeters of height a year,” Dalling said.
This means each frond is a major investment of resources that the plant repurposes after the leaf dies. The slow growth also means that the tree fern is short enough that when its fronds die, they droop all the way to the ground. The trees reach a maximum height of about two meters, Dalling said.
The finding is “another example of the extraordinary diversity of plant adaptations that exist in resource-poor environments,” he said.
Dalling also is a research associate at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama.
END
Back from the dead: Tropical tree fern repurposes its dead leaves
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
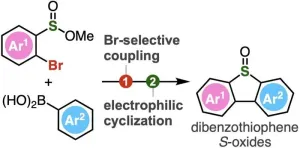
New horizons in chemical biology: A novel approach to synthesize dibenzothiophene s-oxides
2024-01-29
Organic compounds in the field of chemistry range from simple hydrocarbons to complex molecules, with diverse functional groups added to the main carbon backbone. These functional groups impart the compounds distinct chemical properties as well as participate in various chemical transformations, making them important precursors for the synthesis of diverse compounds. Scientists have, therefore, actively engaged in creating molecules that feature novel and highly reactive functional groups.
One such class of compounds are dibenzothiophenes and their derivatives containing ...
Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination
2024-01-29
A sequence variant that increases risk of pregnancy loss
Scientists at deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen and their collaborators from Iceland, Denmark and USA published a study today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology titled “Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination”.
While it is well established that chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of miscarriages the biology behind pregnancy losses with or without chromosomal errors is not well understood. Over 114 thousand women from Iceland, Denmark, UK, USA and Finland who have ...
How obesity dismantles our mitochondria
2024-01-29
The number of people with obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, resulting in a worldwide epidemic. While lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a role in the development and progression of obesity, scientists have come to understand that obesity is also associated with intrinsic metabolic abnormalities. Now, researchers from University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on how obesity affects our mitochondria, the all-important energy-producing structures of our cells.
In a study published January ...
Cancer treatment two and a half times more effective when tumours have defective "energy factories"
2024-01-29
Cancer Research UK-funded scientists have made an unusual discovery that could help to identify patients who are up to two and a half times more likely to respond to currently available cancer drugs.
Scientists at the Cancer Research UK Scotland Institute and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre in the USA have “rewired” the DNA of mitochondria – energy factories found in every living cell. They found that creating mutations in parts of this DNA determines how well cancer will respond to immunotherapy – treatments which harness the body’s natural defences ...
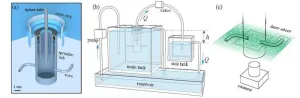
How does a “reverse sprinkler” work? Researchers solve decades-old physics puzzle
2024-01-29
For decades scientists have been trying to solve Feynman’s Sprinkler Problem: How does a sprinkler running in reverse—in which the water flows into the device rather than out of it—work? Through a series of experiments, a team of mathematicians has figured out how flowing fluids exert forces and move structures, thereby revealing the answer to this long-standing mystery.
“Our study solves the problem by combining precision lab experiments with mathematical modeling that explains how a reverse sprinkler operates,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author ...
Neuroblastoma: Liquid biopsies to detect relapse of childhood cancer early
2024-01-29
(Utrecht/Vienna, 29.1.2024) Neuroblastoma mainly affects toddlers and young children - in the EU region there are 1500 new cases per year. Neuroblastoma is a malignant tumor of the peripheral nervous system and around 50% of patients are high-risk cases. Recurrences occur frequently, and conventional therapies are no longer effective for these children. With liquid biopsies it is possible to monitor therapy success and to predict the recurrence of the tumor in time to take medical countermeasures. Scientists from leading European ...
Speaking in a local accent might make social robots seem more trustworthy and competent
2024-01-29
Social robots can help us with many things: teaching, learning, caring. Because they’re designed to interact with humans, they’re designed to make us comfortable — and that includes the way they talk. But how should they talk? Some research suggests that people like robots to use a familiar accent or dialect, while other research suggests the opposite.
“Surprisingly, people have mixed feelings about robots speaking in a dialect — some like it, while others prefer standard language,” said Katharina Kühne of the University of Potsdam, lead author ...
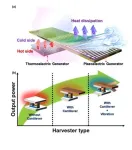
Hybrid energy harvesters that harness heat and vibration simultaneously
2024-01-29
Harvesting energy sources such as heat, vibration, light, and electromagnetic waves from everyday environments such as industrial sites and automobiles and converting them into electrical energy is known as energy harvesting. Energy harvesting makes it easier to power today's popular IoT sensors and wireless devices that are located in environments where battery replacement is difficult.
Dr. Hyun-Cheol Song and Dr. Sunghoon Hur of Electronic Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a hybrid energy harvesting ...
Organ donations after MAiD made up 14% of deceased donations in Quebec
2024-01-29
Organ donation after medical assistance in dying (MAiD) represented 14% of Quebec's total deceased donations in 2022, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230883.
To understand the impact of organ donation after MAiD, Quebec researchers analyzed data on all patients referred to Transplant Québec for possible organ donation after MAiD from January 2018 to December 2022. This represented the first 5 full years when organ donation after MAiD was allowed in the province. Over the 5-year period, Transplant Québec received 245 referrals for donation after MAiD, ...
Polycystic ovarian syndrome: new review to help diagnose and manage
2024-01-29
A new review in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) is aimed at helping clinicians diagnose and manage polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), an endocrine disorder that affects about 10% of femaleshttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231251.
This disorder affects females of reproductive age and is associated with infertility, miscarriage and pregnancy complications. Its long-term health consequences include hypertension, cancer risks, and metabolic and psychological impacts. Patients usually present to health care between ages 18 and 39 years complaining of menstrual cycle irregularities, ...