(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- Clinical research led by Indiana University School of Medicine investigators and their collaborators in Uganda has revealed that hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Their latest findings enhance strong evidence of hydroxyurea’s effectiveness and could ultimately reduce death in children in Africa, the continent most burdened by the disease.
The group’s research, recently published in the journal Blood, revealed that hydroxyurea treatment resulted in a remarkable 60% reduction in severe or invasive infections, including malaria, bacteremia, respiratory tract infections and gastroenteritis, among Ugandan children with sickle cell anemia.
“Our investigation provides powerful justifications for hydroxyurea’s use in children with sickle cell anemia in Africa,” said Dr. Chandy John, the Ryan White Professor of Pediatrics at IU School of Medicine and co-lead investigator of the latest study. “Given the high rates of infection in this region, we hope our evidence will encourage ministries of health to continue supporting and expanding access to hydroxyurea for young patients who can greatly benefit from the treatment.”
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder that alters the structure of red blood cells and affects oxygen distribution throughout the body, increasing susceptibility to serious health complications and life-threatening infections. According to the World Health Organization, more than 300,000 children worldwide are born with sickle cell disease each year, with a high prevalence found in African countries.
While hydroxyurea has had U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval as a sickle cell disease treatment for children since 2017, its accessibility and acceptance in Africa have been comparatively limited. As hydroxyurea has become more recognized in African countries for its effectiveness in treating sickle-cell-related complications, John and his colleagues noticed a knowledge gap about the treatment’s effect on infections. This led the research group to incorporate hydroxyurea treatment and analysis into their established clinical trial, Zinc for Infection Prevention in Sickle Cell Anemia.
During the study, the researchers examined the effects of hydroxyurea on 117 children in Uganda and focused on a range of infections. After hydroxyurea treatment, results showed a substantial decrease in the incidence of these infections. Additionally, eight of the nine deaths that occurred in the trial were children whose parents declined hydroxyurea treatment. The only death in a child on hydroxyurea treatment occurred four days after starting treatment, providing insufficient time for hydroxyurea to have an effect.
Of the five children for whom a cause of death was known, all five died of infectious causes. The high death rate in the study, despite expert clinical care by study personnel, provides further evidence of the urgent need for additional interventions to decrease mortality in children with sickle cell disease in Africa.
“Infections commonly precede other complications related to sickle cell anemia and often result in hospitalizations that can lead to death,” said Dr. Ruth Namazzi, site principal investigator, first author on the study and a lecturer in the Department of Pediatrics and Child Health at Makerere University in Uganda. “We believe incorporating hydroxyurea treatment as the standard of care for sickle cell anemia across Africa will not only reduce infections but will more importantly save countless lives.”
Additional IU researchers who contributed to the study include Caitlin Bond, Andrea Conroy, Dibyadyuti Datta and Michael Goings. They collaborated with Namazzi; Dr. Robert Opoka of Global Health Uganda; Dr. Abner Tagoola of Jinja Regional Referral Hospital; Jeong Hoon Jang of Yonsei University; and Dr. Russell E. Ware of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
END
Hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Manchester and SPIE announce $1 million endowment for postgraduate scholarships
2024-01-29
The University of Manchester and SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics have announced the establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics.
The $500k gift from the SPIE Endowment Matching Program will be matched 100% by the University and will be used to support both early-career and returning researchers from the University’s Photon Science Institute in partnership with the Royce Institute, the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation.
The partnership was announced today (29 January) during the SPIE Photonics West conference in San Francisco.
Photonics is the study of light and its interactions ...
Argonne scientists help scale up nanomaterials for sustainable manufacturing
2024-01-29
New material is self-assembling, long-lasting and recyclable.
As electronic devices get smaller, the materials needed to create them get smaller as well. Nanoscience is the study of extremely small materials that find uses in energy storage, electronics, health and safety applications and more.
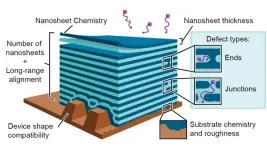
Now a team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed a new self-assembly method to fabricate multilayered 2D nanosheets. A nanosheet is an extremely small, lasagna-like material made of ultrathin layers of polymers and nanoparticles.
These nanosheets have significantly ...
OU scientists tests revolutionary imaging technique for pancreatic cancer
2024-01-29
Researchers at OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences have embarked on a revolutionary new research study that could improve the detection of a deadly disease — pancreatic cancer — and give patients a chance to live longer, healthier lives.
The research focuses on an innovative combination of imaging techniques: a newly created contrast agent that recognizes pancreatic cancer cells, paired with Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography, or MSOT. Together, the approach can detect pancreatic cancer cells the width of an eyelash ...
Rising sea levels could lead to more methane emitted from wetlands
2024-01-29
As sea levels rise due to global warming, ecosystems are being altered. One small silver lining, scientists believed, was that the tidal wetlands found in estuaries might produce less methane – a potent greenhouse gas – as the increasing influx of seawater makes these habitats less hospitable to methane-producing microbes.
However, research from biologists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley indicates that these assumptions aren’t always true. After examining the microbial, chemical, and geological features of 11 wetland zones, the team found that a wetland region exposed ...
Study urges people to think twice before going on a diet
2024-01-29
A new qualitative study highlights the negative interpersonal and psychological consequences associated with “yo-yo dieting,” also known as weight cycling. The work underscores how toxic yo-yo dieting can be and how difficult it can be for people to break the cycle.
“Yo-yo dieting – unintentionally gaining weight and dieting to lose weight only to gain it back and restart the cycle – is a prevalent part of American culture, with fad diets and lose-weight-quick plans or drugs normalized as people pursue beauty ...
Astronomers spot 18 black holes gobbling up nearby stars
2024-01-29
Star-shredding black holes are everywhere in the sky if you just know how to look for them. That’s one message from a new study by MIT scientists, appearing today in the Astrophysical Journal.
The study’s authors are reporting the discovery of 18 new tidal disruption events (TDEs) — extreme instances when a nearby star is tidally drawn into a black hole and ripped to shreds. As the black hole feasts, it gives off an enormous burst of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Astronomers have detected previous tidal disruption events by looking for characteristic bursts in the optical and X-ray bands. To date, these searches have ...
The DiAL-Health study will help determine how intermittent fasting and calorie counting can improve a person’s “healthspan”
2024-01-29
January is a time when many people are looking for new diet routines, and intermittent fasting is trending, as are traditional calorie cutting programs.
Research conducted with animal models suggests that intermittent fasting slows aging, and those animals live longer. Researchers at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham are conducting the DiAL-Health study to see if eating for 8 hours and fasting for 16 each day shows similar results in people. These researchers ...
From simulation to reality: Making social media a safer space for kids through AI
2024-01-29
Like it or not, social media has become the new mall for kids. It’s where they want to be, and it’s a place they can easily go—often with no guidance, no oversight, and no guardrails. And when the content gets ugly or confusing or weird, it can be tough for them to know what to do.
Dominic DiFranzo, an assistant professor of computer science and engineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science, has devoted his research to helping kids better navigate the perils of social media. He and his team have recently received two grants from the National Science Foundation to develop artificial intelligence tools ...
Shah studying fingerprinting technology for enhancing 5G/NextG O-RAN supply chain risk management
2024-01-29
Vijay Shah, Assistant Professor, Cybersecurity Engineering, received funding for the project: "Fingerprinting Technology for Enhancing 5G/NextG O-RAN Supply Chain Risk Management."
In this project, Shah is focusing on distinctive power signatures and electromagnetic emanations to fortify supply chain risk management of 5G/Next G networks.
This technology has the potential to create a robust framework for comprehensive validation and testing across the entire lifespan of deployed Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) systems. This, in turn, could ...
From Baby Boomers to Gen Alpha – Is it time to stop talking about generations?
2024-01-29
'Millennials don't really want to work. They're far too focused on avocado toast and chai lattes!' Just one of the many clichés expressed by workers over the age of fifty. And those being criticized? Well, they often reply with a bored 'OK, Boomer' followed by an eye roll and some ironic remark about the excessively performance-driven worldview of those born between the mid 1950s and the mid 1960s. Work, it seems, just isn't as important to the young as it is to older generations. But it's not just about baby boomers and millennials. Parked between them is Generation X, ...