(Press-News.org)
Hf-based carbides are highly desirable candidates for thermal protection applications above 2000 ℃ due to their extremely high melting point and favorable mechanical properties. However, as a crucial indicator for composition design and performance assessment, the static oxidation behavior of Hf-based carbides at their potential service temperatures has been rarely studied.
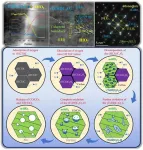
In a study published in the KeAi journal Advanced Powder Materials, a group of researchers from Central South University and China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology revealed the static oxidation mechanism of (Hf, Ti)C bulks at 2500 ℃, as well as the effect of Ti substitutions on their oxidation behaviors.
"The addition of Ti element can make the microstructure of HfC oxide layer more complex,” explained Shiyan Chen, lead author of the study. “Typically, such a composite oxide layer has better protective properties.”
The thickness of the oxide layer on the surface of (Hf, Ti)C was reduced by 62.29 % compared with that on the HfC monocarbide surface after oxidation at 2500 ℃ for 2000 s. The dramatic improvement in oxidation resistance was attributed to the unique oxide layer structure consisting of various crystalline oxycarbides, HfO2 and carbon.
“The Ti-rich oxycarbide ((Ti, Hf)CxOy) dispersed within HfO2 formed the major structure of the oxide layer. A coherent boundary with lattice distortion existed at the HfO2 / (Ti, Hf)CxOy interface along the (111) crystal plane direction, which served as an effective oxygen diffusion barrier,” added Chen.
The Hf-rich oxycarbide ((Hf, Ti)CxOy) together with (Ti, Hf)CxOy, HfO2, and precipitated carbon constituted a dense transition layer, ensuring favorable bonding between the oxide layer and the matrix. Furthermore, the Ti content affects the diffusion of carbon in (Hf, Ti)C lattice and the distribution of Ti-rich oxycarbide, which will further determine the structural integrity of the oxide layer. Based on the results of oxidation kinetics, 30%-40 at. % Ti substitution provides the best enhancement of oxidation resistance.
According to Professor Zhaoke Chen, co-lead and corresponding author, this study represents a novel exploration in the field of ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs). "Our study enhances the comprehension of the structural evolution during ultra-high temperature oxidation. The findings offer theoretical guidance for optimizing the composition of UHTCs to broaden their applications at ultra-high temperatures,” said Chen.
###
Contact the author: Zhaoke Chen and Xiang Xiong, State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China; Zhaoke Chen: chenzhaoke2008@csu.edu.cn, Xiang Xiong: xiongx@csu.edu.cn
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
END
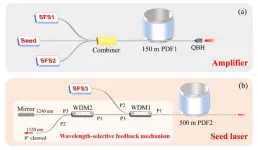
Laser sources operating at the 1.2 μm wavelength band have some unique applications in photodynamic therapy, biomedical diagnosis and oxygen sensing. Additionally, they can be adopted as pump sources for mid-infrared optical parametric generation as well as visible light generation by frequency doubling. Laser generation at 1.2 μm waveband has been achieved with different solid-state lasers including semiconductor laser, diamond Raman laser, and fiber laser. Among these three types, fiber laser thanks to its simple structure, good beam quality, and operation flexibility, is a great choice for 1.2 μm waveband laser generation.
Researchers ...
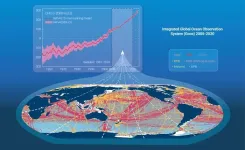
We know that our climate is changing. Extreme weather events are becoming more common, sea levels are rising and overall, our planet is getting warmer. Monitoring these changes is critical. One of the best indicators of climate change is the Ocean Heat Content (OHC) estimate, a measurement of overall oceanic temperature calculated by gathering water temperature data in oceans around the world in differing locations, at varying depths and across time. The data necessary to calculate the OHC over such a wide-spread area is gathered by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS), an integrated network of platforms ...
Soil microbiome has far-reaching significance, particularly for rice production, which can be better explained with a Japanese proverb: “Rice grows with soil fertility, while upland crops depend on fertilization”. Therefore, understanding the paddy field microbiome is crucial for sustainable soil fertility and rice production. This would also lead us to overcome the global food shortage problem as rice is the primary food source for nearly half of the world's population. Among the paddy field microbes, bacteria, fungi, and archaea are well-studied, while protists, the vast majority of eukaryotes, are largely unknown. Protists are the most diverse eukaryotic microorganisms ...
Ahead of the 2024 US presidential election, The BMJ today launches a forward-looking series that highlights the lessons that can be learned from the US’s covid-19 experience and the actions that are needed to prevent the loss of another million citizens in the next pandemic and improve and protect population health.
The articles, written by leading clinicians and researchers across the US, explore topics such as how systemic racism and economic inequality contributed to covid-19 disparities; mass incarceration and poor prison health as a driver of the pandemic; ...
An analysis published today in the The BMJ examines the risks faced by frontline workers in the United States during the pandemic and suggests reforms that could protect population health and save lives.
Lead author Professor David Michaels at the George Washington University and his colleagues note that from the onset laws and regulations in the United States inadequately protected frontline workers. The gaps allowed a rapid spread of disease in US workplaces like meat packing plants. At the same time, these essential workers were rarely seen as a population that needed special attention ...
Results of a large-scale innovative Citizen Science experiment called Project M which involved over 1000 scientists, 800 samples and 110 UK secondary schools in a huge experiment will be published in the prestigious RSC (Royal Society of Chemistry) journal CrystEngComm on 29 January 2024. The paper is titled: “Project M: Investigating the effect of additives on calcium carbonate crystallisation through a school citizen science program”. The paper shares a giant set of results from the school citizen scientists who collaborated with a team at Diamond to find out how different additives affect the different forms of calcium carbonate produced. These additives affect the ...
Washington, D.C.—Researchers have identified 2 strains of probiotics that can be used to reduce weight in obese dogs. The research is published this week in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
In the new study, the research team investigated metabolic diseases in companion animals and set out to identify probiotics suitable for long-term and safe treatment. “The initial challenge involved selecting specific metabolic diseases for examination, leading us to focus on the prevalent issue of 'obesity in pets,’” said study principal investigator Younghoon Kim, Ph.D., professor in the ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA – An intricate, honeycomb-like structure of struts and beams could withstand a supersonic impact better than a solid slab of the same material. What’s more, the specific structure matters, with some being more resilient to impacts than others.
That’s what MIT engineers are finding in experiments with microscopic metamaterials — materials that are intentionally printed, assembled, or otherwise engineered with microscopic architectures that give the overall material exceptional properties.
In a study appearing today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the engineers report on a new way ...
Global tree-planting campaigns have reached fad-like proportions over the past decade, and it’s easy to understand their appeal. Healthy forests help in the fight against climate change by absorbing some of our excess carbon dioxide emissions, and they can provide wildlife habitat and quality-of-life benefits for local human communities too. So why not plant more trees? It seems like an easy win.
But the problem is, there’s a huge difference between simply planting a tree and making sure that trees survive and grow over the long-term. And without the necessary ecological understanding or long-term planning and ...
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 29 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...