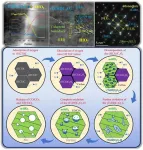
Superfluids could share characteristic with common fluids
A theoretical framework for measuring the Reynolds similitude in superfluids could help demonstrate the existence of quantum viscosity
2024-01-30
(Press-News.org) Every fluid — from Earth’s atmosphere to blood pumping through the human body — has viscosity, a quantifiable characteristic describing how the fluid will deform when it encounters some other matter. If the viscosity is higher, the fluid flows calmly, a state known as laminar. If the viscosity decreases, the fluid undergoes the transition from laminar to turbulent flow. The degree of laminar or turbulent flow is referred to as the Reynolds number, which is inversely proportional to the viscosity. The Reynolds law of dynamic similarity or Reynolds similitude, states that if two fluids flow around similar structures with different length scales, they are hydrodynamically identical provided they exhibit the same Reynolds number.
However, this Reynolds similitude is not applied to quantum superfluids, as they do not have viscosity — at least, that’s what researchers have believed. Now, a researcher from the Nambu Yoichiro Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Physics at Osaka Metropolitan University in Japan has theorized a way to examine the Reynolds similitude in superfluids, which could demonstrate the existence of quantum viscosity in superfluids.
Dr. Hiromitsu Takeuchi, a lecturer in the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University, published his approach on January 11, 2024, in Physical Review B.
“Superfluids have long been considered an obvious exception to the Reynolds similitude,” Dr. Takeuchi said, explaining that the Reynolds law of similitude states that if two flows have the same Reynolds number, then they are physically identical. “The concept of quantum viscosity overturns the common sense of superfluid theory, which has a long history of more than half a century. Establishing similitude in superfluids is an essential step to unify classical and quantum hydrodynamics.”
However, quantum superfluids can have turbulence, resulting in a quantum quandary: Turbulence in fluids requires dissipation, so how can superfluid turbulence experience dissipation without viscosity? They must have dissipation and may follow the Reynolds similitude, but the right approach to examine it had not yet been developed.
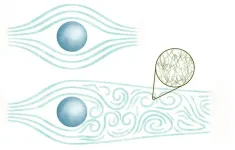
These characteristics could be examined, Dr. Takeuchi theorizes, by analyzing how a solid sphere falls into a superfluid. By combining the terminal speed of the sphere’s fall with the resistance the sphere encounters from the fluid as it falls, researchers can determine an analogue for the Reynolds similitude. This means effective viscosity, called the quantum viscosity, can be measured.
“This study focuses on a theoretical issue in understanding quantum turbulence in superfluids and shows that the Reynolds similitude in superfluids can be verified by measuring the terminal velocity of an object falling in a superfluid,” Dr. Takeuchi said. “If this verification can be made, then this suggests that quantum viscosity exists even in pure superfluids at absolute zero. I can’t wait to see it verified through experimentation.”
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is the third largest public university in Japan, formed by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in 2022. OMU upholds "Convergence of Knowledge" through 11 undergraduate schools, a college, and 15 graduate schools. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter: @OsakaMetUniv_en, or Facebook.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-30
There is substantial geographic variation across the U.S. health care system to diagnose and treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease with disease-modifying therapies, and engaging primary care providers in the effort may be a key to accelerating delivery of emerging new treatments, according to a new RAND report.
Enabling primary care practitioners to diagnose and evaluate patients for treatment eligibility would make the biggest impact on reducing wait times for specialists and increase the number of people treated with disease-modifying therapies from 2025 through 2044.
While primary care providers are technically capable of performing cognitive assessments, ...
2024-01-30
A new causal link has been found between the presence of oncofoetal ecosystems and recurrence and response to immunotherapy in primary liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
The findings will pave the way to use the presence of oncofoetal ecosystems as a biomarker to treat HCC, a disease with a poor prognosis that is typically diagnosed late
Singapore, 30 January 2024 - A team of clinician-scientists and researchers from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and global research partners, has found a causal link between the presence of oncofoetal ...
2024-01-30
Hf-based carbides are highly desirable candidates for thermal protection applications above 2000 ℃ due to their extremely high melting point and favorable mechanical properties. However, as a crucial indicator for composition design and performance assessment, the static oxidation behavior of Hf-based carbides at their potential service temperatures has been rarely studied.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Advanced Powder Materials, a group of researchers from Central South University and China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology revealed the static oxidation mechanism ...
2024-01-30
Laser sources operating at the 1.2 μm wavelength band have some unique applications in photodynamic therapy, biomedical diagnosis and oxygen sensing. Additionally, they can be adopted as pump sources for mid-infrared optical parametric generation as well as visible light generation by frequency doubling. Laser generation at 1.2 μm waveband has been achieved with different solid-state lasers including semiconductor laser, diamond Raman laser, and fiber laser. Among these three types, fiber laser thanks to its simple structure, good beam quality, and operation flexibility, is a great choice for 1.2 μm waveband laser generation.
Researchers ...
2024-01-30
We know that our climate is changing. Extreme weather events are becoming more common, sea levels are rising and overall, our planet is getting warmer. Monitoring these changes is critical. One of the best indicators of climate change is the Ocean Heat Content (OHC) estimate, a measurement of overall oceanic temperature calculated by gathering water temperature data in oceans around the world in differing locations, at varying depths and across time. The data necessary to calculate the OHC over such a wide-spread area is gathered by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS), an integrated network of platforms ...
2024-01-30
Soil microbiome has far-reaching significance, particularly for rice production, which can be better explained with a Japanese proverb: “Rice grows with soil fertility, while upland crops depend on fertilization”. Therefore, understanding the paddy field microbiome is crucial for sustainable soil fertility and rice production. This would also lead us to overcome the global food shortage problem as rice is the primary food source for nearly half of the world's population. Among the paddy field microbes, bacteria, fungi, and archaea are well-studied, while protists, the vast majority of eukaryotes, are largely unknown. Protists are the most diverse eukaryotic microorganisms ...
2024-01-30
Ahead of the 2024 US presidential election, The BMJ today launches a forward-looking series that highlights the lessons that can be learned from the US’s covid-19 experience and the actions that are needed to prevent the loss of another million citizens in the next pandemic and improve and protect population health.
The articles, written by leading clinicians and researchers across the US, explore topics such as how systemic racism and economic inequality contributed to covid-19 disparities; mass incarceration and poor prison health as a driver of the pandemic; ...
2024-01-30
An analysis published today in the The BMJ examines the risks faced by frontline workers in the United States during the pandemic and suggests reforms that could protect population health and save lives.
Lead author Professor David Michaels at the George Washington University and his colleagues note that from the onset laws and regulations in the United States inadequately protected frontline workers. The gaps allowed a rapid spread of disease in US workplaces like meat packing plants. At the same time, these essential workers were rarely seen as a population that needed special attention ...
2024-01-30
Results of a large-scale innovative Citizen Science experiment called Project M which involved over 1000 scientists, 800 samples and 110 UK secondary schools in a huge experiment will be published in the prestigious RSC (Royal Society of Chemistry) journal CrystEngComm on 29 January 2024. The paper is titled: “Project M: Investigating the effect of additives on calcium carbonate crystallisation through a school citizen science program”. The paper shares a giant set of results from the school citizen scientists who collaborated with a team at Diamond to find out how different additives affect the different forms of calcium carbonate produced. These additives affect the ...
2024-01-29
Washington, D.C.—Researchers have identified 2 strains of probiotics that can be used to reduce weight in obese dogs. The research is published this week in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
In the new study, the research team investigated metabolic diseases in companion animals and set out to identify probiotics suitable for long-term and safe treatment. “The initial challenge involved selecting specific metabolic diseases for examination, leading us to focus on the prevalent issue of 'obesity in pets,’” said study principal investigator Younghoon Kim, Ph.D., professor in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Superfluids could share characteristic with common fluids
A theoretical framework for measuring the Reynolds similitude in superfluids could help demonstrate the existence of quantum viscosity