(Press-News.org) Life has a challenging tempo. Sometimes, it moves faster or slower than we’d like. Nevertheless, we adapt. We pick up the rhythm of conversations. We keep pace with the crowd walking a city sidewalk.
“There are many instances where we have to do the same action but at different tempos. So the question is, how does the brain do it," says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Assistant Professor Arkarup Banerjee.
Now, Banerjee and collaborators have uncovered a new clue that suggests the brain bends our processing of time to suit our needs. And it’s partly thanks to a noisy critter from Costa Rica named Alston’s singing mouse.
This special breed is known for its human-audible vocalizations, which last several seconds. One mouse will sing out a longing cry, and another will respond with a tune of its own. Notably, the song varies in length and speed. Banerjee and his team looked to determine how neural circuits in the mice’s brains govern their song’s tempo.
The researchers pretended to engage in duets with the mice while analyzing a region of their brains called the orofacial motor cortex (OMC). They recorded neurons’ activity over many weeks. They then looked for differences among songs with distinct durations and tempos.
They found that OMC neurons engage in a process called temporal scaling. “Instead of encoding absolute time like a clock, the neurons track something like relative time,” Banerjee explains. “They actually slow down or speed up the interval. So, it’s not like one or two seconds, but 10%, 20%.”
The discovery offers new insight into how the brain generates vocal communication. But Banerjee suspects its implications go beyond language or music. It might help explain how time is computed in other parts of the brain, allowing us to adjust various behaviors accordingly. And that might tell us more about how our beautifully complex brains work.
“It’s this three-pound block of flesh that allows you to do everything from reading a book to sending people to the moon," says Banerjee. "It provides us with flexibility. We can change on the fly. We adapt. We learn. If everything was a stimulus-response, with no opportunity for learning, nothing that changes, no long-term goals, we wouldn’t need a brain. We believe the cortex exists to add flexibility to behavior.”
In other words, it helps make us who we are. Banerjee’s discovery may bring science closer to understanding how our brains enable us to interact with the world. The possible implications for technology, education, and therapy are as unlimited as our imagination.
END
How a mouse’s brain bends time
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Religious people coped better with the Covid-19 pandemic, research suggests
2024-01-30
People of religious faith may have experienced lower levels of unhappiness and stress than secular people during the UK’s Covid-19 lockdowns in 2020 and 2021, according to new University of Cambridge research.
The findings follow a recently published Cambridge-led study suggesting that worsening mental health after experiencing Covid infection – either personally or in those close to you – was also somewhat ameliorated by religious belief. This study looked at the US population during early 2021.
University of Cambridge economists argue ...
IHI launches a new interdisciplinary initiative to revolutionize the way Alzheimer’s disease is detected, diagnosed, prevented, and treated
2024-01-30
Stockholm, January 30, 2024 — Members of the AD-RIDDLE consortium announced today that they will begin a new initiative that aims to bridge the gap between Alzheimer’s research, implementation science, and precision medicine. The AD-RIDDLE programme will offer healthcare professionals a suite of validated solutions for timely detection and diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and dementias, to match individuals with the right interventions at the right time, enabling people to better understand what they can do to reduce risk and prevent cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s disease represents a major public ...
Goats can tell if you are happy or angry by your voice alone
2024-01-30
HONG KONG (18 Jan 2024) — Goats can tell the difference between a happy-sounding human voice and an angry-sounding one, according to research co-led by Professor Alan McElligott, an expert in animal behaviour and welfare at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK).
The study reveals that goats may have developed a sensitivity to our vocal cues over their long association with humans, according to the study published in Animal Behaviour.
Long known for their own sonorous vocal skills, goats in the study tended to spend longer gazing towards the source of the sound after a change in the valence of a human voice, i.e., when the playback switched from a happier to ...
Scientists identify how fasting may protect against inflammation
2024-01-30
Cambridge scientists may have discovered a new way in which fasting helps reduce inflammation – a potentially damaging side-effect of the body’s immune system that underlies a number of chronic diseases.
In research published in Cell Reports, the team describes how fasting raises levels of a chemical in the blood known as arachidonic acid, which inhibits inflammation. The researchers say it may also help explain some of the beneficial effects of drugs such as aspirin.
Scientists have known for some time that our diet – particular a high calorie Western diet – can increase our risk of diseases ...
Superfluids could share characteristic with common fluids
2024-01-30
Every fluid — from Earth’s atmosphere to blood pumping through the human body — has viscosity, a quantifiable characteristic describing how the fluid will deform when it encounters some other matter. If the viscosity is higher, the fluid flows calmly, a state known as laminar. If the viscosity decreases, the fluid undergoes the transition from laminar to turbulent flow. The degree of laminar or turbulent flow is referred to as the Reynolds number, which is inversely proportional to the viscosity. The Reynolds law of dynamic similarity or Reynolds similitude, states that if two fluids flow around similar structures with different length ...
Alzheimer’s treatment roadblocks can be eased by engaging primary care providers in screenings
2024-01-30
There is substantial geographic variation across the U.S. health care system to diagnose and treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease with disease-modifying therapies, and engaging primary care providers in the effort may be a key to accelerating delivery of emerging new treatments, according to a new RAND report.
Enabling primary care practitioners to diagnose and evaluate patients for treatment eligibility would make the biggest impact on reducing wait times for specialists and increase the number of people treated with disease-modifying therapies from 2025 through 2044.
While primary care providers are technically capable of performing cognitive assessments, ...
New study identifies link between presence of oncofoetal ecosystem and liver cancer recurrence
2024-01-30
A new causal link has been found between the presence of oncofoetal ecosystems and recurrence and response to immunotherapy in primary liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
The findings will pave the way to use the presence of oncofoetal ecosystems as a biomarker to treat HCC, a disease with a poor prognosis that is typically diagnosed late
Singapore, 30 January 2024 - A team of clinician-scientists and researchers from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and global research partners, has found a causal link between the presence of oncofoetal ...
Unveiling the effect of Ti substitutions on the static oxidation behavior of (Hf,Ti)C at 2500 ℃
2024-01-30
Hf-based carbides are highly desirable candidates for thermal protection applications above 2000 ℃ due to their extremely high melting point and favorable mechanical properties. However, as a crucial indicator for composition design and performance assessment, the static oxidation behavior of Hf-based carbides at their potential service temperatures has been rarely studied.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Advanced Powder Materials, a group of researchers from Central South University and China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology revealed the static oxidation mechanism ...
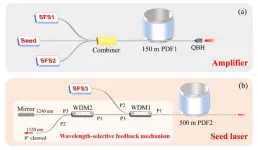
High power fiber laser at 1.2 μm waveband
2024-01-30
Laser sources operating at the 1.2 μm wavelength band have some unique applications in photodynamic therapy, biomedical diagnosis and oxygen sensing. Additionally, they can be adopted as pump sources for mid-infrared optical parametric generation as well as visible light generation by frequency doubling. Laser generation at 1.2 μm waveband has been achieved with different solid-state lasers including semiconductor laser, diamond Raman laser, and fiber laser. Among these three types, fiber laser thanks to its simple structure, good beam quality, and operation flexibility, is a great choice for 1.2 μm waveband laser generation.
Researchers ...
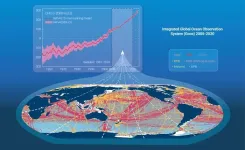
Integrated design of Global Ocean Observing System essential to monitor climate change
2024-01-30
We know that our climate is changing. Extreme weather events are becoming more common, sea levels are rising and overall, our planet is getting warmer. Monitoring these changes is critical. One of the best indicators of climate change is the Ocean Heat Content (OHC) estimate, a measurement of overall oceanic temperature calculated by gathering water temperature data in oceans around the world in differing locations, at varying depths and across time. The data necessary to calculate the OHC over such a wide-spread area is gathered by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS), an integrated network of platforms ...