(Press-News.org)
The composition of microbiota found in the gut influences how susceptible mice are to respiratory virus infections and the severity of these infections, according to researchers from the Center for Translational Antiviral Research in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University.
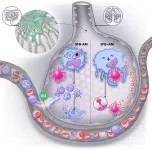
The findings, published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, report that segmented filamentous bacteria, a bacterial species found in the intestines, protected mice against influenza virus infection when these bacteria were either naturally acquired or administered.
This protection against infection also applied to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes COVID-19. To maintain this protection, the study noted that segmented filamentous bacteria required immune cells in the lungs called basally resident alveolar macrophages.
In this study, the researchers investigated how differences in specific microbial species can impact outcomes of respiratory virus infections and how they might do so, which hasn’t been well defined previously. They studied mice with discrete microbiome differences and mice differing in only the presence or absence of segmented filamentous bacteria. Viral titers in the lung were measured several days after infection and varied significantly depending on the nature of the microbiome of the different animal groups.
“These findings uncover complex interactions that mechanistically link the intestinal microbiota with the functionality of basally resident alveolar macrophages and severity of respiratory virus infection,” said Dr. Andrew Gewirtz, co-senior author of the study and Regents’ Professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.
The study found that in segmented filamentous bacteria-negative mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages were quickly depleted as respiratory virus infection progressed. However, in segmented filamentous bacteria-colonized mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages were altered to resist influenza virus infection depletion and inflammatory signaling.
The basally resident alveolar macrophages disabled influenza virus, in large part by activating a component of the immune system referred to as the complement system.
“We find it remarkable that the presence of a single common commensal bacterial species, amidst the thousands of different microbial species that inhabit the mouse gut, had such strong impacts in respiratory virus infection models and that such impacts were largely attributable to reprogramming of basally resident alveolar macrophages,” said Dr. Richard Plemper, co-senior author of the study, Regents’ Professor and director of the Center for Translational Antiviral Research at Georgia State. “If applicable to human infections, these findings will have major implications for the future risk assessment of a patient to advance to severe disease.”
“We find it highly unlikely that segmented filamentous bacteria is the only gut microbe capable of impacting the phenotype of alveolar macrophages, and consequently, proneness to respiratory virus infection,” Gewirtz said. “Rather, we hypothesize that gut microbiota composition broadly influences proneness to respiratory virus infection. Microbiota mediated programming of basally resident alveolar macrophages may not only influence the severity of acute respiratory virus infection, but may also be a long-term post-respiratory virus infection health determinant.”
The study’s primary authors were virologist Carolin M. Lieber from the Center for Translational Antiviral Research and immunologist Vu L. Ngo from the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State. Other contributing authors were Hae-ji Kang and Michal Kuczma of the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State and Kaori Sakamoto of the University of Georgia.
The study is funded by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
END
About The Study: This study found that the use of a smartphone-based mall walking program combined with physical shopping mall facilities and lottery-based digital incentive coupons may motivate people to increase their daily number of walking steps.
Authors: Masamichi Hanazato, Ph.D., of Chiba University in Chiba-shi, Chiba, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53957)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial of 1,735 patients undergoing primary bariatric surgery found that both laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass were performed with a low perioperative risk without clinically significant differences between groups.
Authors: Suzanne Hedberg, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Gothenburg in Gothenburg, Sweden is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53141)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
When it comes to having surgery, older adults don’t just base their decision on how much pain they’ll feel and how quickly they’ll recover, a new study finds.
Many also have serious concerns about how much they’ll have to pay out of their own pockets, how much work they’ll miss, and whether they’ll catch COVID-19 in the hospital or surgery center.
And a majority of those who called themselves very concerned about these issues ended up not having an operation that they had considered having, the study finds. The percentage who didn’t go through with surgery was much lower among those who said they’d been very concerned about pain or the ...
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue titled “Perioperative Blood Management” in JMIR Perioperative Medicine. The premier, peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and focuses on how technology and data science can improve care delivery and surgical patient outcomes. The new theme issue aims to explore the latest advancements, challenges, and patient-centered innovative approaches in optimizing blood-related practices before, during, and after surgical procedures.
JMIR Perioperative Medicine welcomes contributions from global researchers, clinicians, and experts in ...
A new way of creating color uses the scattering of light of specific wavelengths around tiny, almost perfectly round silicon crystals. This Kobe University development enables non-fading structural colors that do not depend on the viewing angle and can be printed. The material has a low environmental and biological impact and can be applied extremely thinly, promising significant weight improvements over conventional paints.
An object has color when light of a specific wavelength is reflected. With traditional pigments, this happens by molecules absorbing other colors from white light, but over time this interaction makes the molecules degrade and the color fades. ...
Teams led by professors Jinyang Liang and Fiorenzo Vetrone from the Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre at the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) have developed a new system for imaging nanoparticles. It consists of a high-precision, short-wave infrared imaging technique capable of capturing the photoluminescence lifetimes of rare-earth doped nanoparticles in the micro- to millisecond range.
This groundbreaking discovery, which was published in the journal Advanced Science, paves the way for promising applications, particularly in the biomedical and information security fields.
Rare-earth ...
Plastic drinking straws that get into marine ecosystems make beaches unsightly and pose problems for turtles and seabirds. So, people increasingly favor alternatives marketed as biodegradable or compostable. But do marine microorganisms break apart those straws? Researchers conducted experiments with seawater and report in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering that some commercial bioplastic or paper straws might disintegrate within eight to 20 months in coastal ocean systems and switching to ...
Washington, D.C.—Tomato juice can kill Salmonella Typhi and other bacteria that can harm people's digestive and urinary tract health, according to research published this week in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology. Salmonella Typhi is a deadly human-specific pathogen that causes typhoid fever.
“Our main goal in this study was to find out if tomato and tomato juice can kill enteric pathogens, including Salmonella Typhi, and if so, what qualities they ...
The 37th International Geological Congress (IGC 2024) in August 2024, Busan, Korea, will highlight a growing concern amid urgent threats posed by accelerated climate and environmental changes. This will prompt collaborative efforts towards ensuring the sustainability of our planet.
Abnormally high temperatures across the globe during the past year were expected to make 2023 the hottest year in Earth's history. This realization underscores the concept of climate change, which was once confined to academic desks but has since permeated into our daily existence.
Geologists now assert that the rapid climate and environmental changes necessitate ...
Excessive administration of analgesic drugs frequently results in medical accidents. To prevent the occurrence of these accidents, a drug infusion pump featuring a technology for safely detecting medication administration has been developed for the first time in the world.
The research team led by Senior Researcher Dong-kyu Lee of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seog-hyun Ryu, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, has succeeded in developing the technology for customized sensor modules capable of measuring the extremely low flow rate of analgesic drug infusion pumps as well as the existence ...