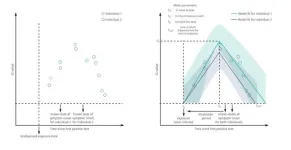
(Press-News.org) A new study co-led by Associate Professor Kristin Cleverley of the Lawrence Bloomberg Faculty of Nursing has found evidence that Psychosis Spectrum Symptoms (PSS) are often present in youth accessing mental health services.
From a profile of the initial 417 youth aged 11-24 participating in the study, 50 per cent were shown to meet the threshold for Psychosis Spectrum Symptoms, a number Cleverley says was higher than expected, meaning there is a large number of children with these symptoms accessing mental health services.
Cleverley, who is also the CAMH Chair in Mental Health Nursing Research, says that what is novel about this study is that researchers are assessing early indicators that might predict whether someone is more at risk of developing Psychosis Spectrum Disorder, and examine whether there is a point at which earlier intervention for that youth could be more effective.
“Traditionally, early psychosis care starts when there is a serious presentation of psychotic symptoms, which usually occurs in the late teen years,” says Cleverley. “The current approach to identifying children at risk of developing a psychotic disorder is only about 5 per cent effective, but with this study we can start to assess certain patterns or changes in function that can signal if an earlier intervention may be beneficial.”
Psychosis Spectrum Disorder can be extremely disabling, and is linked to cognitive impairment, long-term disability, and higher rates of death by suicide than other mental illnesses. Even without a diagnosis of psychosis, Psychosis Spectrum Symptoms can severely affect youth.
This study is one of three projects being led as part of the Toronto Adolescent and Youth (TAY) Cohort Study that is set to follow 1500 youth over the course of five years. The goal of the cohort study is to better understand the populations of youth seeking mental health treatment, how their mental health symptoms and functioning change over time, and whether early predictors of psychosis spectrum disorder can be determined.
This study was co-designed with patient and caregivers in addition to involving extensive engagement from clinicians. A novel aspect of the TAY Cohort Study is youth are given access to a patient-facing dashboard of their research results that is also integrated into their clinical record.
“We wanted to ensure that the study was embedded in the clinical program so that research assessments could be immediately utilized within clinical practice, including supporting decisions about interventions or services,” says Cleverley.
This longitudinal study will include a follow-up every six months, and will provide researchers access to information about whether symptoms in these youth become chronic or episodic, and whether these changes are related to developmental milestones or environmental stressors, or changes to mental health services.
“Our goal with this research is really to characterize this population better so that we can identify new strategies that will complement existing strategies for early identification of youth at risk of psychosis,” says Cleverley. “It also creates an important opportunity for graduate students and researchers to develop sub-studies for this sample that will enable further research to improve youth mental health outcomes.”
END
Researchers find early symptoms of psychosis spectrum disorder in youth higher than expected
New study focuses on importance of data in improving mental health supports for youth.
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pitt receives new grant to improve opioid use disorder treatment
2024-01-30
PITTSBURGH – The University of Pittsburgh School of Pharmacy’s Program Evaluation and Research Unit (PERU) has received a five-year, $7.8 million grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse to improve quality of care for patients with opioid use disorder across Pennsylvania.
The project will establish the Helping to End Addiction Long-term (HEALing) Measures Center at Pitt, which will focus on developing and implementing measurement-based care into 20 community opioid treatment programs across Pennsylvania with the goal of enhancing treatment ...
Researchers craft new way to make high-temperature superconductors – with a twist
2024-01-30
An international team that includes Rutgers University–New Brunswick scientists has developed a new method to make and manipulate a widely studied class of high-temperature superconductors.
This technique should pave the way for the creation of unusual forms of superconductivity in previously unattainable materials.
When cooled to a critical temperature, superconductors can conduct electricity without resistance or energy loss. These materials have intrigued physicists for decades because they can achieve a state of ...
Study suggests secret for getting teens to listen to unsolicited advice
2024-01-30
A new study may hold a secret for getting your teenager to listen to appreciate your unsolicited advice.
The University of California, Riverside, study, which included “emerging adults” — those in their late teens and early 20s — found teens will appreciate parents’ unsolicited advice, but only if the parent is supportive of their teens’ autonomy.
Parents support autonomy by providing clear guidelines for limitations and rules that will be enforced. They ...
Tech inefficiencies, piles of (electronic) paperwork, and increased patient volume contribute to burnout of primary care physicians, study finds
2024-01-30
Burnout is an occupational phenomenon that results from chronic workplace stress, according to the World Health Organization. Burnout often includes emotional exhaustion, negative feelings or mental distance from one’s job, and a low sense of accomplishment at work. COVID-19 increased feelings of burnout in primary care physicians, and a new study, sought to understand primary care clinicians’ perspectives on burnout during the COVID-19 pandemic, the causes of burnout, and strategies to improve clinician well-being.
Inefficiencies of electronic health records systems and high levels of documentation contribute ...
XRCC1: A potential prognostic and immunological biomarker in low-grade gliomas
2024-01-30
“We conducted a comprehensive investigation into the potential of XRCC1 as a valuable diagnostic and prognostic indicator in diverse cancer types.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 30, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “XRCC1: a potential prognostic and immunological biomarker in LGG based on systematic pan-cancer analysis.”
X-ray repair cross-complementation ...
Functional bladder tissue regenerated using bone marrow cells
2024-01-30
Scientists from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Northwestern University succeeded in regenerating fully functional urinary bladder tissue in a long-term study utilizing a non-human primate model. This unique model initially created by the Sharma Research Group explores long term bladder tissue regeneration at both anatomical and physiological levels. The Group used a novel biodegradable scaffold seeded with stem and progenitor cells from the animal’s own bone marrow, which demonstrated a higher degree of success than intestinal segments ...
Tribal program takes addiction treatment on the road
2024-01-30
With the national opioid epidemic disproportionately affecting American Indians and Alaska Natives, a tribal confederation in Oregon decided to take matters into their own hands.
The Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde not only opened Oregon’s first tribally owned opioid treatment program in Salem in 2021, but a year later, the tribe also began what is believed to be the nation’s first tribally operated mobile medication unit. The mobile bus runs a daily circuit from the tribal reservation in Grand Ronde to McMinnville to Salem, seeing patients and dispensing medications directly to tribal members struggling with an opioid use disorder.
The program appears ...
The emergence of successive SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern during 2020-22 created a need to understand the drivers of such growth
2024-01-30
The emergence of successive SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern during 2020-22 created a need to understand the drivers of such growth; this study uses a Bayesian model to reveal how a set of key covariates (the infecting variant, symptom status, age and number of prior exposures) affect viral kinetics at both individual and population levels
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002463
Article Title: Combined analyses of ...
Mutations in the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase 1 gene SOD1 can cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS) in a process that involves dissociation of the SOD1 dimer
2024-01-30
Mutations in the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase 1 gene SOD1 can cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS) in a process that involves dissociation of the SOD1 dimer; this study shows that a novel cyclic thiosulfinate cross-linker has favorable drug-like properties and can stabilize the SOD1 dimer in vivo, with therapeutic implications for fALS
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002462
Author ...
Prestigious NIH grant explores repetitive DNA sequences and cell dysfunction
2024-01-30
Dr. Jeannine Gerhardt, an assistant professor of stem cell biology in obstetrics and gynecology and in reproductive medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, has received a five-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), part of the National Institutes of Health, for the study of repetitive DNA and RNA sequences and the mechanisms by which they cause cell dysfunction and diseases.
The NIGMS Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award is intended to support recipients’ research more broadly and flexibly than standard project grants, which must specify proposed research thoroughly in advance.
“This award is particularly nice because ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
[Press-News.org] Researchers find early symptoms of psychosis spectrum disorder in youth higher than expectedNew study focuses on importance of data in improving mental health supports for youth.