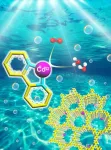
Anchoring single Co sites on bipyridine-based CTF for photocatalytic oxygen evolution
2024-01-31
(Press-News.org)
Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductors is regarded as a promising technique for producing hydrogen fuel from solar energy. The oxygen evolution half reaction has proven to be the bottleneck for photocatalytic overall water splitting owing to the high energy barrier and the sluggish kinetics. It is a big challenge to develop efficient photocatalysts for the advancement of water oxidation.
Similar to graphene carbon nitride, π-stacked covalent triazine frameworks (CTFs) have gained much attention in photocatalytic water splitting in recent years. The fully conjugated structure with the regular channels in the crystalline network will provide defined pathways for efficient charge-carrier transport and inhibit the charge-carrier recombination. The rich nitrogen content naturally results in the extraordinary heteroatomic effect (HAE), which can affect the electron distribution within the structure. Moreover, a distinct advantages of CTFs are their physicochemical properties, such as the band gap position and photoactivity, the posibility of being systematically tuned by selection of monomers, the synthesis strategies and introduction of cocatalyst.
Several strategies have been proposed to promote the photocatalytic oxygen evolution efficiency, including tuning electron-donating phenyl units, increasing crystallinity of the skeleton and exfoliating the bulk materials into ultrathin nanosheets. However, most of the efforts have been focused on the structural design of CTFs or enhancing charge carrier transfer efficiency, while cocatalysts have been largely overlooked. It should be noted that the metal-based cocatalysts easily aggregate to form nanoparticles due to their high surface energies, and only a small fraction of the atoms on the surface of this nanoparticles can be regarded as active sites, which greatly reduces the photocatalytic efficiency. Hence, inspired by the single atomic catalyst, the development of highly crystalline CTFs with the appropriate energy band structure in combination with the single sites cocatalyst is an effective approach to achieve high performance photocatalytic OER.
Recently, Professor Bien Tan, Xiaoyan Wang, and co-workers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China, proposed an effective strategy for anchoring single cobalt sites into a bipyridine-based covalent triazine framework (CTF-Bpy) to enhance photocatalytic oxygen evolution. The newly developed CTF-Bpy-Co catalyst has exhibited remarkable improvements in photocatalytic oxygen evolution performance, with an oxygen evolution rate of up to 3359 μmol g–1 h–1 in the initial 1 h and an average oxygen evolution rate of up to 1503 μmol g–1 h–1 for 5 h (λ ≥ 420 nm), exceeding most of the reported porous organic polymers. This innovative approach may offer valuable insights for achieving superior performance in photocatalytic overall water splitting without the need for sacrificial agents. The results were published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64552-8).
###
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks among the top one journals in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 16.5. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-31
Poison ivy ranks among the most medically problematic plants. Up to 50 million people worldwide suffer annually from rashes caused by contact with the plant, a climbing, woody vine native to the United States, Canada, Mexico, Bermuda, the Western Bahamas and several areas in Asia.
It’s found on farms, in woods, landscapes, fields, hiking trails and other open spaces. So, if you go to those places, you’re susceptible to irritation caused by poison ivy, which can lead to reactions that require medical attention. Worse, most people don’t know ...
2024-01-31
Eating up to three daily servings of the Korean classic, kimchi, may lower men’s overall risk of obesity, while radish kimchi is linked to a lower prevalence of midriff bulge in both sexes, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Kimchi is made by salting and fermenting vegetables with various flavourings and seasonings, such as onion, garlic, and fish sauce.
Cabbage and radish are usually the main vegetables used in kimchi, which contains few calories and is rich in dietary fibre, microbiome enhancing lactic acid bacteria, vitamins, and polyphenols.
Previously published experimental studies ...
2024-01-31
An increase in annual cardiorespiratory fitness by 3% or more is linked to a 35% lower risk of developing, although not dying from, prostate cancer, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The findings prompt the researchers to conclude that men should be encouraged to improve their level of fitness to help lower their chances of getting the disease.
There are relatively few known risk factors for prostate cancer, note the researchers. And while there’s good evidence for the beneficial effects of physical activity on ...
2024-01-31
A high quality diet at the age of 1 may curb the subsequent risk of inflammatory bowel disease, suggests a large long term study, published online in the journal Gut.
Plenty of fish and vegetables and minimal consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks at this age may be key to protection, the findings indicate.
A linked editorial suggests that it may now be time for doctors to recommend a ‘preventive’ diet for infants, given the mounting evidence indicative of biological plausibility.
Cases of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are increasing globally. Although there is no obvious ...
2024-01-31
The government in post after the election should declare a national health and care emergency, calling on all parts of society to help improve health, care, and wellbeing, say experts in the first report of The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS.
The new government should, in effect, relaunch the NHS with a renewed long term vision and plan, they argue.
"The NHS has never seemed so embattled—and its core principle of ‘free to all at the point of use’ has never been so under threat,” said Kamran ...
2024-01-31
East Hanover, NJ – January 30, 2024 – Amidst the backdrop of a remarkable four-year streak of growth, the employment indicators for people with disabilities reached unprecedented milestones in 2023. This achievement stands in stark contrast to the experiences of people without disabilities who faced a more severe decline during the COVID-19 pandemic and a slower recovery, not surpassing their pre-pandemic employment levels until 2023. That’s according to the National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) 2023 Year-End Special Edition, ...
2024-01-31
**EMBARGOED UNTIL 7:01 P.M. ET TUESDAY, JAN 30**
Evolutionary biologists at Johns Hopkins Medicine report they have combined PET scans of modern pigeons along with studies of dinosaur fossils to help answer an enduring question in biology: How did the brains of birds evolve to enable them to fly?
The answer, they say, appears to be an adaptive increase in the size of the cerebellum in some fossil vertebrates. The cerebellum is a brain region responsible for movement and motor control.
The research findings are published in the Jan. 31 issue of the Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Scientists have long thought that the cerebellum should be important ...
2024-01-30
A recent study co-authored by Dr. Matthew Segar, a third-year cardiovascular disease fellow at The Texas Heart Institute and led by his research and residency mentor, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center’s Dr. Ambarish Pandey, utilized a machine learning-based approach to identify, understand, and predict diuretic responsiveness in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF).
The study “A Phenomapping Tool and Clinical Score to Identify Low Diuretic Efficiency in Acute Decompensated ...
2024-01-30
Clear legal rules outlining the use of the sperm and eggs of those who are incapacitated must remain in place to protect the vulnerable from being involved in fertility treatment without their consent, a new study says.
There are strict laws in England and Wales involving the use of reproductive materials, but the research outlines how recent court cases have weakened this existing rigorous consent regime.
It warns this could create a common law exception to informed consent, leaving the current law in a delicate position. The research says it is “not outside the realms of possibility” that some people may try to take ...
2024-01-30
An interview with Eric J. Topol, MD, a world-renowned cardiologist, best-selling author of several books on personalized medicine, and the founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, California, has been published. in the new peer-reviewed journal, AI in Precision Oncology. Dr. Topol is an advocate for using digital technologies and artificial intelligence in health care. click here to read the interview now.
Douglas Flora, MD, Editor-in-Chief of AI in Precision Oncology, interviewed Dr. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anchoring single Co sites on bipyridine-based CTF for photocatalytic oxygen evolution