Dissipative soliton vanishes, breathing dynamics occur
2024-01-31
(Press-News.org)
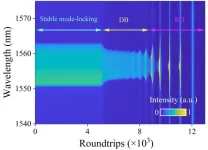
Solitons are quasiparticles that propagate along a non-dissipative wave. Put another way, they are waveforms that hold their shape as they move—like a single wave moving across the surface of a pond. They can also show the particle-like behavior, such as collision, attraction, and repulsion. Ultrafast fiber laser is an ideal platform to explore nonlinear dissipation dynamics, but also deepen the understanding of optical soliton properties. In dissipative system, dissipative soliton can be obtained due to the balance between nonlinearity and dispersion, gain and loss. In recent years, with the development of emerging time-stretch dispersive Fourier transform (TS-DFT) technique, the real-time buildup dynamics of breathing dissipative soliton have been widely observed. Since the pump power changes greatly during the extinction process, we speculate whether breathing dynamics can occur during the annihilation of solitons. At present, there is a lack of comprehensive research on the transient breathing dynamics and the impact of breathing characteristics during the extinction process.
Researchers led by Associate Prof. Yusheng Zhang at Zhejiang Normal University, China, are interested in ultrafast measurement, where the rich nonlinear dynamics of solitons can be revealed. This technique can convert the optical signals in spectral domain into the time domain, enabling the ultrafast spectral characterization. Their idea is to start with buildup of dissipative soliton. This way, by controlling the pump power, the dissipative soliton receives transient change that Q-switched instabilities occur. This discovery has the potential to significantly advance our understanding of laser dynamics, and offers novel opportunities for the development of diverse operational frameworks within the field of ultrafast laser systems. The work entitled “Transient breathing dynamics during extinction of dissipative solitons in mode-locked fiber lasers” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Jan. 19, 2024).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-31
DALLAS, Jan. 30, 2024 — A new survey conducted by the American Heart Association, which is marking one hundred years of service saving lives, suggests that increased visibility of the need for CPR has had a positive impact on someone’s willingness to respond if they are bystanders in a cardiac emergency. However, there remains a significant gap in awareness that emphasizes the urgent need for collaboration between governments, communities, businesses and the media to promote and provide lifesaving training. To help close this gap, the ...
2024-01-31
In agroecosystems where manure is applied as organic fertilizer, these antibiotic residues exert strong selective pressure on soil microbial communities. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) from animal manure would increase the concentration of ARB in soils. The influencing mechanisms of soil types on the distribution of ARB were worthy of further exploration. This study demonstrates that CTC-manure induced more resistance of soil indigenous microbes in fluvo-aquic soil, Lactobacillus, Dyella, Ralstonia, and Bacillus ...
2024-01-31
A first of its kind study of the 2019-2020 ‘Black Summer’ bushfires in Australia has revealed that the tourism industry nationwide took an immediate hit of $2.8 billion in total output to its broader supply chains and almost 7300 jobs disappeared nationwide.
The fires four years ago triggered widespread tourism shutdowns in many parts of the country in the lead up to the peak Christmas and New Year season, resulting in $1.7 billion direct losses to the tourism industry, which triggered the larger drop in supply chain output.
“These results are an illustration of what can be expected in the future not only in Australia, but in other ...
2024-01-31
When researchers want to study how COVID makes us sick, or what diseases such as Alzheimer's do to the body, one approach is to look at what's happening inside individual cells.
Researchers sometimes grow the cells in a 3D scaffold called a "hydrogel." This network of proteins or molecules mimics the environment the cells would live in inside the body.
New research led by the University of Washington demonstrates a new class of hydrogels that can form not just outside cells, but also inside of them. The team created these hydrogels from protein building blocks designed using a computer to form a specific structure. These hydrogels exhibited similar mechanical properties ...
2024-01-31
A study study published today reports that BIPOC individuals who were infected with COVID-19 experienced greater negative aftereffects in health and work loss than did similarly infected white participants.
Despite similar symptom prevalence, Hispanic participants compared to non-Hispanic participants and BIPOC participants compared to white participants had more negative impacts following a COVID-19 infection in terms of health status, activity level and missed work, the authors wrote.
The findings appeared in the journal Frontiers ...
2024-01-31
Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductors is regarded as a promising technique for producing hydrogen fuel from solar energy. The oxygen evolution half reaction has proven to be the bottleneck for photocatalytic overall water splitting owing to the high energy barrier and the sluggish kinetics. It is a big challenge to develop efficient photocatalysts for the advancement of water oxidation.
Similar to graphene carbon nitride, π-stacked covalent triazine frameworks (CTFs) have gained much attention in photocatalytic water splitting in recent years. The fully conjugated structure with the regular channels in the crystalline network will provide defined pathways for ...
2024-01-31
Poison ivy ranks among the most medically problematic plants. Up to 50 million people worldwide suffer annually from rashes caused by contact with the plant, a climbing, woody vine native to the United States, Canada, Mexico, Bermuda, the Western Bahamas and several areas in Asia.
It’s found on farms, in woods, landscapes, fields, hiking trails and other open spaces. So, if you go to those places, you’re susceptible to irritation caused by poison ivy, which can lead to reactions that require medical attention. Worse, most people don’t know ...
2024-01-31
Eating up to three daily servings of the Korean classic, kimchi, may lower men’s overall risk of obesity, while radish kimchi is linked to a lower prevalence of midriff bulge in both sexes, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Kimchi is made by salting and fermenting vegetables with various flavourings and seasonings, such as onion, garlic, and fish sauce.
Cabbage and radish are usually the main vegetables used in kimchi, which contains few calories and is rich in dietary fibre, microbiome enhancing lactic acid bacteria, vitamins, and polyphenols.
Previously published experimental studies ...
2024-01-31
An increase in annual cardiorespiratory fitness by 3% or more is linked to a 35% lower risk of developing, although not dying from, prostate cancer, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The findings prompt the researchers to conclude that men should be encouraged to improve their level of fitness to help lower their chances of getting the disease.
There are relatively few known risk factors for prostate cancer, note the researchers. And while there’s good evidence for the beneficial effects of physical activity on ...
2024-01-31
A high quality diet at the age of 1 may curb the subsequent risk of inflammatory bowel disease, suggests a large long term study, published online in the journal Gut.
Plenty of fish and vegetables and minimal consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks at this age may be key to protection, the findings indicate.
A linked editorial suggests that it may now be time for doctors to recommend a ‘preventive’ diet for infants, given the mounting evidence indicative of biological plausibility.
Cases of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are increasing globally. Although there is no obvious ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dissipative soliton vanishes, breathing dynamics occur