(Press-News.org) In a rare but serious complication of cancer, the body’s own immune system can start attacking the brain, causing rapid-onset memory loss and cognitive deficits. What triggers this sudden biological civil war was largely unknown.
Now, researchers at University of Utah Health have found that some tumors can release a protein that looks like a virus, kickstarting an out-of-control immune reaction that may damage brain cells.
Their findings published in Cell on Jan. 31, 2024.
A rapid immune attack
Jason Shepherd, Ph.D., associate professor of neurobiology at University of Utah Health and last author on the study, explains that the swift escalation of symptoms—which can include memory and behavioral changes, loss of coordination, and even seizures—is a hallmark of the disease, called anti-Ma2 paraneoplastic neurological syndrome. The disease is one of a group of cancer-related neurological syndromes that occur in less than one in 10,000 people with cancer. The precise symptoms of these diseases vary, but all involve rapid immune reactions against the nervous system. “The symptoms come in quickly and can be quite debilitating,” Shepherd says.
“This fascinating research illustrates how tumor cells can manipulate their environment,” says Neli Ulrich, Ph.D., executive director of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah and a Jon M. and Karen Huntsman Presidential Professor in Cancer Research at the U. “We hope that this innovative transdisciplinary research will positively impact both the lives of cancer patients and of those who experience neurological symptoms.”
Stacey L. Clardy, M.D., Ph.D., a neurologist at U of U Health and a coauthor on the study, adds, “Most patients begin to experience these unusual neurologic symptoms before they even know they have a cancer.”
These rapid-onset symptoms are the result of the immune system suddenly starting to target specific proteins that are found in the brain. Scientists knew that this flare of immunity often targets a protein called PNMA2. But nobody knew why PNMA2 provokes such a strong immune response, which left researchers at a loss for ways to prevent it. “We do not understand what is happening at the cellular or molecular level to actually cause the syndrome,” Clardy says, “and understanding the mechanism of disease is crucial to developing better treatments.”
A virus lookalike
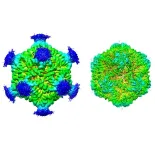
To figure out how PNMA2 kickstarts an immune reaction, Junjie Xu, a graduate researcher in neurobiology at U of U Health and the lead author on the study, examined the protein’s structure using advanced microscopy. When he saw the first clear image of the protein, he was “so, so excited,” Xu says. Multiple PNMA2 proteins had spontaneously self-organized into 12-sided complexes that bore a striking resemblance to the geometric protein shells of some viruses.
One of the immune system’s healthy functions is to attack viruses, and PNMA2’s virus-like structure makes it particularly prone to being targeted as well, the researchers found. In fact, in experiments in mice, the immune system only attacked PNMA2 protein when it was assembled into virus-like complexes.
Wrong place, wrong time
The location of PNMA2 in the body is also a crucial piece of the puzzle, the scientists found. “This protein normally is only expressed in the brain, in neurons,” Xu says, “but some cancer cells can express it, which can trigger an immune response.”
As long as PNMA2 stays in the brain, the immune system won’t react to it. But rarely, a tumor elsewhere in the body will start producing PNMA2 protein. And when the immune system detects PNMA2 protein outside the brain, it reacts like it would to any foreign invader. The immune system makes antibodies that bind to the unfamiliar substance, and those antibodies direct immune cells to attack.
But, once activated, the immune system doesn’t just attack the PNMA2 produced by the cancer. It also targets the parts of the brain that produce PNMA2 normally, including regions involved in memory, learning, and movement. The brain normally has a degree of protection from the immune system, but cancer weakens that barrier, leaving the brain especially vulnerable to this immune onslaught.
In future work, the researchers aim to figure out which aspect of the immune response leads to patients’ rapid cognitive decline—the antibodies themselves, immune cells making their way into the brain, or some combination of the two.
Understanding how the immune system causes neurological symptoms may help scientists design targeted treatments, Shepherd says. “If we show that PNMA2 antibodies are the culprit that really drives the neurological symptoms, you could devise a way to block those antibodies from getting into the brain or mop them up with something as a treatment… If you can alleviate some of those neurological symptoms, it really would be huge.”
END
Brain protein’s virus-like structure may help explain cancer-induced memory loss
2024-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds brain mechanism for physical exercise improving mood
2024-01-31
"Only exercise can remove all kinds of doubts," Goethe said. Physical exercise is the lubricant between the body and the mind. Alleviation of anxiety by motor activity forms an integral part of our daily life; whether going for a walk to refresh our mind or running excessively in the park to recuperate from a stressful event, we are all well aware of the beneficial impact. In fact, the plain view that exercise can prevent anxiety and depression has been supported by accumulating prospective cohort studies in recent years. Yet, apart from some general interactions between the periphery of our body and our ...
Symbiotic autonomous robot ecosystem enhances safety and efficiency on nuclear facilities decommissioning
2024-01-31
Nuclear facilities, particularly during decommissioning, face significant challenges due to hazardous materials and environments. Traditional methods often rely heavily on human intervention, posing risks and inefficiencies. A groundbreaking research introduces a symbiotic autonomous robot ecosystem, designed to transform nuclear facility decommissioning. This innovative approach leverages a Cyber-Physical System (CPS) coordinated through a digital twin interface, significantly enhancing safety, efficiency, and operational awareness ...
Alleviate the drought in the east Hungarian plains
2024-01-31
Intensive agricultural cultivation and the resulting changes in soil structure cause low humidity in the near-surface air during heat waves in really dry years. As a result, summer cold fronts roar across the Plain without the usual thunderstorms and precipitation, researchers at the Institute of Geography and Earth Sciences at Eötvös Loránd University explain in a review of articles on topics ranging from geodynamics to soil science to meteorology what made the summer of 2022 so severe in the eastern part of the country.
In 2022, the 7-week period starting in mid-June was disastrous for eastern Hungary. Almost no rain fell for weeks, and in the eastern part of the country, ...
Researchers overview recent progress and challenges in silicon-based anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
2024-01-31
Research in recent years displays that several chemical modifications (binders, composite materials, and electrolytes) provide superior stability and enhance electrochemical performance in Si-based anodes in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Thus far, several different chemical interactions on structural alterations to Si-based anode materials have been tried to enhance Li+ kinetics, structural stability, and volume development control throughout the delithiation/lithiation process.
Despite significant advancements, Si and Si-based electrodes are still in their infancy and are still far from finding widespread practical use. Si-based anodes face some difficulties, including substantial ...
News on drug-induced skin swelling
2024-01-31
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors - ACE inhibitors for short - are effective antihypertensive drugs. They block the formation of the hormone angiotensin II, which plays a central role in the development of high blood pressure. On the other hand, these drugs increase the concentration of the vasoactive signaling substance bradykinin. Among other things, this can lead to acute swelling of the skin or mucous membranes. In general, such swellings are not life-threatening. However, if they affect the tongue, throat or larynx, angioedema can be life-threatening for the patient due to the potential risk of suffocation. Research to date suggests that susceptibility to such drug-induced angioedema ...
Innovation on the design, construction, and experiments of OMEGA-based SSPS prototype: The Sun-Chasing Project
2024-01-31
Space solar power satellite (SSPS) is a tremendous energy system that collects and converts solar power to electric power in space, and then transmits the electric power to earth, spacecraft, or moving targets via microwave. It is regarded as one of the most potential ways to solve the problem of energy crisis.
In 2022, a team of researchers from Xidian University in China has completed a full-link and full-system ground demonstration and verification system for an SSPS, named the Sun-Chasing Project. Their study, recently published in Engineering, introduces the design concept of OMEGA 2.0 SSPS, the related key technologies, and the development of ground demonstration ...
SCAI publishes expert consensus statement on management of calcified coronary lesions requiring intervention
2024-01-31
WASHINGTON—Coronary artery calcification is increasing in prevalence, leading to greater risks both during procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and adverse events in the short and long term. Along with these challenges, treatment options are expanding, increasingly including calcium modification prior to stent implantation. A newly published SCAI Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Calcified Coronary Lesions outlines methods for interventional cardiologists to identify various types of calcified coronary lesions ...
Firing nerve fibers in the brain are supplied with energy on demand
2024-01-31
Brain function depends on the swift movement of electrical signals along axons, the long extensions of nerve cells that connect billions of brain cells. The nerve fibers are insulated by a fatty layer called myelin, which is produced by specialized cells called oligodendrocytes. These cells wrap around and insulate nerve fibers ensuring the rapid and efficient transmission of signals that is essential for brain function.
Oligodendrocytes sense and respond to the electrical signals
Now, a team of neuroscientists led by Aiman Saab at the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University ...
Engineering viruses to kill deadly pathogens
2024-01-31
Northwestern University researchers have successfully coaxed a deadly pathogen to destroy itself from the inside out.
In the new study, researchers modified DNA from a bacteriophage or “phage,” a type of virus that infects and replicates inside of bacteria. Then, the research team put the DNA inside Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), a deadly bacterium that is also highly resistant to antibiotics. Once inside the bacterium, the DNA bypassed the pathogen’s defense mechanisms ...
NIH study shows higher mortality rates for patients on respiratory support in rural intermediate care units
2024-01-31
NIH study shows higher mortality rates for patients on respiratory support in rural intermediate care units
Findings highlight the importance of providing ICU-level care to rural patients with respiratory failure
A new National Institutes of Health-supported study finds that patients receiving ventilator life support in the intermediate care units – a potentially less costly alternative for people not sick enough for the intensive care units (ICUs) but too ill for the general ward – of rural hospitals had significantly higher death rates than patients in the same type of ...