(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Auckland are running a trial of castor oil as a potential safe and natural treatment for dry-eye disease following a successful pilot study.
While exact figures aren’t available for New Zealand, in Australia, it is estimated dry-eye disease affects around 58 percent of the population aged over 50.
Advancing age, menopause, increased screen time, contact lens wear are just some of the risk factors for developing dry eye disease.
Blepharitis is the most common cause of dry-eye disease, accounting for more than 80 percent of cases. It is a chronic condition with no known cure.
“Currently, patients are left grappling with symptoms of dryness, grittiness and, in some cases, watery eyes that feel uncomfortable impacting on their quality of life and work productivity,” says doctoral candidate and lead clinical investigator Catherine Jennings.
Current treatments, such as antibacterials and anti-inflammatories, are generally unsuitable for long-term use, due to significant side-effects and potential for antimicrobial resistance.
“Often patients are left feeling helpless when attempting to manage a chronic condition,” Jennings says.
The current trial is of a product containing cold-pressed castor oil enhanced with mānuka and kanuka oils applied using a rollerball attached to a small glass bottle.
“The previous pilot study, conducted by our research team, was unique in its use of castor oil in such an application on the eyelids, with the product not known to be used anywhere else in the world for treating blepharitis,” says Jennings.
Castor oil comes from a flowering tropical or subtropical shrub from the species Riccinus communis. It has been used therapeutically for millenia, including more recently in eye cosmetics and eye makeup removers.
In the pilot study, 26 patients with blepharitis were treated with cold-pressed castor oil over four weeks. They had measurable improvements in symptoms, such as reduced redness of the lid margin, decreased thickening of the eyelid, and a decline in bacterial profusion, as well as reduced eyelash crusting.
Building on the success of the pilot study, the research team is now engaged in the more extensive double-blinded, randomised and placebo-controlled study. They are aiming to recruit 92 participants and generate robust scientific evidence for clinicians.
The ultimate goal is to sustainably improve quality of life for this large group of patients using a natural, safe and effective product, principal investigator Professor Jennifer Craig says.
“Castor oil has been proposed as a natural product that could offer a safe, effective and easy-to-use alternative to existing therapies,” Craig says.
“My hope is this study will produce evidence-based guidance for clinicians with regard to offering castor oil as a possible management option for patients suffering from blepharitis, so they continue to enjoy a great quality of life, read the books they love, be productive in their work environment and enjoy other visual hobbies.”
END
Natural therapy shows promise for dry-eye disease
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers study role of post-transcriptional splicing in plant response to light
2024-02-02
In a study recently published in the PNAS on Jan. 30, a research team led by Prof. CAO Xiaofeng from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Southern University of Science and Technology, reported a new understanding of how light affects plant growth.
Light plays a central role in plant growth and development, providing an energy source and governing various aspects of plant morphology. Post-transcriptional splicing (PTS) has been previously discovered to generate polyadenylated full-length transcripts. These transcripts, ...
Gene-editing offers hope for people with hereditary disorder
2024-02-02
A group of patients with a hereditary disorder have had their lives transformed by a single treatment of a breakthrough gene-editing therapy, according to the lead researcher.
The patients from New Zealand, the Netherlands and the UK have hereditary angioedema, a genetic disorder characterised by severe, painful and unpredictable swelling attacks. These interfere with daily life and can affect airways and prove fatal.
Now researchers from the University of Auckland, Amsterdam University Medical Center and Cambridge University Hospitals have successfully treated more than ten patients with the CRISPR/Cas9 therapy, ...
New molecule from University step closer to treatment for rare disease
2024-02-02
A molecule created at the University of Auckland is one step closer to becoming a treatment for an extremely rare and severely debilitating neurological disorder called Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Children with the disorder showed significant improvements in a phase two clinical trial in the US, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, which is listed on the Australian Securities Exchange, said in December.
Next steps would be a phase three trial and seeking approval from the US Food & Drug Administration. The molecule, NNZ-2591, comes from work years ago ...
Machine learning to battle COVID-19 bacterial co-infection
2024-02-02
University of Queensland researchers have used machine learning to help predict the risk of secondary bacterial infections in hospitalised COVID-19 patients.
The machine learning technique can help detect whether antibiotic use is critical for patients with these infections.
Associate Professor Kirsty Short from the School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences said secondary bacterial infections can be extremely dangerous for those hospitalised with COVID-19.
“Estimates of the incidents of secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19 ...
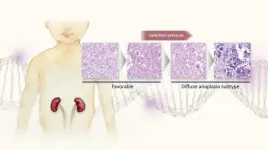
Some tumors ‘grow bad’: Why a dangerous subtype of Wilms tumor is so resistant to chemotherapy
2024-02-02
An international team, led by researchers at Nagoya University in Japan, may have determined why the diffuse anaplasia (DA) subtype of Wilms tumor (WT) resists chemotherapy. This subtype grows even when it has a high burden of DNA damage and increases the mutation rate of tumor protein 53 (TP53), a gene that plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and division. The team’s findings, published in Modern Pathology, suggest new ways to treat this subtype.
WT, also known as nephroblastoma, is the most common childhood cancer originating in the kidney. Fortunately, the survival rate of adolescents ...
Disrupted cellular function behind type 2 diabetes in obesity
2024-02-02
Disrupted function of “cleaning cells” in the body may help to explain why some people with obesity develop type 2 diabetes, while others do not. A study from the University of Gothenburg describes this newly discovered mechanism.
It is well known that obesity increases the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. It is also well known that some people who gain weight suffer from the disease and others do not. The reasons for these differences are not clear, but they are related ...
USC launches School of Advanced Computing
2024-02-02
USC President Carol Folt launched the university’s first new school in more than a decade: the USC School of Advanced Computing, a cornerstone of her $1 billion advanced computing initiative. The school seeks to educate all students, regardless of their major, in the ethical use of computing technology as part of the president’s Frontiers of Computing initiative.
Gaurav Sukhatme — a professor of computer science and electrical and computer engineering, and executive vice dean of the USC Viterbi School of ...
A clutch stretch goes a long way
2024-02-02
Kyoto, Japan -- Cell biology has possibly never jumped to the next level in the same way.
In multicellular organisms, cell migration and mechanosensing are essential for cellular development and maintenance. These processes rely on talin, the key focal adhesion -- or FA -- protein, central in connecting adjacent cellular matrices and enabling force transmission between them.
Talins are commonly considered fully extended at FAs between actin filaments -- or F-actin -- and the anchor-like integrin receptor.
Yet, a research ...
Psychological care delivered over the phone is an effective way to combat loneliness and depression, according to a major new study
2024-02-02
The study, led by a team based at the University of York and Hull York Medical School and at Tees, Esk and Wear Valleys NHS Foundation Trust, found levels of depression reduced significantly and the benefits were greater than those seen for antidepressants.
Participants in the study reported their levels of emotional loneliness fell by 21% over a three-month period and the benefits remained after the phone calls had ceased, suggesting an enduring impact.
The Behavioural Activation in Social ...
Insulin prices in US are more than twice as high as in other wealthy nations
2024-02-02
The gross price of insulin in the U.S. is more than nine times higher than in 33 high-income comparison nations, according to a new RAND report.
Although the cost differences of insulin between the U.S. and other nations varied depending on the comparison country and the type of insulin, U.S. prices were always higher -- often five to 10 times higher -- than those in other countries. The new report updates findings from earlier RAND work about U.S. insulin prices.
After accounting for rebates and other discounts often offered by drug ...