(Press-News.org) Embargoed until 11am ET USA/4pm GMT UK on Friday 2 February (Current Biology embargo)
-With pictures-
Fruit flies have provided scientists with new insight into the genetic basis for the rapid evolution of male external genitalia driven by sexual selection.
Secondary sexual characteristics such as peacocks’ tails and the male external genitalia of insects are known to be among the fastest evolving animal body parts.
It is thought that this is driven by sexual selection including through female choice and the different evolutionary needs of each sex to find the right mate and maximise their fitness.
Now scientists at Durham University and Oxford Brookes University, UK, have found one of the genes that contributes to genital evolution between two closely related species of fruit fly.
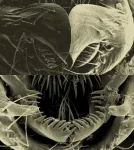
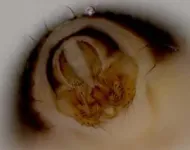
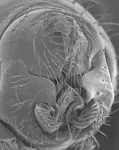
The researchers looked at the posterior lobes of the male genitalia of Drosophila simulans and Drosophila mauritiana. Both are species of the Drosophila melanogaster subgroup of fruit flies.
These lobes have rapidly changed in shape and size in less than 240,000 years and those of Drosophila simulans are much bigger than those of Drosophila mauritiana.
They found that evolved higher levels of the gene Sox21b repressed the size of the genital lobes in Drosophila mauritiana, contributing to them having smaller genital lobes than Drosophila simulans.
As the posterior lobes are used by the male to grasp female flies during sex, the researchers say their findings could now help to better understand the effect sexual selection has on the genome to drive changes in genitalia shape and size.
The study is published in the journal Current Biology.
Sexual selection has been shown to drive evolutionary change in the genitalia of other insects and animals, but this is a rare case where a gene behind it has been identified.
The research team edited the genome of Drosophila mauritiana and Drosophila simulans to show that changes in Sox21b changed the posterior lobe shape and size. This also affected the mating duration of these flies.
Project lead Professor Alistair McGregor, in the Department of Biosciences, Durham University, said: “The genital posterior lobes of male fruit flies play a really important role in sex.
“Identifying genes responsible for differences in size and shape of genital structures between species allows manipulation of Drosophila male genitalia in a way that replicates the variation that exists in nature.
“We can now do more detailed behaviour experiments to determine if this variation is the target of female choice, if it gives males different ability to secure mating, as an increase mating duration seems to suggest, or if this is driven by the conflicting interests of males and females.”
Research co-author Dr Daniela Santos Nunes, of the Department of Biological and Medical Sciences, at Oxford Brookes University, said: “Although Drosophila simulans and Drosophila mauritiana can mate with each other, this happens very rarely and indeed D mauritiana females are much choosier than D simulans females.
“Therefore, identifying their own species by genital size, could be one way that these particular species ensure they are mating more efficiently and are therefore reinforcing the divergence of their species.
“This reveals part of the genetic basis of how male genital evolution has been driven over thousands of years due to sexual selection.”
The research was funded by UKRI’s Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council and Natural Environment Research Council.
ENDS
END
Fruit flies give further insight into evolution of male genitalia driven by sexual selection
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Availability of mental telehealth services in the US
2024-02-02
About The Study: The findings of this study of 1,404 mental health treatment facilities indicate that there were no differences in the availability of mental telehealth services based on the prospective patient’s clinical condition, perceived race or ethnicity, or sex; however, differences were found at the facility-, county-, and state-level. These findings suggest widespread disparities in who has access to which telehealth services throughout the U.S.
Authors: Jonathan Cantor, Ph.D., of the RAND Corporation in Santa Monica, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Risk of venous thromboembolic events after surgery for cancer
2024-02-02
About The Study: This study including 432,000 patients who underwent major surgery for eight cancer types found an increased rate of venous thromboembolism associated with cancer surgery. The risk persisted for about two to four months postoperatively but varied between cancer types. The increased rate is likely explained by the underlying cancer disease and adjuvant treatments. The results highlight the need for individualized venous thromboembolism risk evaluation and prophylaxis regimens for patients undergoing different surgery for different cancers.
Authors: Johan ...
Geographic differences in telehealth found among mental health clinics
2024-02-02
Telehealth availability for mental health care varies significantly across states -- from less than half of treatment facilities contacted in states like Mississippi and South Carolina to every facility contacted in states like Maine and Oregon, according to a new RAND study.
Researchers found there were differences in services offered depending on whether a mental health treatment facility was located in in a rural or metropolitan area.
The types of services offered -- and the types of telehealth modalities available -- also varied widely among ...
Changes in health care access and preventive health screenings by race and ethnicity
2024-02-02
About The Study: The results of this study of 89,000 adults suggest that wellness visits and preventive health screenings in the U.S. have not returned to pre-pandemic levels. Screening rates for blood pressure, cholesterol, blood glucose, and common cancers were lower in 2021 versus 2019, and varied across racial and ethnic groups, with Asian adults experiencing the most pronounced declines. These findings support the need for public health efforts to increase the use of preventive health screenings among eligible adults.
Authors: Rishi K. Wadhera, ...
New therapeutic strategy for metastatic prostate cancer patients resistant to standard treatment
2024-02-02
A team of researchers from the Badalona Applied Research Group in Oncology (B·ARGO) and the Urologic Tumours Unit of the Institut Català d'Oncologia (ICO) and the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP) have found a new therapeutic strategy for patients with a specific subtype of metastatic prostate cancer resistant to standard chemotherapy treatment with docetaxel.
In this study, published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology, they propose a new treatment based on a combination of kinase inhibitors in patients who inevitably stop responding to docetaxel. The team found that resistance to this drug is associated with the hyperactivation ...
Audiogene, the first clinical trial in France for a gene therapy to treat hearing loss in children
2024-02-02
The aim of this clinical trial, which has just received approval in France, is to assess the safety and efficacy of a new gene therapy drug in children aged between 6 and 31 months with profound hearing loss. Audiogene was developed by a French consortium composed of teams from the Hearing Institute, an Institut Pasteur research center; the ENT Department and Pediatric Audiology Research Center at Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital (AP-HP); Sensorion and Fondation Pour l'Audition. The trial has also been submitted to other European countries and is currently undergoing assessment.
Audiogene is the first clinical trial in France to test a gene therapy drug, SENS-501, ...
Vaccine targeting KRAS in pancreatic and colorectal cancer shows promise
2024-02-02
A new vaccine shows encouraging early results as a potential off-the-shelf treatment for certain patients with pancreatic or colorectal cancer, according to a study co-led by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). The vaccine targets tumors with mutations (or changes) in the KRAS gene, a driving force in many cancers.
This cancer vaccine is different from another type of pancreatic cancer vaccine, which is custom-made for each patient using messenger RNA (mRNA). Both are therapeutic vaccines given after surgery ...
A physical qubit with built-in error correction
2024-02-02
There has been significant progress in the field of quantum computing. Big global players, such as Google and IBM, are already offering cloud-based quantum computing services. However, quantum computers cannot yet help with problems that occur when standard computers reach the limits of their capacities because the availability of qubits or quantum bits, i.e., the basic units of quantum information, is still insufficient. One of the reasons for this is that bare qubits are not of immediate use for running a quantum algorithm. While the binary bits of customary computers store information in the form of fixed values of either 0 or 1, qubits can represent 0 and ...
Biodegradable sensor monitors levels of pesticides via direct contact with surface of fruit and vegetables
2024-02-02
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) and the Federal University of Viçosa (UFV) in Brazil have developed a sustainable sensor that can be placed directly on the surface of a vegetable or fruit to detect the presence of pesticides. Known for this reason as “plant-wearable”, it is made of cellulose acetate, a material derived from wood pulp.
The device has the potential to help assure food safety in a world that increasingly suffers from a shortage of food and the environmental and health problems caused ...
Paper: Multistate foodborne illness outbreaks impact restaurant stock price, public perception
2024-02-02
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — As demand for food from restaurants soars in the U.S., so does the importance in understanding the impacts of foodborne illness outbreaks. A new paper co-written by a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign expert in food marketing and food policy finds that outbreaks spanning multiple states bring swift financial losses, increased media attention and a public-relations hit that makes smaller outbreaks more financially damaging.
In the U.S., more than 60% of foodborne illness outbreaks occur at restaurants, and the vast majority of those outbreaks are confined ...