(Press-News.org) With a $300,000 grant, the Welch Foundation is supporting University of Texas at Arlington research into why some types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the bacteria that causes the lung disease tuberculosis (TB), do not respond to treatments.
Since its founding in 1954, the Houston-based Welch Foundation has contributed to the advancement of chemistry through research grants, departmental programs, endowed chairs and other special projects in Texas.
“As one of the nation’s largest private funding sources for chemical research, it is our job to ensure we support the field in a way that advances the field while changing lives,” said Adam Kuspa, president of the foundation. “TB has an enormous impact on society, and I look forward to seeing how Dr. Kayunta Johnson-Winters’ research can help advance our understanding of this dreaded disease.”
Johnson-Winters, associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UTA, is leading the project.
“I’m honored that the Welch Foundation sees the value in supporting our research. TB is a global pandemic that is killing about 1.5 million people per year,” Johnson-Winters said. “An estimated 1.8 billion people—about a quarter of the world’s population—are infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Of those carrying the bacterium, about 10% will become ill with the disease, enabling them to infect others.”
Since TB is caused by a bacterium, it can be treated with antibiotics. Infected individuals must take a combination of antibiotics diligently over six to 12 months to stamp out the infection. Patients who stop taking their medications mid-treatment are more likely to see their infection return, only this time, the infection does not respond to treatments.
This new drug-resistant TB can lead to a new infection in the original patient, who can then spread the disease-resistant TB to other people. Drug-resistant TB is much more difficult to treat, often requiring a regimen of a least five medications over 15 to 24 months.
With this new award, Johnson-Winters will study the enzymes within Mtb to understand why they act differently to certain interventions. The grant will also provide resources for additional purification equipment, columns and chemicals needed to further the research. The funds will also support specialized software that will allow researchers to get a better understanding of what is occurring within the enzymes.
“Once we’ve performed our experiments, we will also prepare a library of the mutations to better understand the mechanism of specific enzymes that are targeted for treatment for those hard-to-treat TB disease cases,” Johnson-Winters said.
END
Welch Foundation supports Johnson-Winters' TB research
Grant helps UTA advance understanding of deadly disease
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
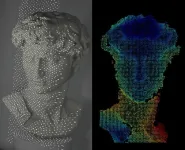
A sleeker facial recognition technology tested on Michelangelo’s David
2024-02-02
Many people are familiar with facial recognition systems that unlock smartphones and game systems or allow access to our bank accounts online. But the current technology can require boxy projectors and lenses. Now, researchers report in ACS’ Nano Letters a sleeker 3D surface imaging system with flatter, simplified optics. In proof-of-concept demonstrations, the new system recognized the face of Michelangelo’s David just as well as an existing smartphone system.
3D surface imaging is a common tool used in smartphone facial recognition, as well as in computer vision and autonomous driving. These systems typically consist of a dot projector that contains multiple components: ...
Plant groupings in drylands support ecosystem resilience
2024-02-02
Many complex systems, from microbial communities to mussel beds to drylands, display striking self-organized clusters. According to theoretical models, these groupings play an important role in how an ecosystem works and its ability to respond to environmental changes. A new paper in PNAS focused on the spatial patterns found in drylands offers important empirical evidence validating the models.
Drylands make up 40 percent of the Earth’s landmass and are places where water is the limiting resource for life. They often display a characteristic ...
Scientists see an ultra-fast movement on surface of HIV virus
2024-02-02
DURHAM, N.C. – As the HIV virus glides up outside a human cell to dock and possibly inject its deadly cargo of genetic code, there’s a spectacularly brief moment in which a tiny piece of its surface snaps open to begin the process of infection.
Seeing that structure snap open and shut in mere millionths of a second is giving Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI) investigators a new handle on the surface of the virus that could lead to broadly neutralizing antibodies for an AIDS vaccine. Their findings appear Feb. 2 in Science Advances.
Being able to attach an antibody specifically to ...
Gene editing precisely repairs immune cells
2024-02-02
Some hereditary genetic defects cause an exaggerated immune response that can be fatal. Using the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool, such defects can be corrected, thus normalizing the immune response, as researchers led by Klaus Rajewsky from the Max Delbrück Center now report in “Science Immunology.”
Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) is a rare disease of the immune system that usually occurs in infants and young children under the age of 18 months. The condition is severe and has a high mortality rate. It is caused by various gene mutations that prevent cytotoxic T cells from functioning normally. These ...
COPD: The effect of low-dose cadmium, a highly toxic metal, on airway epithelial cells
2024-02-02
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Cigarette smoke exposure is associated with the development and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, which is the third leading cause of death worldwide.
Cigarette smoke contains 2 to 3 micrograms of cadmium, a highly toxic metal and environmental pollutant, per cigarette. Burning tobacco releases cadmium oxide that can be adsorbed onto microparticles in smoke that travel deep into the lungs. Furthermore, the body is not able to remove cadmium, which accumulates in longtime smokers.
In ...
Regulation makes crypto markets more efficient
2024-02-02
First-of-its-kind research on cryptocurrency finds that the most regulated coins create the most efficient markets.
That crypto regulation, often provided by cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance, can also help protect investors by providing reliable, public information.
“Both small and institutional investors should know, if they invest in coins without any regulation, they may suffer from price manipulation or a severe lack of insider information,” said Liangfei Qiu, a University of Florida professor of business and one of the authors of the new study.
“Instead, they may want to invest in coins listed with platforms ...
Centuries-old texts penned by early astronomers Copernicus and Sacrobosco find new home at RIT
2024-02-02
The ancient astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus was the first scientist to document the theory that the sun is the center of the universe in his book, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres). That first edition book, along with a delicate manuscript from astronomer Johannes de Sacrobosco, that is contrary to Copernicus’ groundbreaking theory, has now found a permanent home at Rochester Institute of Technology.
The texts were donated to RIT’s Cary Graphic Arts Collection, one of the world’s premier libraries on graphic communication history and practices. The donor is Irene ...
Mechanism discovered that protects tissue after faulty gene expression
2024-02-02
The genetic material, in the form of DNA, contains the information that is crucial for the correct functioning of every human and animal cell. From this information repository, RNA, an intermediate between DNA and protein, the functional unit of the cell, is generated. During this process, the genetic information must be tailored for specific cell functions. Information that is not needed (introns) is cut out of the RNA and the important components for proteins (exons) are preserved. A team of researchers led by Professor Dr Mirka Uhlirova at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of ...
Proteins suggest a path to reduce drug resistance in a form of cancer
2024-02-02
RICHLAND, Wash.—Doctors have nearly a dozen new targeted drugs to treat patients with acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, yet three of four patients still die within five years. Some patients succumb within just a month or two, despite the battery of drugs used to treat the aggressive blood disease, where blood cells don’t develop properly.
A new study draws on a field of science known as proteogenomics to try to improve the outlook. In a paper published Jan. 16 in Cell Reports Medicine, scientists report new ...
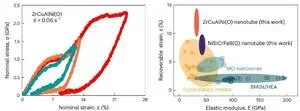
Unveiling Oxidation-induced Super-elasticity in Metallic Glass Nanotubes
2024-02-02
Oxidation can degrade the properties and functionality of metals. However, a research team co-led by scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently found that severely oxidized metallic glass nanotubes can attain an ultrahigh recoverable elastic strain, outperforming most conventional super-elastic metals. They also discovered the physical mechanisms underpinning this super-elasticity. Their discovery implies that oxidation in low-dimension metallic glass can result in unique properties for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
[Press-News.org] Welch Foundation supports Johnson-Winters' TB researchGrant helps UTA advance understanding of deadly disease