(Press-News.org) The production of aluminium generates around 180 million tonnes of toxic red mud every year. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung, a centre for iron research, have now shown how green steel can be produced from aluminium production waste in a relatively simple way. In an electric arc furnace similar to those used in the steel industry for decades, they convert the iron oxide contained in the red mud into iron using hydrogen plasma. With this process, almost 700 million tonnes of CO2-free steel could be produced from the four billion tonnes of red mud that have accumulated worldwide to date – which corresponds to a good third of annual steel production worldwide. And as the Max Planck team shows, the process would also be economically viable.
According to forecasts, demand for steel and aluminium will increase by up to 60 percent by 2050. Yet the conventional production of these metals has a considerable impact on the environment. Eight percent of global CO2 emissions come from the steel industry, making it the sector with the highest greenhouse gas emissions. Meanwhile, aluminium industry produces around 180 million tonnes of red mud every year, which is highly alkaline and contains traces of heavy metals such as chromium. In Australia, Brazil and China, among others, this waste is at best dried and disposed of in gigantic landfill sites, resulting in high processing costs. When it rains heavily, the red mud is often washed out of the landfill, and when it dries, the wind can blow it into the environment as dust. In addition, the highly alkaline red mud corrodes the concrete walls of the landfills, resulting in red mud leaks that have already triggered environmental disasters on several occasions, for example in China in 2012 and in Hungary in 2010. In addition, large quantities of red mud are also simply disposed of in nature.
Potential to save 1.5 billion tonnes of CO2 in the steel industry
"Our process could simultaneously solve the waste problem of aluminium production and improve the steel industry's carbon footprint," says Matic Jovičevič-Klug, who played a key role in the work as a scientist at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung. In a study published in the journal Nature, the team shows how red mud can be utilized as a raw material in the steel industry. This is because the waste from aluminium production consists of up to 60 percent iron oxide. The Max Planck scientists melt the red mud in an electric arc furnace and simultaneously reduce the contained iron oxide to iron using a plasma that contains ten percent hydrogen. The transformation, known in technical jargon as plasma reduction, takes just ten minutes, during which the liquid iron separates from the liquid oxides and can then be extracted easily. The iron is so pure that it can be processed directly into steel.
The remaining metal oxides are no longer corrosive and solidify on cooling to form a glass-like material that can be used as a filling material in the construction industry, for example. Other research groups have produced iron from red mud using a similar approach with coke, but this produces highly contaminated iron and large quantities of CO2. Using green hydrogen as a reducing agent avoids these greenhouse gas emissions. "If green hydrogen would be used to produce iron from the four billion tonnes of red mud that have been generated in global aluminium production to date, the steel industry could save almost 1.5 billion tonnes of CO2," says Isnaldi Souza Filho, Research Group Leader at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung.
An economical process, including with green hydrogen and electricity
The heavy metals in the red mud can also be virtually neutralized using the process. "After reduction, we detected chromium in the iron," says Matic Jovičevič-Klug. "Other heavy and precious metals are also likely to go into the iron or into a separate area. That's something we'll investigate in further studies. Valuable metals could then be separated and reused." And heavy metals that remain in the metal oxides are firmly bound within them and can no longer be washed out with water, as can happen with red mud.
However, producing iron from red mud directly using hydrogen not only benefits the environment twice over; it pays off economically too, as the research team demonstrated in a cost analysis. With hydrogen and an electricity mix for the electric arc furnace from only partially renewable sources, the process is worthwhile, if the red mud contains 50 percent iron oxide or more. If the costs for the disposal of the red mud are also considered, only 35 percent iron oxide is sufficient to make the process economical. With green hydrogen and electricity, at today's costs – also taking into account the cost of landfilling the red mud – a proportion of 30 to 40 percent iron oxide is required for the resulting iron to be competitive on the market. "These are conservative estimates because the costs for the disposal of the red mud are probably calculated rather low," says Isnaldi Souza Filho. And there's another advantage from a practical point of view: electric arc furnaces are widely used in the metal industry – including in aluminium smelters – as they are used to melt down scrap metal. In many cases, the industry would therefore need to invest only a little to become more sustainable. "It was important for us to also consider economic aspects in our study," says Dierk Raabe, Director at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung. "Now it's up to the industry to decide whether it will utilize the plasma reduction of red mud to iron."
END
Green steel from toxic red mud
An economical process with green hydrogen can be used to extract CO2-free iron from the red mud generated in aluminium production
2024-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Women’s blood lipids metabolism better in countering effects of sleep apnea
2024-02-05
Sleep apnea, which involves recurring, temporary interruptions of breathing during sleep, can disturb regulation of blood lipid levels, a key factor in the development of cardiovascular disease. A University of Ottawa research team has shown that the impact of sleep apnea on the metabolism of blood lipids differs by sex, with women regulating their blood lipids better than men.
The study was conducted by Nicholas Goulet, Caroline Marcoux, Renée Morin, Jean-François Mauger and Vincent Bourgon, under the supervision of Pascal ...
Healthy lifestyle and cognition in older adults with common neuropathologies of dementia
2024-02-05
About The Study: This study found that in older adults, a healthy lifestyle may provide a cognitive reserve to maintain cognitive abilities independently of common neuropathologies of dementia.
Authors: Klodian Dhana, M.D., Ph.D., of Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.5491)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Officer-involved killings of unarmed black people and racial disparities in sleep health
2024-02-05
About The Study: Sleep duration among Black survey respondents worsened after exposure to officer-involved killings of unarmed Black individuals in their area of residence. The findings were specific to officer involved killings of unarmed Black people, and no adverse outcomes on sleep health were found for white respondents. These findings underscore the role of structural racism in shaping racial disparities in sleep health.
Authors: Atheendar S. Venkataramani, M.D., Ph.D., of the University ...
Injuries from legal interventions involving conducted energy devices
2024-02-05
About The Study: This study of emergency department visits for physical injuries from use of conducted energy devices, such as TASERs, by police departments found that most visits involved young Black and white males from low-income areas. Black individuals were overrepresented in the sample versus the U.S. population, consistent with research demonstrating increased risk of police violence in Black populations.
Authors: Kevin N. Griffith, Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center ...
Losing sleep over killings of unarmed Black individuals by police
2024-02-05
PHILADELPHIA – Black adults across the United States suffer from sleep problems following exposure to news about unarmed Black individuals killed by police during police encounters, according to new findings published today in JAMA Internal Medicine from researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine. The issue, researchers said, may compound the risk factors that poor sleep already poses for many chronic and mental health conditions, from depression to post traumatic stress disorder.
Researchers conducted two separate analyses examining changes in sleep duration in the U.S. non-Hispanic Black population before and after exposure to such deaths ...
New technology unscrambles the chatter of microbes
2024-02-05
Researchers from University of California San Diego, as part of a large collaboration with scientists around the world, have developed a new search tool to help researchers better understand the metabolism of microorganisms. Microbes are key players in virtually all biological and environmental systems, yet limitations in current techniques used to study microbial metabolism make it difficult to decode their interactions and activities.
The new research, published February 5, 2023 in Nature Microbiology, directly addresses these limitations, which could ultimately transform our understanding of both human health and the environment.
“Humans are walking ecosystems in which microbes vastly ...
Pulmonary rehabilitation is difficult for millions of Americans to access
2024-02-05
New Haven, Conn. — Pulmonary rehabilitation, an essential component of care for patients with chronic respiratory conditions, is difficult for millions of Americans to access, a new Yale-led study reveals. The findings, researchers say, reveal geographic regions where this type of care is most lacking and illustrate the potential for telemedicine in helping to bridge this gap.
The study was published Feb. 5 in JAMA Network Open.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a multidisciplinary program that incorporates exercise and strategic techniques to improve quality of life and overall health for patients with respiratory conditions like chronic ...
Bacterial test for raw, organic milk may require more precision
2024-02-05
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell food scientists show that a standard quality test used for raw, organic milk is insufficient for distinguishing between specific groups of bacteria, suggesting that the criteria for determining milk quality at processing plants needs to be updated.
Their work was published Jan. 20 in the Journal of Dairy Science.
“Testing milk should not be one size fits all,” as tests should be used appropriately to give the best feedback to dairy producers, said lead author Renee Lee ’21, ...
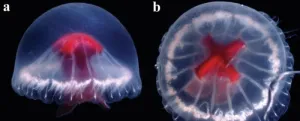
Brazilian researcher helps describe a novel species of jellyfish discovered in a remote location in Japan
2024-02-05
A gelatinous animal with a diameter of about 10 cm and a red stomach resembling the Cross of St George when seen from above. This is Santjordia pagesi, a newly described species of medusa. Medusae are a type of free-swimming, umbrella-shaped jellyfish with a reduced stalk.
The new species is described in an article published in the journal Zootaxa. The study was conducted by an international group of researchers that included a Brazilian scientist supported by FAPESP.
The scientist in question is André Morandini, last author ...
Small but mighty – study highlights the abundance and importance of the ocean’s tiniest inhabitants
2024-02-05
Tiny plankton – measuring less than 20µm (or 0.02mm) in diameter – make up the majority of plankton in the ocean and play a critical role in the planet’s health, according to new research.
However, scientists say challenges in identifying them have led to them becoming a silent majority that is currently being overlooked when it comes to global ocean policy.
The study is one of the first to explore the abundance and importance of these tiny ocean inhabitants around the UK coastline, with the technology capable of monitoring them only having been introduced in around 2010.
However, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Green steel from toxic red mudAn economical process with green hydrogen can be used to extract CO2-free iron from the red mud generated in aluminium production