(Press-News.org) In the human body, the lungs and their vasculature can be likened to a building with an intricate plumbing system. The lungs’ blood vessels are the pipes essential for transporting blood and nutrients for oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal. Much like how pipes can get rusty or clogged, disrupting normal water flow, damage from respiratory viruses, like SARS-CoV-2 or influenza, can interfere with this “plumbing system.”
In a recent study, researchers looked at the critical role of vascular endothelial cells in lung repair. Their work, published in Science Translational Medicine, was led by Andrew Vaughan of the University of Pennsylvania’s School of Veterinary Medicine and shows that, by using techniques that deliver vascular endothelial growth factor alpha (VEGFA) via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), that they were able to greatly enhance modes of repair for these damaged blood vessels, much like how plumbers patch sections of broken pipes and add new ones.
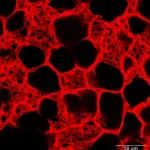
Confocal imaging demonstrating the dense network of capillary blood vessels in the lung that allow oxygen to move into our bloodstream. This complex vascular network can be severely disrupted upon viral infections like influenza and COVID-19, which greatly contributes to disease severity and mortality. (Image: Courtesy of Gan Zhao)
“While our lab and others have previously shown that endothelial cells are among the unsung heroes in repairing the lungs after viral infections like the flu, this tells us more about the story and sheds light on the molecular mechanisms at play,” says Vaughan, assistant professor of biomedical sciences at Penn Vet. “Here we’ve identified and isolated pathways involved in repairing this tissue, delivered mRNA to endothelial cells, and consequently observed enhanced recovery of the damaged tissue. These findings hint at a more efficient way to promote lung recovery after diseases like COVID-19.”
They found VEGFA’s involvement in this recovery, while building on work in which they used single cell RNA sequencing to identify transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2) as a major signaling pathway. The researchers saw that when TGFBR2 was missing it stopped the activation of VEGFA. This lack of signal made the blood vessel cells less able to multiply and renew themselves, which is vital for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the tiny air sacs of the lungs.
“We’d known there was a link between these two pathways, but this motivated us to see if delivering VEGFA mRNA into endothelial cells could improve lung recovery after disease-related injury,” says first author Gan Zhao, a postdoctoral researcher in the Vaughan Lab.
The Vaughan Lab then reached out to Michael Mitchell of the School of Engineering and Applied Science, whose lab specializes in LNPs, to see if delivery of this mRNA cargo would be feasible.
“LNPs have been great for vaccine delivery and have proven incredibly effective delivery vehicles for genetic information. But the challenge here was to get the LNPs into the bloodstream without them heading to the liver, which is where they tend to congregate as its porous structure lends favor to substances passing from the blood into hepatic cells for filtration,” says Mitchell, an associate professor of bioengineering at Penn Engineering and a coauthor of the paper. “So, we had to devise a way to specifically target the endothelial cells in the lungs.”
Lulu Xue, a postdoctoral researcher in the Mitchell Lab and a co-first author of the paper, explains that they engineered the LNP to have an affinity for lung endothelial cells, this is known as extra hepatic delivery, going beyond the liver.
“We’ve seen evidence in the literature suggesting it’s doable, but the systems we’d seen are made up of positively charged lipids which were too toxic,” Xue says. “This led me to developing an ionizable lipid that’s not positively charged when it enters the bloodstream but gets charged when it gets to the endothelial cells, thereby releasing the mRNA.”
Their LNPs proved effective in delivering VEGFA into endothelial cells and as a result the researchers saw a marked improvement in vascular recovery in their animal models. Within the animal models, the researchers saw improved oxygen levels, and in some the treatment helped them recover their weight better than the control group. These treated mice also had less lung inflammation, shown by lower levels of certain markers in their lung fluid, and their lungs showed less damage and scarring, with more healthy blood vessels.
“Although we went in hoping for this outcome, it was a real thrill to see how effective, safe, and efficiently this all panned out, so we’re looking forward to testing this delivery platform for other cell types in the lung, and it will be important to evaluate whether TGFB signaling is important in other injury contexts including chronic conditions like emphysema and COPD,” Vaughan says. “With this proof-of-concept being well validated, we’re sure that we’ll pave the way for new mRNA-based strategies for treating lung injury.”
Andrew Vaughan is an assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine.
Michael Mitchell is an associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and the director of the Lipid Nanoparticle Synthesis Core at the Penn Institute for RNA Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania.
Gan Zhao is a postdoctoral researcher in the Vaughn Lab at Penn Vet.
Lulu Xue is a postdoctoral researcher in the Mitchell Lab at Penn Engineering.
Other authors include Stephanie Adams-Tzivelekidis, Maria E. Gentile, Aaron I. Weiner, and Joanna Wong from Penn Vet; Ningqiang Gong and Xuexiang Han from Penn Engineering; and Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh, Maria C. Basil, Christian A. Bermudez, Edward Cantu, Yaqi Cao, Joshua M. Diamond, Susan M. Lin, Edward E. Morrisey, Terren K. Niethamer, Ana N. Nottingham, and Drew Weissman in the Perelman School of Medicine at Penn.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01HL153539 and R01HL164350 and award DP2 TR002776, the Margaret Q. Landenberger Foundation, a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award at the Scientific Interface; and the National Science Foundation (Award CBET-2145491).
END
Researchers breathe new life into lung repair
A collaborative effort from teams across Penn culminates in new techniques to repair lung tissue after damage from flu and COVID-19.
2024-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promoting prosocial behavior in the classroom and beyond
2024-02-06
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Christi Bergin has devoted 40 years of her life to helping teachers and their students. Throughout her career, she’s noticed two simultaneous trends in the field that seem to be connected: a rise in disruptive classroom behavior, and an exodus of teachers from the profession who leave due to stress and burnout.
To help combat these trends, Bergin, a professor emerita in the University of Missouri College of Education and Human Development, has focused her research on improving prosocial behavior — actions that show kindness, compassion, empathy and respect — in classrooms and communities.
Not ...
Perceptions of manhood and masculinities among disabled violently injured Black men in a hospital-based violence intervention program
2024-02-06
Black men with firearm-acquired disabilities face negative physical and psychological impacts on their manhood, independence and mobility, according to a Rutgers Health study.
The study, published in the American Journal of Men’s Health, explored the relationship between Black manhood/masculinities and firearm-acquired disabilities. Participants’ disabilities also impacted their perceptions of independence. Specifically, participants felt that they were a burden to their caretakers because of their reliance on them. This loss of independence ...
Two new freshwater fungi species in China enhance biodiversity knowledge
2024-02-06
Researchers have discovered two new freshwater hyphomycete (mould) species, Acrogenospora alangii and Conioscypha yunnanensis, in southwestern China.
This discovery, detailed in a study published in MycoKeys, marks the addition of these species to the Acrogenospora and Conioscypha genera, further enriching the diversity of freshwater fungi known in the region.
A research team consisting of Lu Li, Hong-Zhi Du and Ratchadawan Cheewangkoon from Chiang Mai University, Thailand, as well as Vinodhini Thiyagaraja and Rungtiwa Phookamsak from Kunming Institute of Botany, China, and Darbhe Jayarama Bhat from King Saud University, Saudi Arabia, employed comprehensive morphological ...
Apex predators not a quick fix for restoring ecosystems, 20-year CSU study finds
2024-02-06
A Colorado State University experiment spanning more than two decades has found that removal of apex predators from an ecosystem can create lasting changes that are not reversed after they return – at least, not for a very long time.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation and published in Ecological Monographs, challenges the commonly held belief that the reintroduction of wolves to Yellowstone National Park restored an ecosystem degraded by their absence.
Researchers in CSU’s Warner College of Natural Resources ...
Do digital technologies offer a better way to loan people money?
2024-02-06
A new paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics, published by Oxford University Press, finds that a new form of digital technology—essentially preventing people from using an asset for which they have a loan if they don’t make payments, rather than repossessing the asset itself—may be a better way for lenders to secure loans, particularly for loan recipients in developing countries.
Using collateral to secure debt helps overcome economic frictions, lowering the cost of providing credit. More than 80% of total household debt in the United States is secured by ...
Fiona M. Watt receives the 2024 ISSCR Achievement Award for her seminal work with skin stem cells
2024-02-06
Evanston, IL—The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) will award its 2024 ISSCR Achievement Award to Fiona M. Watt, D.Phil., F.R.S., F.Med.Sci., EMBO Director and leader of a research group at EMBL - Heidelberg, Germany. The award recognizes the transformative body of work of an investigator that has had a major impact on the field of stem cell research or regenerative medicine. Dr. Watt will present her research during Plenary VII on 13 July at the ISSCR 2024 Annual Meeting in Hamburg, Germany. ISSCR 2024 is the world’s leading gathering of the brightest minds in stem cell research and cell and regenerative medicine.
“Fiona is a giant in stem cell ...
Jun Wu receives the 2024 ISSCR Outstanding Young Investigator Award for his innovative work on stem cell-based embryo and chimera models
2024-02-06
Evanston, IL—The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is honoring Jun Wu, Ph.D. with the 2024 ISSCR Outstanding Young Investigator Award. Dr. Wu is an associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, U.S.A. and a New York Stem Cell Foundation–Robertson Investigator.
The award recognizes the exceptional achievements of an investigator in the early part of his or her independent career in stem cell research. Dr. Wu will present his work during Plenary II, New Technologies to Engineer and Phenotype Stem Cell Systems, on 10 July during the ISSCR 2024 Annual Meeting taking place in Hamburg, Germany. ...
Sergiu P. Paşca receives the 2024 ISSCR Momentum Award for his pioneering work in neurodevelopment and disease
2024-02-06
Evanston, IL— The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) will present this year’s ISSCR Momentum Award to Sergiu P. Paşca, M.D., Kenneth T. Norris, Jr. Professor and the Uytengsu Director of Stanford Brain Organogenesis, Stanford University, U.S.A. The award recognizes the exceptional achievements of a mid-career investigator whose innovative research has established a major area of stem cell-related research with a strong trajectory for future success.
Dr. Paşca will present his research during Plenary VII on 13 July 2024 during the ISSCR 2024 Annual Meeting in Hamburg, Germany. ISSCR 2024 is the world’s leading ...
Understanding neurodiversity across the UK population - study
2024-02-06
A new study has provided insight into how experiences and features of neurodiversity vary amongst adults in the UK.
There is variation in people’s attributes and experiences across all populations. Neurodivergent people, such as people with a diagnosis of ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia, or autism, may experience the world in distinctive ways. But, we are only beginning to appreciate how traits and experiences associated with neurodivergence differ across the whole population.
Now, new research from the University of Birmingham has provided a more detailed picture of what neurodiversity looks like amongst adults in the UK.
The research is published in JCPP Advances.
Ian Apperly, ...
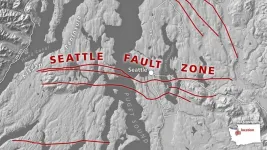
A new origin story for deadly Seattle fault
2024-02-06
American Geophysical Union
6 February 2024
AGU Release No. 24-04
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/seattle-fault-may-have-origins-in-an-ancient-tear-in-the-continent
Seattle fault may have origins in an ancient tear in the continent
Magnetic data suggest the hazardous Seattle fault zone developed as the edge of the continent tore itself in two more than 50 million years ago, providing a possible new origin story for the fault
AGU ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] Researchers breathe new life into lung repairA collaborative effort from teams across Penn culminates in new techniques to repair lung tissue after damage from flu and COVID-19.