(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of more than 1 million patients with stroke, the Target: Stroke quality initiative was associated with improvement in thrombolysis frequency, timeliness, and outcomes for all racial and ethnic groups. However, disparities persisted, indicating a need for further interventions.
Authors: Gregg C. Fonarow, M.D., of the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55927)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55927?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=020724
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Trends in stroke thrombolysis care metrics and outcomes by race and ethnicity
JAMA Network Open
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New direct links discovered between the brain and its surrounding environment
2024-02-07
In a recent study of the brain’s waste drainage system, researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, collaborating with investigators at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of the National Institute of Health (NIH), discovered a direct connection between the brain and its tough protective covering, the dura mater. These links may allow waste fluid to leave the brain while also exposing the brain to immune cells and other signals coming from the dura. This challenges the conventional wisdom which has suggested that the brain is cut off from its ...
Stress influences brain and psyche via immune system
2024-02-07
Chronic stress has far-reaching consequences for our bodies. For example, many stress-related psychiatric illnesses such as depression are associated with changes in the immune system. However, the underlying mechanisms of how these changes affect the brain are still largely unknown.
Enzyme from immune cells in the blood affects nerves in the brain
An international research team led by the University of Zurich (UZH), and the University Hospital of Psychiatry Zurich (PUK) and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, has now uncovered a novel mechanism. “We were able to show that ...
Mimas' surprise: Tiny moon holds young ocean beneath icy shell
2024-02-07
Hidden beneath the heavily cratered surface of Mimas, one of Saturn's smallest moons, lies a secret: a global ocean of liquid water. This astonishing discovery, led by Dr. Valéry Lainey of the Observatoire de Paris-PSL and published in the journal Nature, reveals a "young" ocean formed just 5 to 15 million years ago, making Mimas a prime target for studying the origins of life in our Solar System.
“Mimas is a small moon, only about 400 kilometers in diameter, and its heavily cratered surface gave no hint of the hidden ocean beneath," says Dr Nick Cooper, ...
Quantum materials: Discovered new state of matter with chiral properties
2024-02-07
An international research group has discovered a new state of matter characterized by the existence of a quantum phenomenon called chiral current. These currents are generated on an atomic scale by a cooperative movement of electrons, unlike conventional magnetic materials whose properties originate from the quantum characteristic of an electron known as spin and their ordering in the crystal.
Chirality is a property of extreme importance in science, for example, it is fundamental also to understand DNA. ...
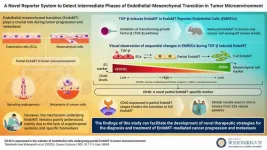
Towards a better understanding of endothelial cell transformation in cancer progression
2024-02-07
In a new study, Tokyo Medical and Dental University researchers shed light on partial endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the tumor microenvironment
Tokyo, Japan - Endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT, also termed as EndMT), a biological process resulting in the formation of mesenchymal (or lineage-committed) phenotypes from endothelial cells (lining blood vessels), plays a crucial role in tumor progression. Despite the important role of EndoMT, the underlying mechanism and characteristics of cells in intermediate/partial EndoMT remain largely unexplored. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a system to study these EndoMT stages.
In ...
After prison, perpetrators of genocide say they’ve changed
2024-02-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – After serving decades in prison, Rwandans convicted of crimes of genocide returned to their communities articulating a “narrative of redemption,” saying they were good people, despite their past crimes.
And they were hopeful about their prospects for reintegrating into their communities.
Many of these former prisoners had been convicted of murder, often of their own neighbors, connected to the 1994 genocide in Rwanda. But they said they had changed – even while minimizing their role in the killings.
In ...
Japan's electric vehicle transition by 2035 may be insufficient to combat the climate crisis, but there are solutions
2024-02-07
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have found that Japan's current policy of stopping the sale of gas vehicles by 2035 and transitioning only to hybrids and electric vehicles may be insufficient to reduce the country's CO2 emissions and prevent it from reaching its decarbonization target goals. In fact, emissions may temporarily increase.
The team's analysis showed that along with the policy, the Japanese government must simultaneously work to increase production of clean ...
From the research bench to the patient’s bedside: Project on Medical Microwave Imaging awarded with 1.5M€
2024-02-07
The European project entitled “Bone, Brain, Breast and Axillary Medical Microwave Imaging Twinning (3BAtwin)” has been awarded with €1.5M to reinforce our training on Medical Microwave Imaging (MMWI). The project is led by the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) (Portugal), in collaboration with University of Galway (Ireland) and Turin Polytechnic University (Italy).
The goal of this twinning project is to accelerate the transition of Medical Microwave Imaging “from the research bench ...
New resource for selecting best treatment path for young children with cancerous tumors published by NCCN
2024-02-07
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 7, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today published its first ever set of treatment recommendations pertaining to neuroblastoma. Neuroblastoma is a type of solid tumor cancer that typically occurs in early childhood, with the majority diagnosed before age five.[1] Neuroblastoma is the most common type of solid tumor (outside of brain tumors) in children, with more than 700 cases diagnosed in the United States every year.[2] Research innovations ...
Gut microbiome changes during pregnancy may influence immune system response
2024-02-07
Highlights:
Alterations in gut microbiota may influence immune system changes during pregnancy.
However, the connection isn’t well known.
Researchers in China analyzed gut microbiota, metabolites and cytokines in healthy pregnant and non-pregnant young women.
The new study identifies numerous pathways by which the gut microbiome may change the immune system.
Washington, D.C.—During pregnancy, a woman’s immune system changes dramatically but researchers don’t yet understand all the underlying mechanisms. A new study shows how the gut microbiota may play a role.
In a paper published this week in mSystems, researchers in China report that during pregnancy, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Trends in stroke thrombolysis care metrics and outcomes by race and ethnicityJAMA Network Open