Breaking through barriers
2024-02-08
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) overcome scientific roadblocks and develop a model to assess the biology of the human placental barrier
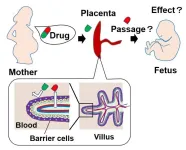
Tokyo, Japan – During pregnancy, the human placenta plays multiple essential roles, including hormone production and nutrient/waste processing. It also serves as a barrier to protect the developing fetus from external toxic substances. However, the placental barrier can still be breached by certain drugs. In a recent article published in Nature Communications, a team led by researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) developed a trophoblast stem (TS) cell-based organoid model of the placental barrier to support further biological research.
Villi in the human placenta help form the barrier and are surrounded by a layer of cells called trophoblasts. Because the structural nature of villi is critical for its function, cell lines and other methods used to replicate placental physiology in laboratory experiments have proven inadequate. Primary placental cells are also difficult to maintain in culture. Therefore, the TMDU group aimed to develop an effective in vitro model of placental villi using TS cells.
“TS cells have the capacity to differentiate into all kinds of placental cells consisting of the human placenta.,” says Dr. Takeshi Hori, lead author of the study. “However, it has been challenging to make the barrier model using TS cells.”
First of all, the team then generated trophoblast organoids, a type of three-dimensional cell model that can more effectively mimic the structural and biological details of an organ. After testing three types of culture medium, they determined the optimal conditions to support the formation of spherical organoids.
“The outer layer of the organoid contained a single layer of cells called syncytiotrophoblasts,” explains Dr. Hirokazu Kaji, senior author. “This layer effectively displayed the barrier function that we were aiming to mimic with this model.”
Based on the culture conditions of the spherical organoids, the researchers established flatter organoids with a column-type container to easily asses the translocation of compounds through the barrier layer. The researchers used various methods to confirm the barrier integrity and maturation levels of the plane organoids and to ensure the robustness of the system. Their analysis also showed that the model could be used to assess how well different compounds could cross the barrier, specifically by examining the permeability coefficients.
“Using the organoids as a model of the placental barrier will help scientists better understand general placental biology and potential drug toxicity,” says Dr. Hori. “We also designed our model in a manner such that the cells could be easily cultured and it could be evaluated using microscopic observation.”
The TS cell-based organoid model generated in this study effectively addresses many of the difficulties that have previously hampered laboratory-based assessments of placental physiology. It will be a useful tool for not only elucidating details of the development of this organ, but also for evaluating the transfer rates and toxicity levels of various compounds. This will be critical in the drug development process to avoid damaging the placenta or harming the fetus.
###
The article, “Trophoblast stem cell-based organoid models of the human placental barrier,” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45279-y
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-08
Under strict embargo until 10.00 GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
A new King’s College London scanning study of 390 babies has shown distinct patterns between term and pre-term babies in the moment-to-moment activity and connectivity of brain networks.
Supported by Wellcome and the National institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre, this is the first study to analyse how the communication between brain areas changes moment-to-moment in the first few weeks of life.
Published in Nature Communications, the study also found that these dynamic ...
2024-02-08
White actors are featured more frequently and more prominently on posters for American-produced films than non-white actors despite recent increases in the representation of actors from other ethnic groups, according to a study published in Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.
Galit Fuhrmann Alpert and colleagues investigated trends in the ethnic diversity of actors featured on over 45,000 posters advertising over 24,000 English-speaking films produced in the USA between 1960 and 2021. Actors were assigned to one of four ethnic groups; white, Black, Indian, or Asian using an algorithm trained on the FairFace image dataset, which contains equal numbers ...
2024-02-08
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 01:00hrs GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals and cells
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
CDD causes seizures and impaired development in children, and medications are limited to managing symptoms rather than tackling the root cause of the disease. The disorder involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which ...
2024-02-08
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies are presented in the peer-reviewed Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM). Biofield therapies (BFTs), such as External Qigong, Healing Touch, Reiki, and Therapeutic Touch, are a related group of integrative medicine interventions in which practitioners use their hands on or above a client’s body to stimulate healing and well-being. Click here to read the article now.
The guidelines call for including details of the intervention protocols relevant to biofield therapy trials. The Reporting Evidence Guidelines comprises ...
2024-02-08
DETROIT– A team of researchers from Wayne State University was awarded a $1.4 million, three-year grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for the study, “Cytochrome c acetylation drives prostate cancer aggressiveness and Warburg effect.”
The study, led by Maik Hüttemann, Ph.D., professor of molecular medicine and genetics, and biochemistry, microbiology and immunology at Wayne State University’s School of Medicine, aims to establish the role of the protein cytochrome c, which the team proposes is ...
2024-02-08
Australian geologists have used plate tectonic modelling to determine what most likely caused an extreme ice-age climate in Earth’s history, more than 700 million years ago.
The study, published in Geology, helps our understanding of the functioning of the Earth's built-in thermostat that prevents the Earth from getting stuck in overheating mode. It also shows how sensitive global climate is to atmospheric carbon concentration.
“Imagine the Earth almost completely frozen over,” said the study’s lead author, ARC Future Fellow ...
2024-02-08
A person’s chance of surviving while receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for cardiac arrest in hospital declines rapidly from 22% after one minute to less than 1% after 39 minutes, finds a US study published by The BMJ today.
Similarly, the likelihood of leaving hospital with no major brain damage declines from 15% after one minute of CPR to less than 1% after 32 minutes with no heartbeat.
The researchers say the findings provide insights that may help guide hospital teams, patients and their families in deciding how long to continue resuscitation.
In-hospital ...
2024-02-08
An online programme of physical and mental health rehabilitation can improve quality of life for adults with long covid, finds a trial published by The BMJ today.
The eight week REGAIN programme, delivered in online group sessions, led to sustained improvements in fatigue, pain, and depression compared with usual care.
The researchers say this accessible, resource-efficient programme can be delivered at scale and will assist clinicians in the treatment of this complex condition.
Post-covid-19 condition (commonly known as long covid) ...
2024-02-08
The anxiety of headteachers across England increased “substantially” throughout the pandemic, finds the largest study of its type to-date.
The results of the research, which examined thousands of teachers’ anxiety about work at 75 touchpoints from October 2019 to July 2022, show that senior leaders in schools suffered – even “much more” when compared with junior colleagues.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Educational Review, are the latest to demonstrate the mental ...
2024-02-08
A life-threatening mold infection known as health care-associated Fusarium solani meningitis can be associated with a delayed, but devastating, injury to the brainstem and its blood supply among those infected, according to physicians from UTHealth Houston.
A report, led by first author Nora Strong, MD, and senior author Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner, MD, was published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Strong is a second-year postdoctoral fellow in infectious diseases with McGovern Medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breaking through barriers