(Press-News.org) Waltham — February 8, 2024 — For patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA), the use of robotic-assisted surgery and surgical navigation techniques is not associated with an increased risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), suggests a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Computer navigation (CN) and robotic assistance (RA) do not alter the risk of PJI after total hip replacement surgery, according to the new research by Alberto V. Carli, MD, and colleagues of Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
Could CN and RA increase risks during hip replacement?
Computer navigation and robotic assistance are increasingly used during THA. These technologies have shown beneficial effects, including more accurate component positioning and a lower risk of postoperative instability. However, "[I]t remains unknown as to whether use of [CN and RA] leads to an improvement in long-term functional outcomes or implant longevity," according to the authors.
The use of CN and RA requires the presence of additional equipment and personnel in the operating room, and has been linked to longer operating times. Together, these factors might lead to an increased risk of surgical-site contamination and PJI, a major cause of implant failure after THA.
Dr. Carli and colleagues analyzed their hospital's experience of nearly 13,000 patients undergoing primary THA between 2018 and 2021. During this time, CN was used during THA in 21% of patients and RA in 16%. The remaining 63% of patients underwent conventional THA without CN or RA.
Similarly low rates of PJI, with or without new technologies
Using a technique called propensity-score matching, the researchers identified groups of patients with similar risk factors undergoing THA by conventional methods or with the use of RA (2,003 patients in each group) or CN (2,664 patients in each group). Ninety-day rates of PJI were compared between groups, with adjustment for other factors.
Both technologies were associated with small increases in operative times, compared to conventional THA: two minutes longer with CN and 11 minutes longer with RA. Previous studies have raised concerns that longer surgical times might lead to increased risk of complications.
However, in the new study, the incidence of PJI was similar among groups: 0.4% for both CN and RA compared with rates of 0.2% and 0.4% for the respective propensity-matched conventional THA cohorts. In adjusted analyses, there were no significant differences in PJI risk.
“Although computer navigation and robotic assistance are currently used in a minority of THA procedures, the increase in the use of such technology appears to be inevitable in the coming decades," the researchers write. Their study adds new evidence that, in matched groups of patients with similar characteristics, the risks of PJI are comparable, with or without the use of CN or RA.
The authors point out some limitations of the study – notably including the overall low rate of PJI at their specialized, high-volume orthopaedic surgery center. Dr. Carli and coauthors conclude: "While the long-term clinical, functional, and implant-longevity outcomes associated with the use of computer navigation or robotic assistance remain to be elucidated, the findings of the present study are reassuring with respect to the risk of infection."
Read Article [ Robotics and Navigation Do Not Affect the Risk of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty ]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health.
###
About The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS) has been the most valued source of information for orthopaedic surgeons and researchers for over 125 years and is the gold standard in peer-reviewed scientific information in the field. A core journal and essential reading for general as well as specialist orthopaedic surgeons worldwide, The Journal publishes evidence-based research to enhance the quality of care for orthopaedic patients. Standards of excellence and high quality are maintained in everything we do, from the science of the content published to the customer service we provide. JBJS is an independent, non-profit journal.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in information, software, and services for professionals in healthcare, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,900 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and YouTube.
END
Robotic-assisted surgery and navigation don't affect infection risk after hip arthroplasty
'Reassuring' evidence on safety of new technologies presented in Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
2024-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
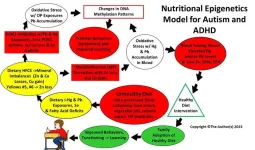
New study shows nutritional epigenetics education improves diet and attitude in parents of children with autism and ADHD
2024-02-09
In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported the results of a clinical trial in which parents who received nutritional epigenetics education significantly reduced their consumption of ultra-processed foods while increasing their intake of whole and/or organic foods. The education intervention used curriculum focused on the constructs of the nutritional epigenetics model that explains how autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may develop from the excess consumption of ultra-processed ...
Immune genes are altered in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
2024-02-09
· First-of-its-kind study of immune genes in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
· Immune T cells are altered and entering brain
· Uncertain whether changes precipitate the disease
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study has found the immune system in the blood of Alzheimer’s patients is epigenetically altered. That means the patients’ behavior or environment has caused changes that affect the way their genes work.
Many of these altered immune genes are the same ones that increase an ...
The Biophysical Journal names Erdinc Sezgin the 2023 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Awardee
2024-02-09
ROCKVILLE, MD – Erdinc Sezgin, of Karolinska Institutet, Sweden will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 10-14 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “Influence of the Extracellular Domain Size on the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins.” The paper was published in Volume 121, Issue ...
Research reveals the key to an irresistible online dating profile
2024-02-09
In writing a good online dating profile, the average love-seeker is likely to fill it up with all the appealing qualities and interests that make them special. They paraglide and do hot yoga on the weekends; enjoy Riesling on the beach or seeing indie bands in basements; are a Libra with Scorpio rising; or have a dog or three kids or an iguana. There’s one thing they routinely leave out, however: what they want to know about their potential partner.
Yet, that detail might the most important thing to include, according ...
Surprisingly vibrant colour of 12-million-year-old snail shells
2024-02-09
Snail shells are often colourful and strikingly patterned. This is due to pigments that are produced in special cells of the snail and stored in the shell in varying concentrations. Fossil shells, on the other hand, are usually pale and inconspicuous because the pigments are very sensitive and have already decomposed. Residues of ancient colour patterns are therefore very rare. This makes this new discovery by researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Natural History Museum Vienna (NHMW) all the more astonishing: they found pigments in ...
In the Cerrado, crop diversification has beneficial effects on wildlife and reduces the presence of boars
2024-02-09
There are no substitutes for native vegetation, but replacing large areas of monoculture with diversified crops in places where agricultural activities are widespread can have beneficial effects on the mammals that still inhabit the region.
This is one of the conclusions of a study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) supported by FAPESP. They focused on the northeast of São Paulo state, where the predominant biome is the Cerrado (Brazilian savanna). The region is one of the nation’s agribusiness centers.
An article on the study is published in the Journal of Applied Ecology. The study showed that ...
How electron spectroscopy measures exciton “holes”
2024-02-09
Semiconductors are ubiquitous in modern technology, working to either enable or prevent the flow of electricity. In order to understand the potential of two-dimensional semiconductors for future computer and photovoltaic technologies, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen, Marburg and Cambridge investigated the bond that builds between the electrons and holes contained in these materials. By using a special method to break up the bond between electrons and holes, they were able to gain a ...
IPIAD: an augmentation to standard treatment of PDAC using five repurposed drugs
2024-02-09
“This paper presents the rationale for adding five already approved and marketed generic drugs from general medical practice to the current standard current first line chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).”
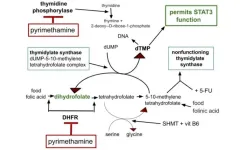
BUFFALO, NY- February 9, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on February 7, 2024, entitled, “IPIAD- an augmentation regimen added to standard treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using already-marketed repurposed drugs irbesartan, pyrimethamine, itraconazole, azithromycin, and dapsone.”
In this new paper, researcher Richard E. Kast from IIAIGC Study Center presents the ...
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry opens dental clinic for special-needs children, adults
2024-02-09
SAN ANTONIO, Feb. 9, 2024 – The UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry has opened a special-care dental clinic, the first of its kind in an academic setting in South Texas that will serve people of all ages with intellectual, developmental, cognitive or physical disabilities.
With spacious, specially designed treatment rooms featuring adjustable sound and lighting and even a “Zen Den” multi-sensory room to help reduce anxiety, the Phil and Karen Hunke Special Care Clinic occupies approximately ...
This ultrasound sticker senses changing stiffness of deep internal organs
2024-02-09
MIT engineers have developed a small ultrasound sticker that can monitor the stiffness of organs deep inside the body. The sticker, about the size of a postage stamp, can be worn on the skin and is designed to pick up on signs of disease, such as liver and kidney failure and the progression of solid tumors.
In an open-access study that will appear in Science Advances, the team reports that the sensor can send sound waves through the skin and into the body, where the waves reflect off internal organs and back out to the sticker. The pattern of the reflected waves can be read as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Robotic-assisted surgery and navigation don't affect infection risk after hip arthroplasty'Reassuring' evidence on safety of new technologies presented in Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery