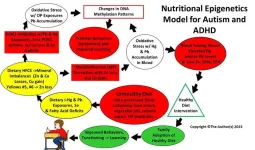
(Press-News.org) In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported the results of a clinical trial in which parents who received nutritional epigenetics education significantly reduced their consumption of ultra-processed foods while increasing their intake of whole and/or organic foods. The education intervention used curriculum focused on the constructs of the nutritional epigenetics model that explains how autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may develop from the excess consumption of ultra-processed foods.
Consumption of ultra-processed foods leads to heavy metal exposures and dietary deficits that create mineral imbalances such as zinc and calcium losses. Inadequate zinc stores can disrupt the function of the metal transporter metallothionein (MT) gene preventing the elimination of heavy metals found in ultra-processed foods. The bioaccumulation of mercury and/or lead is common in children with autism and ADHD who are often zinc deficient. Mercury, lead, and other heavy metals are known to suppress the paraoxonase (PON1) gene. Paraoxonase is required by the body to detoxify the neurotoxic organophosphate pesticide residues found routinely in the food supply by the United States Department of Agriculture. Children with autism and ADHD are more susceptible to the harmful effects of organophosphate pesticide exposures.
Parents who received nutritional epigenetics education learned how to reduce their children’s dietary exposures to heavy metal and organophosphate pesticide residues. The parents learned how to read food ingredient labels and changed their diet as they avoided buying foods with allowable heavy metal and pesticide residues. In learning how specific food ingredients contribute to heavy metal exposures, impact nutrient status and/or gene behavior, parents gained the knowledge they needed to feed themselves and their children a healthier diet. By the end of the education intervention, parents had changed their minds about their ability to control their child’s behavior through diet.
Children behave better when they feel better. Because the severity of symptoms in autism and ADHD correlate directly to the heavy metal levels in blood, children with less heavy metal exposure show improvements in behavior and cognition. In addition, because heavy metals, in single or multi-metallic combination, create conditions for gut dysbiosis, improvements in diet can reduce inflammation and improve gut health. Reducing ultra-processed food consumption can alleviate symptoms associated with gut dysbiosis which is often a co-morbid condition found in children with autism and ADHD.
Autism and ADHD are preventable, but the prevalence of these neurodevelopmental disorders will continue to increase in the United States until changes are made to reduce the allowable heavy metal residues in the ultra-processed food supply. The US Congress released two reports in 2021 on the problem of heavy metals in baby foods. The first report issued on February 4, 2021, revealed baby foods are tainted with dangerous levels of arsenic, lead, cadmium, and mercury. The second report, issued on September 29, 2021, confirmed new disclosures from manufacturers show dangerous levels of heavy metals in even more baby foods.
Press Contact:
Jacalyn Macy Hallford, Media Contact, Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, jmhallford@foodingredient.info
END
New study shows nutritional epigenetics education improves diet and attitude in parents of children with autism and ADHD
2024-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune genes are altered in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
2024-02-09
· First-of-its-kind study of immune genes in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
· Immune T cells are altered and entering brain
· Uncertain whether changes precipitate the disease
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study has found the immune system in the blood of Alzheimer’s patients is epigenetically altered. That means the patients’ behavior or environment has caused changes that affect the way their genes work.
Many of these altered immune genes are the same ones that increase an ...
The Biophysical Journal names Erdinc Sezgin the 2023 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Awardee
2024-02-09
ROCKVILLE, MD – Erdinc Sezgin, of Karolinska Institutet, Sweden will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 10-14 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “Influence of the Extracellular Domain Size on the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins.” The paper was published in Volume 121, Issue ...
Research reveals the key to an irresistible online dating profile
2024-02-09
In writing a good online dating profile, the average love-seeker is likely to fill it up with all the appealing qualities and interests that make them special. They paraglide and do hot yoga on the weekends; enjoy Riesling on the beach or seeing indie bands in basements; are a Libra with Scorpio rising; or have a dog or three kids or an iguana. There’s one thing they routinely leave out, however: what they want to know about their potential partner.
Yet, that detail might the most important thing to include, according ...
Surprisingly vibrant colour of 12-million-year-old snail shells
2024-02-09
Snail shells are often colourful and strikingly patterned. This is due to pigments that are produced in special cells of the snail and stored in the shell in varying concentrations. Fossil shells, on the other hand, are usually pale and inconspicuous because the pigments are very sensitive and have already decomposed. Residues of ancient colour patterns are therefore very rare. This makes this new discovery by researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Natural History Museum Vienna (NHMW) all the more astonishing: they found pigments in ...
In the Cerrado, crop diversification has beneficial effects on wildlife and reduces the presence of boars
2024-02-09
There are no substitutes for native vegetation, but replacing large areas of monoculture with diversified crops in places where agricultural activities are widespread can have beneficial effects on the mammals that still inhabit the region.
This is one of the conclusions of a study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) supported by FAPESP. They focused on the northeast of São Paulo state, where the predominant biome is the Cerrado (Brazilian savanna). The region is one of the nation’s agribusiness centers.
An article on the study is published in the Journal of Applied Ecology. The study showed that ...
How electron spectroscopy measures exciton “holes”
2024-02-09
Semiconductors are ubiquitous in modern technology, working to either enable or prevent the flow of electricity. In order to understand the potential of two-dimensional semiconductors for future computer and photovoltaic technologies, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen, Marburg and Cambridge investigated the bond that builds between the electrons and holes contained in these materials. By using a special method to break up the bond between electrons and holes, they were able to gain a ...
IPIAD: an augmentation to standard treatment of PDAC using five repurposed drugs
2024-02-09
“This paper presents the rationale for adding five already approved and marketed generic drugs from general medical practice to the current standard current first line chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).”
BUFFALO, NY- February 9, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on February 7, 2024, entitled, “IPIAD- an augmentation regimen added to standard treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using already-marketed repurposed drugs irbesartan, pyrimethamine, itraconazole, azithromycin, and dapsone.”
In this new paper, researcher Richard E. Kast from IIAIGC Study Center presents the ...
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry opens dental clinic for special-needs children, adults
2024-02-09
SAN ANTONIO, Feb. 9, 2024 – The UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry has opened a special-care dental clinic, the first of its kind in an academic setting in South Texas that will serve people of all ages with intellectual, developmental, cognitive or physical disabilities.
With spacious, specially designed treatment rooms featuring adjustable sound and lighting and even a “Zen Den” multi-sensory room to help reduce anxiety, the Phil and Karen Hunke Special Care Clinic occupies approximately ...
This ultrasound sticker senses changing stiffness of deep internal organs
2024-02-09
MIT engineers have developed a small ultrasound sticker that can monitor the stiffness of organs deep inside the body. The sticker, about the size of a postage stamp, can be worn on the skin and is designed to pick up on signs of disease, such as liver and kidney failure and the progression of solid tumors.
In an open-access study that will appear in Science Advances, the team reports that the sensor can send sound waves through the skin and into the body, where the waves reflect off internal organs and back out to the sticker. The pattern of the reflected waves can be read as ...
Yale joins the ‘Snowball’ fight over global deep freeze periods
2024-02-09
New Haven, Conn. — A Yale-led research team has picked a side in the “Snowball Earth” debate over the possible cause of planet-wide deep freeze events that occurred in the distant past.
According to a new study, these so-called “Snowball” Earth periods, in which the planet’s surface was covered in ice for thousands or even millions of years, could have been triggered abruptly by large asteroids that slammed into the Earth.
The findings, detailed in the journal Science Advances, may answer a question ...