The Biophysical Journal names Erdinc Sezgin the 2023 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Awardee
2024-02-09
(Press-News.org) ROCKVILLE, MD – Erdinc Sezgin, of Karolinska Institutet, Sweden will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 10-14 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “Influence of the Extracellular Domain Size on the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins.” The paper was published in Volume 121, Issue 20 of Biophysical Journal.
The influence of membrane lipids and the cytoskeletal matrix on the dynamics of membrane proteins has been studied extensively. However, the effects of extracellular domain (ECD) between various proteins. Through the clever engineering of reconstituted proteins into membranes, Sezgin and his colleagues began to investigate the fundament question of how ECD size and/or glycosylation affects membrane protein mobility and ability to access ordered lipid domains. They discovered that larger ECDs (either through protein mass or glycosylation) diffused slower and were more likely to be excluded from ordered domains. These observations begin to make connections between various models (lipid rafts, kinetic segregation, cytoskeletal compartmentalization) that explain distinct-yet-coupled aspects of how membrane organization controls cell signaling.
“The Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award was created to recognize and honor the groundbreaking work being done by scientists in the early stages of their research careers and the potential for future discoveries in biophysics,” said Vasanthi Jayaraman, Editor-in-Chief. “We congratulate Dr. Sezgin for his research on the role of extracellular domain size in determining location and dynamics in the lipid membrane. This has opened the door to a new mechanism of cell signaling.”
The Biophysical Journal is the Biophysical Society's flagship journal which was first published in 1960 and has been published in partnership with Cell Press since 2009. The journal spans a wide range of subjects and disciplines that provide quantitative insight into fundamental problems at the molecular, cellular, systems, and whole-organism levels.
###
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to lead development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, publications, and committee and outreach activities. Its 7,500 members are located throughout the United States and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-09
In writing a good online dating profile, the average love-seeker is likely to fill it up with all the appealing qualities and interests that make them special. They paraglide and do hot yoga on the weekends; enjoy Riesling on the beach or seeing indie bands in basements; are a Libra with Scorpio rising; or have a dog or three kids or an iguana. There’s one thing they routinely leave out, however: what they want to know about their potential partner.
Yet, that detail might the most important thing to include, according ...
2024-02-09
Snail shells are often colourful and strikingly patterned. This is due to pigments that are produced in special cells of the snail and stored in the shell in varying concentrations. Fossil shells, on the other hand, are usually pale and inconspicuous because the pigments are very sensitive and have already decomposed. Residues of ancient colour patterns are therefore very rare. This makes this new discovery by researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Natural History Museum Vienna (NHMW) all the more astonishing: they found pigments in ...
2024-02-09
There are no substitutes for native vegetation, but replacing large areas of monoculture with diversified crops in places where agricultural activities are widespread can have beneficial effects on the mammals that still inhabit the region.
This is one of the conclusions of a study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) supported by FAPESP. They focused on the northeast of São Paulo state, where the predominant biome is the Cerrado (Brazilian savanna). The region is one of the nation’s agribusiness centers.
An article on the study is published in the Journal of Applied Ecology. The study showed that ...
2024-02-09
Semiconductors are ubiquitous in modern technology, working to either enable or prevent the flow of electricity. In order to understand the potential of two-dimensional semiconductors for future computer and photovoltaic technologies, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen, Marburg and Cambridge investigated the bond that builds between the electrons and holes contained in these materials. By using a special method to break up the bond between electrons and holes, they were able to gain a ...
2024-02-09
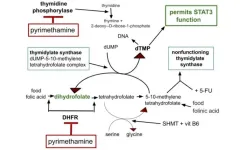
“This paper presents the rationale for adding five already approved and marketed generic drugs from general medical practice to the current standard current first line chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).”
BUFFALO, NY- February 9, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on February 7, 2024, entitled, “IPIAD- an augmentation regimen added to standard treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using already-marketed repurposed drugs irbesartan, pyrimethamine, itraconazole, azithromycin, and dapsone.”
In this new paper, researcher Richard E. Kast from IIAIGC Study Center presents the ...
2024-02-09
SAN ANTONIO, Feb. 9, 2024 – The UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry has opened a special-care dental clinic, the first of its kind in an academic setting in South Texas that will serve people of all ages with intellectual, developmental, cognitive or physical disabilities.
With spacious, specially designed treatment rooms featuring adjustable sound and lighting and even a “Zen Den” multi-sensory room to help reduce anxiety, the Phil and Karen Hunke Special Care Clinic occupies approximately ...
2024-02-09
MIT engineers have developed a small ultrasound sticker that can monitor the stiffness of organs deep inside the body. The sticker, about the size of a postage stamp, can be worn on the skin and is designed to pick up on signs of disease, such as liver and kidney failure and the progression of solid tumors.
In an open-access study that will appear in Science Advances, the team reports that the sensor can send sound waves through the skin and into the body, where the waves reflect off internal organs and back out to the sticker. The pattern of the reflected waves can be read as ...
2024-02-09
New Haven, Conn. — A Yale-led research team has picked a side in the “Snowball Earth” debate over the possible cause of planet-wide deep freeze events that occurred in the distant past.
According to a new study, these so-called “Snowball” Earth periods, in which the planet’s surface was covered in ice for thousands or even millions of years, could have been triggered abruptly by large asteroids that slammed into the Earth.
The findings, detailed in the journal Science Advances, may answer a question ...
2024-02-09
Researchers have developed a sensor made from ‘frozen smoke’ that uses artificial intelligence techniques to detect formaldehyde in real time at concentrations as low as eight parts per billion, far beyond the sensitivity of most indoor air quality sensors.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, developed sensors made from highly porous materials known as aerogels. By precisely engineering the shape of the holes in the aerogels, the sensors were able to detect the fingerprint of formaldehyde, a common indoor air pollutant, at room temperature.
The proof-of-concept sensors, which require minimal power, could be adapted to detect ...
2024-02-09
CLEVELAND—University Hospitals (UH) Brain Health & Memory Center is now treating patients with LEQEMBI® (lecanemab), a Food and Drug Administration-approved medication for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
“Those with Alzheimer’s disease often have an abnormal buildup of plaques in their brain that contain a protein called beta-amyloid,” said Charles J. Duffy, MD, PhD, neurologist and Director of the Brain Health & Memory Center within the UH Neurological Institute. “Lecanemab ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The Biophysical Journal names Erdinc Sezgin the 2023 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Awardee