(Press-News.org) Marine heatwaves will become a regular occurrence in the Arctic in the near future and are a product of higher anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emissions – as shown in a study just released by Dr. Armineh Barkhordarian from Universität Hamburg’s Cluster of Excellence for climate research CLICCS.
Since 2007, conditions in the Arctic have shifted, as confirmed by data recently published in the journal Nature Communications Earth & Environment. Between 2007 and 2021, the marginal zones of the Arctic Ocean experienced 11 marine heatwaves, producing an average temperature rise of 2.2 degrees Celsius above seasonal norm and lasting an average of 37 days. Since 2015, there have been Arctic marine heatwaves every year.
The most powerful heatwave to date in the Arctic Ocean was in 2020; it continued for 103 days, with peak temperatures intensity that were four degrees Celsius over the long-term average. The probability of such a heatwave occurring without the influence of anthropogenic greenhouse gases is less than one percent, as calculated by Barkhordarian’s team at the Cluster of Excellence CLICCS. By doing so, they have narrowed down the number of plausible climate scenarios in the Arctic. According to the study, annual marine heatwaves will be the norm.
The Arctic entered a new phase
In the study, Barkhordarian also proves for the first time that heatwaves are produced when sea ice melts early and rapidly after the winter. When this happens, considerable heat energy can accumulate in the water by the time maximum solar radiation is reached in July.
“In 2007, a new phase began in the Arctic,” says Barkhordarian, an expert on climate statistics. “There is less and less of the thicker, several-year-old ice, while the percentage of thin, seasonal ice is consistently increasing.” However, the thin ice is less durable and melts more quickly, allowing incoming solar radiation to warm the water’s surface.
Officially, it is considered to be a marine heatwave when temperatures at the water’s surface are higher than 95 percent of the values from the past 30 years for at least five consecutive days.
“Not just the constant loss of sea ice but also warmer waters can have dramatic negative effects on the Arctic ecosystem,” says Barkhordarian. Food chains could collapse, fish stocks could be reduced, and overall biodiversity could decline.
Background:
Are human beings responsible? Attribution research allows us to compare how the world would have developed without human influences. For the study at hand, the calculations focused on the probability of each heatwave occurring in a world without anthropogenic greenhouse gases. In addition, Barkhordarian and her team reviewed satellite data and drew on coupled climate models for their analyses.
END
Frequent marine heatwaves in the Arctic Ocean will be the norm
2024-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Greenland’s ice sheet is melting - and being replaced by vegetation
2024-02-13
University of Leeds Press Release
Under embargo until 10:00 GMT on 13 February
There are graphics and photographic images that help explain this story – see under Note to editors
Greenland’s ice sheet is melting - and being replaced by vegetation
An estimated 11,000 sq miles or 28,707 sq kilometres of Greenland’s ice sheet and glaciers have melted over the last three decades, according to a major analysis of historic satellite records.
The total area of ice loss is equivalent to the size of Albania, and represents about 1.6 % of Greenland’s ...
New Durham University research opens avenues for more efficient and stable blue OLED displays
2024-02-13
-With pictures-
A new research from scientists at Durham University reveals an unexpected pathway towards brighter, more efficient, and more stable blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
The findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics could help enable the next generation of energy-saving display technologies.
OLED displays, used in most modern smartphones and TVs, rely on light emission from specialised organic molecules.
Obtaining stable, efficient blue emission suitable for displays remains a key challenge.
Now, Durham ...
Study finds childhood bullying linked to distrust and mental health problems in adolescence
2024-02-13
A new study, co-led by UCLA Health and the University of Glasgow, found that young teenagers who develop a strong distrust of other people as a result of childhood bullying are substantially more likely to have significant mental health problems as they enter adulthood compared to those who do not develop interpersonal trust issues.
The study, published in the journal Nature Mental Health on Feb. 13, is believed to be the first to examine the link between peer bullying, interpersonal distrust, and the subsequent development of mental health problems, such as anxiety, depression, hyperactivity and anger.
Researchers ...
Compounds released by bleaching reefs promote bacteria, potentially stressing coral further
2024-02-13
On healthy reefs around the world, corals, algae, fishes and microbes live interconnected and in balance—exchanging nutrients, resources, and chemical signals. New research led by the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa and and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) revealed that when coral bleaching occurs, corals release unique organic compounds into the surrounding water that not only promote bacterial growth overall, but select for opportunistic bacteria that may further stress reefs.
“Our results demonstrate how the impacts of both short-term thermal ...
Short corrective comments can help social media user to spot false information, study shows
2024-02-13
Short and simple comments from ordinary social media users can help others online to spot fake news, a new study shows.
Research shows reading corrections from others online can reduce the perceived accuracy of and engagement with incorrect content.
Experts found the format and strength of corrective comments do not matter much. Social media users do not need to write long and detailed comments to flag false content.
While the study shows the general effectiveness of social correction, it also finds ...
Biomarker-directed combination effective in immunotherapy-resistant lung cancer
2024-02-13
HOUSTON ― A specific combination of targeted therapy and immunotherapy may better help patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) overcome inherent immune resistance and reinvigorate anti-tumor activity, according to a new study led by a researcher from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase II umbrella HUDSON study, published today in Nature Medicine, demonstrated that the anti PD-L1 antibody, durvalumab, coupled with the ATR inhibitor, ceralasertib, provided the greatest clinical benefit of four combinations evaluated.
This pair had an objective response ...
Plant-based diet tied to improved sexual health in men treated for prostate cancer
2024-02-13
A diet that limits meat and dairy but is rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and nuts is linked to less erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, and other common side effects seen in prostate cancer patients, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, the analysis of more than 3,500 men with prostate cancer explored whether eating a more plant-based diet was associated with quality-of-life issues that often arise after treatment. Sorting patients into five groups (quintiles) based on the proportion of plant versus animal foods the men said they eat, the authors found ...
Quality of care for patients who call 911 varies greatly across the United States, study finds
2024-02-13
Emergency medical service (EMS) systems are not consistently providing optimal care based on new national standards of quality to patients who call 911, according to a new study from the Icahn School of Medicine of Mount Sinai.
The study demonstrates that EMS performance on key clinical and patient safety measures varies widely across urban and rural communities. The findings, published in the peer-reviewed Prehospital Emergency Care, identify opportunities that could lead to improved care during 911 responses and improved outcomes for patients across the United States.
“EMS systems in the United States have traditionally relied ...
CRISPR-copies: New tool accelerates and optimizes genome editing
2024-02-13
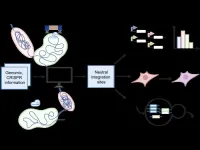
CRISPR/Cas systems have undergone tremendous advancement in the past decade. These precise genome editing tools have applications ranging from transgenic crop development to gene therapy and beyond. And with their recent development of CRISPR-COPIES, researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) are further improving CRISPR’s versatility and ease of use.
“CRISPR-COPIES is a tool that can quickly identify appropriate chromosomal integration sites for genetic engineering in any organism,” said Huimin Zhao, CABBI Conversion Theme Leader ...
Teenagers need better reproductive health education to tackle parenthood fears
2024-02-13
Nearly half of teenagers are worried about having children and many lack knowledge about their reproductive health, find two new studies by UCL researchers.
The studies, published in Human Fertility and Health Education Journal, used survey results from 931 students in England aged 16 to 18, collected between May 2021 and July 2022.
The Human Fertility paper found that a majority of students (64%) still wanted to have children in the future – with nearly half (49%) desiring to have two children.
However, 45% of all participants said that they had concerns about future ...