(Press-News.org) ETRI’s researchers have developed an AI-powered e-sports analysis platform that provides real-time win rate prediction services by analyzing gameplay screens. This platform was notably applied to the highly popular League of Legends (LoL) during a recent international e-sports tournament, garnering positive feedback.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) has developed a technology that recognizes real-time game situations by analyzing play elements extracted from game videos and automatically generates highlights by identifying key play events in the game.
Also, this e-sports service platform, based on AI, not only records gamer profiles from gameplay data but also suggests corresponding play strategies. Overcoming dependence on traditional game developers, paves the way for expansion across various game genres, significantly aiding in the creation of new services and commercialization.
Unlike previous services that were limited to commentary-focused broadcasting due to restricted access to game developer APIs, the research team has developed technology that provides various predictive information in addition to key gameplay indicators through real-time game screen analysis.
The e-sports service platform developed by ETRI offers a suite of software technologies for various game genres, including real-time game situation recognition, automatic highlight generation, gamer profile creation, and play strategy recommendations, all in real-time.
This platform marks a global first in providing real-time win rate prediction technology based on video analysis at an international e-sports tournament. By developing a prediction model that takes into account the specific characteristics of different game phases, it has achieved over 87% accuracy in predictions.
Additionally, the researchers have developed a service for automatically generating game highlights by leveraging technology to recognize key in-game events. Unlike existing services, this allows users to select highlight content based on their preferences, offering versatile applications.
ETRI has developed technology capable of analyzing large-scale play data to create not only individual gamer profiles but also team-level profiles. This innovation enables the recommendation of precise and systematic training programs, extending even to the provision of multifaceted play strategies.
This technology was transferred to Loud Corporation and provided at various events last year, including the 15th Presidential Cup Amateur E-sports Tournament, the 2023 E-sports University League, and the 2023 Korea-China-Japan E-sports Tournament. Furthermore, plans are in place to soon introduce an automatic highlight generation service to the market.
Looking ahead, ETRI plans to develop an e-sports service operation automation platform aimed at supporting small and medium-sized enterprises, as well as local e-sports venues, which are facing challenges in securing human resources and developing new services.
Kim Kyung-hwa, the Director of the Cultural Industry Policy Office at the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, stated, “As the global e-sports industry is experiencing significant growth and its influence on other industries is increasing, we plan to actively support the discovery of creative service models through the convergence of new technologies to secure a leading position in the industry.”
Jung Il-kwon, assistant vice president of ETRI’s Content Research Division, also noted, “The real-time win rate prediction technology applied at the 2023 Korea-China-Japan E-sports Tournament operates independently of the game developers’ APIs, showcasing excellent scalability. We plan to apply this technology to various genres of e-sports, providing an enjoyable viewing experience for the audience and contributing to the revitalization of e-sports broadcasting services.”
###
This research was developed as a part of the “Game Now: E-Sports Services using AI-based Real-time Game Technology” project, sponsored by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
ETRI is a non-profit government-funded research institute. Since its foundation in 1976, ETRI, a global ICT research institute, has been making its immense effort to provide Korea a remarkable growth in the field of ICT industry. ETRI delivers Korea as one of the top ICT nations in the World, by unceasingly developing world’s first and best technologies.
END
ETRI unveils AI analysis service platform at international e-sports tournament
Achieves independency on game vendors and scalability through analysis of game screens. Attains an 87% accuracy rate in match predictions, receiving significant acclaim when applied to the international League of Legends (LoL) tournament
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pancreatic cancer hijacks a brain-building protein
2024-02-14
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) and the University of California, Davis have reached a new breakthrough in pancreatic cancer research—eight years in the making. It could help slow the disease’s deadly spread.
In 2017, as a postdoc in CSHL’s Tuveson lab, Chang-il Hwang and collaborators from the Vakoc lab uncovered a protein essential for jumpstarting metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Now an assistant professor at UC Davis, Hwang recently reunited with CSHL Professors David Tuveson and Christopher Vakoc. The trio once again set their sights on PDAC. The disease is known for its aggressiveness. ...
Pesticides to help protect seeds can adversely affect earthworms’ health
2024-02-14
While pesticides protect crops from hungry animals, pesky insects, or even microbial infections, they also impact other vital organisms, including bees and earthworms. And today, research published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters reveals that worms are affected by the relatively small amounts of chemicals that can leach out of pesticide-treated seeds. Exposure to nonlethal amounts of these insecticides and fungicides resulted in poor weight gain and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage in the worms.
Pesticide treatment can be introduced at several different ...
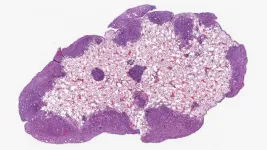
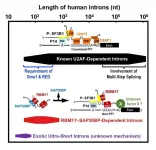
Discovery of a subset of human short introns that are spliced out by a novel mechanism
2024-02-14
In humans, the length of pre-mRNA varies extensively (from 30 to 1,160,411 nucleotides by recent studies). The fundamental mechanism of splicing has been studied with model pre-mRNAs including 158- and 231-nt introns, for historical instance, that are spliced very efficiently in vitro and in vivo. Such an ideal pre-mRNA contains good splicing signal sequences, i.e., the 5′ splice site, the branch-site (BS) sequence, and the polypyrimidine tract (PPT) followed by the 3′ splice site that are recognized by U1 snRNP, U2 snRNP and U2AF2–U2AF1, respectively. Prof. Mayeda says, “Given the diverse lengths ...
Cold-water coral traps itself on mountains in the deep sea
2024-02-14
Corals searching for food in the cold and dark waters of the deep sea are building higher and higher mountains to get closer to the source of their food. But in doing so, they may find themselves trapped when the climate changes. That is shown in the thesis that theoretical ecologist Anna van der Kaaden of NIOZ in Yerseke and the Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development in Utrecht will defend on Feb. 20 at the University of Groningen. “When the water gets warmer, these creatures prefer to be deeper, but a coral doesn’t just walk down the mountain,” Van der Kaaden said.
Deep and dark
Unlike the famous, colorful tropical corals, cold-water corals live ...
Cost-effective to routinely change surgical gloves and instruments as well as being safer
2024-02-14
Surgeons who routinely change surgical gloves and instruments are incurring similar costs to those using the same equipment, a new study has found.
The economic evaluation funded by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) follows a clinical trial conducted at 80 hospitals in Benin, Ghana, India, Mexico, Nigeria, Rwanda, and South Africa which established that routine change of gloves and instruments reduces surgical site infections (SSIs) by 13%.
The evaluation, published by the Lancet Global ...
Scientists discover hidden army of lung flu fighters
2024-02-14
Scientists have long thought of the fluid-filled sac around our lungs merely as a cushion from external damage. Turns out, it also houses potent virus-eating cells that rush into the lungs during flu infections.
Not to be confused with phages, which are viruses that infect bacteria, these cells are macrophages, immune cells produced in the body.
“The name macrophage means ‘big eater.’ They gobble up bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, and dying cells. Really, anything that looks foreign, they take it up and destroy it,” said UC Riverside virologist Juliet Morrison, who led the discovery team. “We were surprised to find them in the lungs ...
USC announces new Leonard D. Schaeffer Institute for Public Policy & Government Service
2024-02-14
USC, together with Leonard and his late wife Pamela Schaeffer, is launching a new institute with a $59 million gift from the Schaeffers to be anchored in Los Angeles and in the university’s new Capital Campus in Washington, D.C. The mission of the Leonard D. Schaeffer Institute for Public Policy & Government Service is to strengthen democracy by training generations of public leaders and advancing evidence-based research to shape policy that addresses the nation’s most pressing issues, USC President Carol Folt announced ...
Nearly 15% of Americans deny climate change is real, AI study finds
2024-02-14
ANN ARBOR—Using social media data and artificial intelligence in a comprehensive national assessment, a new University of Michigan study reveals that nearly 15% of Americans deny that climate change is real.
Scientists have long warned that a warming climate will cause communities around the globe to face increasing risks due to unprecedented levels of flooding, wildfires, heat stress, sea-level rise and more. Though the science is sound—even showing that human-induced, climate-related natural disasters are growing in frequency ...
Red nets signal “stop” to insect pests, reduce need for insecticides
2024-02-14
Red nets are better at keeping away a common agricultural insect pest than typical black or white nets, according to a new study. Researchers experimented with the effect of red, white, black and combination-colored nets on deterring onion thrips from eating Kujo leeks, also called Welsh onions. In both lab and field tests, red nets were significantly better at deterring the insect than other colors. Also, in field tests, onion crops which were either partially or fully covered by red netting required 25-50% less insecticide than was needed for a totally uncovered field. Changing agricultural nets from black or white to red could help reduce pesticide ...
AI tool predicts function of unknown proteins
2024-02-14
A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that draws logical inferences about the function of unknown proteins promises to help scientists unravel the inner workings of the cell.
Developed by KAUST bioinformatics researcher Maxat Kulmanov and colleagues, the tool outperforms existing analytical methods for forecasting protein functions and is even able to analyze proteins with no clear matches in existing datasets[1].
The model, termed DeepGO-SE, takes advantage of large language models similar to those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
[Press-News.org] ETRI unveils AI analysis service platform at international e-sports tournamentAchieves independency on game vendors and scalability through analysis of game screens. Attains an 87% accuracy rate in match predictions, receiving significant acclaim when applied to the international League of Legends (LoL) tournament