(Press-News.org) For his work in furthering the understanding of how the human immune system senses dangerous invading pathogens, Bingxu Li has received the 2024 Michelson Philanthropies & Science Prize for Immunology. Li’s prize-winning essay investigates the role that Stimulator of Interferon Genes, or STING, plays in including multiple distinct defenses against viruses, bacteria, and tumors and in orchestrating myriad downstream responses upon activation – resolving a significant mystery in the field of innate immunity. The sensing and clearance of invading pathogens are crucial to the survival of living systems, ranging from bacteria to humans. This is accomplished by an intricate web of innate immune receptors that detect pathogen-specific molecules called pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS). Once activated, these receptors trigger downstream immune responses designed to defend against the invading pathogen. However, some sensors exhibit additional behaviors upon activation. For example, activation of STING – a well-known human immune sensor – not only induces inflammation, but also triggers non-canonical autophagy, inflammasome activation, and cell death, thus inducing multiple defenses against different types of pathogens. How STING controls these diverse downstream responses has remained unknown. Using various genetic, biochemical, and structural tools, Li and his colleagues at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology discovered that human STING plays a surprising role as an ion channel. To the author’s knowledge, it is the first ion channel that is known to sense danger in mammalian cells. Furthermore, the discovery hints at the adaptability of innate immune proteins like STING, suggesting that they have evolved to acquire diverse new functions over time, without drastic changes.
Finalists for the prize were Gabriele Casirati for his essay “Stem cells in disguise: How epitope editing can empower targeted cancer immunotherapies,” and Carla Nowosad for her essay “Who goes there? How B cells assess risk in the intestine.”
END
Prizewinner’s research unveils STING as a pivotal immune sensor channel
2024-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers observe highly excited ‘roaming’ energy pathway in chemical reactions
2024-02-15
Scientists have observed so-called 'roaming' chemical reactions, those that at certain points move away from the lowest minimum energy 'path of least resistance', in highly excited energy states for the first time.
Chemical reactions are supposed to occur along their minimum energy paths. In recent years, so-called roaming reactions that stray far from this path have begun to be observed, but only for chemical species in their ground state or, at most, their first excited state. However, researchers have now observed a roaming reaction even in highly excited energy states.
The researchers ...
MSU, Carnegie Science introduce a big new idea with the help of tiny plankton
2024-02-15
Researchers at Michigan State University and the Carnegie Institution for Science have developed a model that connects microscopic biology to macroscopic ecology, which could deepen our understanding of nature’s laws and create new opportunities in ecosystem management.
Reporting in the journal Science on Feb. 16, the team showed how microscopic relationships in plankton — such as between an organism’s size and nutrient consumption — scales up to predictably affect food webs.
“Using data that other researchers have measured at the microscale about these organisms, our model can predict what’s happening at the scale of whole ecosystems,” said Jonas ...
First-ever atomic freeze-frame of liquid water
2024-02-15
RICHLAND, Wash.—In an experiment akin to stop-motion photography, scientists have isolated the energetic movement of an electron while “freezing” the motion of the much larger atom it orbits in a sample of liquid water.
The findings, reported today in the journal Science, provide a new window into the electronic structure of molecules in the liquid phase on a timescale previously unattainable with X-rays. The new technique reveals the immediate electronic response when a target is hit with an X-ray, an important step in understanding the effects of radiation exposure on objects and people.
“The chemical reactions induced by radiation ...
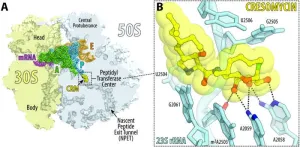
Superbug killer: New synthetic molecule highly effective against drug-resistant bacteria
2024-02-15
A new antibiotic created by Harvard researchers overcomes antimicrobial resistance mechanisms that have rendered many modern drugs ineffective and are driving a global public health crisis.
A team led by Andrew Myers, Amory Houghton Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, reports in Science that their synthetic compound, cresomycin, kills many strains of drug-resistant bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
“While we don’t yet know whether cresomycin and drugs like it are safe ...
With just a little electricity, MIT researchers boost common catalytic reactions
2024-02-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA — A simple technique that uses small amounts of energy could boost the efficiency of some key chemical processing reactions, by up to a factor of 100,000, MIT researchers report. These reactions are at the heart of petrochemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and many other industrial chemical processes.
The surprising findings are reported today in the journal Science, in a paper by MIT graduate student Karl Westendorff, professors Yogesh Surendranath and Yuriy Roman-Leshkov, and two others.
“The results are really striking,” says Surendranath, a professor of chemistry ...
Keeping telomerase in check
2024-02-15
The natural ends of chromosomes appear alarmingly like broken DNA, much as a snapped spaghetti strand is difficult to distinguish from its intact counterparts. Yet every cell in our bodies must have a way of differentiating between the two because the best way to protect the healthy end of a chromosome also happens to be the worst way to repair damaged DNA.
Consider the enzyme telomerase, which is responsible for maintaining protective telomeres at the natural ends of chromosomes. Were telomerase to seal off a broken strand of DNA with a telomere, it would prevent further repair of that break and delete essential genes. Now, a new study in Science describes how cells avoid ...
Competition for food drives the planet’s remaining mass migration of herbivores
2024-02-15
Upending the prevailing theory of how and why multi-species mass-migration patterns occur in Serengeti National Park, researchers from Wake Forest University have confirmed that the millions-strong wildebeest population pushes zebra herds along in competition for the most nutrient-dense grasses.
The study resulting from this research, “Interplay of competition and facilitation in grazing succession by migrant Serengeti herbivores,” appears today in the peer-reviewed journal Science.
For decades, biologists have believed the major grazing ...
UT Dallas Wind Energy Center to expand with new headquarters, resources
2024-02-15
The University of Texas at Dallas’ wind energy research programs have expanded rapidly in recent years, with labs, offices and facilities spread out on campus. In 2020 UT Dallas formed the Wind Energy Center, called UTD Wind, to bring its wind energy programs under one virtual umbrella.
Now, a new initiative will give UTD Wind a physical headquarters for the first time with additional labs, meeting areas and office space. The project also includes additional equipment for wind energy research and education.
UT Dallas has received $1.6 million through the federal Consolidated Appropriations Act to support the expansion, which will bring most of the center’s ...
More Aston University scholarships to encourage graduates from under-represented groups to work in artificial intelligence
2024-02-15
• Eleven scholarships worth £10k each for MSc Applied AI
• They are funded by the Office for Students (OfS)
• Aimed at graduates without a science, tech, engineering or maths degree.
Aston University is offering more opportunities to graduates who want a career in artificial intelligence (AI) but don’t have a science, technology, engineering or maths degree.
The scholarships are offered due to increased funding from the Office for Students (OfS). Each award is worth £10,000 and will be awarded to students enrolling ...
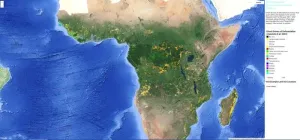
How is deforested land in Africa used?
2024-02-15
Africa's forested areas – an estimated 14 % of the global forest area – are continuing to decline at an increasing rate – mostly because of human activities to convert forest land for economic purposes. As natural forests are important CO2 and biodiversity reservoirs, this development has a significant impact on climate change and effects the integrity of nature. To intervene in a targeted manner in the interests of climate protection and biodiversity, there has been a lack of sufficiently good data and detailed knowledge ...