(Press-News.org) How can humans protect the Earth from “devastating asteroid and comet impacts?” According to the National Academies and their 2023-2032 Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey, ground based astronomical radar systems will have a “unique role” to play in planetary defense.
There is currently only one system in the world concentrating on these efforts, NASA’s Goldstone Solar System Radar, part of the Deep Space Network (DSN). However, a new instrument concept from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) called the next generation RADAR (ngRADAR) system will use the National Science Foundation’s Green Bank Telescope (GBT) and other current and future facilities to expand on these capabilities.
“There are many applications for the future of radar, from substantially advancing our knowledge of the Solar System, to informing future robotic and crewed spaceflight, and characterizing hazardous objects that stray too close to Earth,” shares Tony Beasley, NRAO’s director.
On Saturday, February 17th, scientists will showcase recent results obtained with ground-based radar systems at the American Association for the Advancement of Science’s annual conference in Denver, Colorado.
“NRAO, with the support of the National Science Foundation and oversight by Associated Universities, Inc., has a long history of using radar to further our understanding of the Universe. Most recently the GBT helped confirm the success of NASA’s DART mission, the first test to see if humans could successfully alter the trajectory of an asteroid, “ shares NRAO scientist and ngRADAR project director Patrick Taylor.
The GBT is the world’s largest fully steerable radio telescope. The maneuverability of its 100-meter dish enables it to observe 85 percent of the celestial sphere, allowing it to quickly track objects across its field of view. Adds Taylor, “With the support of Raytheon Technologies, ngRADAR pilot tests on the GBT—using a low-power transmitter with less output than a standard microwave oven—have produced the highest-resolution images of the Moon ever taken from Earth. Imagine what we could do with a more powerful transmitter.”
Scientists sharing their results at AAAS include Edgard G. Rivera-Valentín of Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and Marina Brozović of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages Goldstone and the DSN. Adds Brozović, “The public might be surprised to learn that the technology we use in our current radar at Goldstone hasn’t changed much since World War II. For 99% of our observations, we transmit and receive from this one antenna. New radar transmitter designs, like ngRADAR on the GBT, have the potential to significantly increase the output power and waveform bandwidth, allowing for even higher resolution imaging. It will also produce a scalable and more robust system by using telescope arrays to increase the collecting area.”
“NRAO is an ideal organization to lead these efforts because of the instruments we have available to receive radar signals, like the Very Long Baseline Array has done in our pilot ngRADAR project,” explains Brian Kent, NRAO scientist and director of science communications, who coordinated the presentation at AAAS, “Future facilities like the next generation Very Large Array, as a receiver, will create a powerful combination for planetary science.”
How does ground-based astronomical radar expand our understanding of the Universe? By allowing us to study our nearby Solar System, and everything in it, in unprecedented detail. Radar can reveal the surface and ancient geology of planets and their moons, letting us trace their evolution. It can also determine the location, size, and speed of potentially hazardous Near Earth Objects, like comets or asteroids. Advances in astronomical radar are opening new avenues, renewed investment, and interest in joint industry and scientific community collaborations as a multidisciplinary venture.
About NRAO & GBO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
The Green Bank Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation and is operated by Associated Universities, Inc.
END
Can astronomers use radar to spot a cataclysmic asteroid?
Scientists share their latest findings and the future of radar in planetary science and defense
2024-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Self-monitoring improves physical activity of care-needing elderly
2024-02-16
Self-monitoring of physical activity with an accelerometer and feedback is an effective tool to improve physical activity in elderly people requiring long-term support. The Kobe University study is the first to show that with simple and safe means the physical activity of this demographic can be improved, which is expected to help prevent serious illness and reduce costs for long-term care.
Taking more steps and sitting less is well known as having a significant influence on a wide range of noncommunicable diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, orthopedic diseases and stroke. This is particularly problematic in senior citizens who depend on long-term care such as in day-care ...
WVU close to commercializing microwave technology that can cool down industry’s energy usage
2024-02-16
West Virginia University engineers have secured $3 million in U.S. Department of Energy funding to research a new chemical reactor system that uses microwaves to reduce industrial heat and carbon emissions.
The first-of-its-kind technology would allow industrial facilities to simultaneously produce ethylene and ammonia, two chemicals that contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, within a single microwave reactor. That device uses heat from microwave electromagnetic radiation to carry out chemical reactions.
The ...
New Issue of GEN Biotechnology
2024-02-16
GEN Biotechnology announces the publication of its February 2024 issue. GEN Biotechnology publishes outstanding peer-reviewed research and perspectives in all aspects of biotechnology. The Journal, led by Editor-in-Chief Hana El-Samad, PhD (UCSF; Altos Labs) and Executive Editor Kevin Davies, PhD, is published bimonthly in print and online.
For full-text copies of articles or to arrange interviews with Dr. El-Samad, Dr. Davies, authors, or members of the editorial board, contact Kathryn Ryan at the Publisher.
1. Original Research: ...
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed
2024-02-16
Penn Engineers have developed a new chip that uses light waves, rather than electricity, to perform the complex math essential to training AI. The chip has the potential to radically accelerate the processing speed of computers while also reducing their energy consumption.
The silicon-photonic (SiPh) chip’s design is the first to bring together Benjamin Franklin Medal Laureate and H. Nedwill Ramsey Professor Nader Engheta’s pioneering research in manipulating materials at the nanoscale to perform mathematical computations using light ...
Study shows impact of antidepressants on fetal brain development during pregnancy
2024-02-16
A new study published in Nature Communications provides direct evidence that antidepressant use during pregnancy can impact a child’s brain development and contribute to the risk of mental health disorders later in life.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, focused on the effect of fluoxetine, commonly used in medications such as Prozac and Sarafem for treating depression and perinatal depression, on a developing prefrontal cortex.
Since fluoxetine works by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, the researchers looked at the impact serotonin has on prefrontal ...
First human trial shows ‘wonder’ material can be developed safely
2024-02-16
A revolutionary nanomaterial with huge potential to tackle multiple global challenges could be developed further without acute risk to human health, research suggests.
Carefully controlled inhalation of a specific type of graphene – the world’s thinnest, super strong and super flexible material – has no short-term adverse effects on lung or cardiovascular function, the study shows.
The first controlled exposure clinical trial in people was carried out using thin, ultra-pure ...
Towards more efficient catalysts
2024-02-16
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Harvard Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology, and Utrecht University have reported on a previously elusive way to improve the selectivity of catalytic reactions, adding a new method of increasing the efficacy of catalysts for a potentially wide range of applications in various industries including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and much more.
The research is published in ...
Laboratory study on conditions for spontaneous excitation of "chorus emission," wave of space plasma
2024-02-16
A dipole magnetic field, created by a ring current, is the most fundamental type of magnetic field that is found both in laboratories and in space. Planetary magnetospheres, such as Jupiter's, effectively confine plasma. The RT-1 project aims to learn from nature and create a magnetosphere-type high-performance plasma to realize advanced fusion energy. Simultaneously, the artificial magnetosphere offers a means to experimentally understand the mechanisms of natural phenomena in a simplified and controlled ...
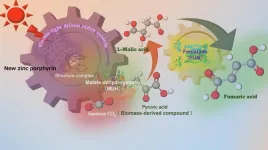
Advanced artificial photosynthesis catalyst uses CO2 more efficiently to create biodegradable plastics
2024-02-16
Amid growing global concern over climate change and plastic pollution, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are making great strides in the sustainable production of fumaric acid – a component of biodegradable plastics such as polybutylene succinate, which is commonly used for food packaging. The researchers have managed to efficiently produce fumaric acid, which is traditionally derived from petroleum, using renewable resources, carbon dioxide, and biomass-derived compounds.
In a previous study, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao of the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at ...
Mystery solved: the oldest fossil reptile from the alps is an historical forgery
2024-02-16
A 280-million-year-old fossil that has baffled researchers for decades has been shown to be, in part, a forgery following new examination of the remnants.
The discovery has led the team led by Dr Valentina Rossi of University College Cork, Ireland (UCC) to urge caution in how the fossil is used in future research.
Tridentinosaurus antiquus was discovered in the Italian alps in 1931 and was thought to be an important specimen for understanding early reptile evolution.
Its body outline, appearing dark against the surrounding rock, was initially interpreted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] Can astronomers use radar to spot a cataclysmic asteroid?Scientists share their latest findings and the future of radar in planetary science and defense