(Press-News.org) Penn Engineers have developed a new chip that uses light waves, rather than electricity, to perform the complex math essential to training AI. The chip has the potential to radically accelerate the processing speed of computers while also reducing their energy consumption.
The silicon-photonic (SiPh) chip’s design is the first to bring together Benjamin Franklin Medal Laureate and H. Nedwill Ramsey Professor Nader Engheta’s pioneering research in manipulating materials at the nanoscale to perform mathematical computations using light — the fastest possible means of communication — with the SiPh platform, which uses silicon, the cheap, abundant element used to mass-produce computer chips.
The interaction of light waves with matter represents one possible avenue for developing computers that supersede the limitations of today’s chips, which are essentially based on the same principles as chips from the earliest days of the computing revolution in the 1960s.
In a paper in Nature Photonics, Engheta’s group, together with that of Firooz Aflatouni, Associate Professor in Electrical and Systems Engineering, describes the development of the new chip. “We decided to join forces,” says Engheta, leveraging the fact that Aflatouni’s research group has pioneered nanoscale silicon devices.
Their goal was to develop a platform for performing what is known as vector-matrix multiplication, a core mathematical operation in the development and function of neural networks, the computer architecture that powers today’s AI tools.
Instead of using a silicon wafer of uniform height, explains Engheta, “you make the silicon thinner, say 150 nanometers,” but only in specific regions. Those variations in height — without the addition of any other materials — provide a means of controlling the propagation of light through the chip, since the variations in height can be distributed to cause light to scatter in specific patterns, allowing the chip to perform mathematical calculations at the speed of light.
Due to the constraints imposed by the commercial foundry that produced the chips, Aflatouni says, this design is already ready for commercial applications, and could potentially be adapted for use in graphics processing units (GPUs), the demand for which has skyrocketed with the widespread interest in developing new AI systems. “They can adopt the Silicon Photonics platform as an add-on,” says Aflatouni, “and then you could speed up training and classification.”
In addition to faster speed and less energy consumption, Engheta and Aflatouni’s chip has privacy advantages: because many computations can happen simultaneously, there will be no need to store sensitive information in a computer’s working memory, rendering a future computer powered by such technology virtually unhackable. “No one can hack into a non-existing memory to access your information,” says Aflatouni.
This study was conducted at the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied science and supported in part by a grant from the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research’s (AFOSR) Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative (MURI) to Engheta (FA9550-21-1-0312) and a grant from the U.S. Office of Naval Research (ONR) to Afaltouni (N00014-19-1-2248).
Other co-authors include Vahid Nikkhah, Ali Pirmoradi, Farshid Ashtiani and Brian Edwards of Penn Engineering.
END
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed
2024-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows impact of antidepressants on fetal brain development during pregnancy
2024-02-16
A new study published in Nature Communications provides direct evidence that antidepressant use during pregnancy can impact a child’s brain development and contribute to the risk of mental health disorders later in life.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, focused on the effect of fluoxetine, commonly used in medications such as Prozac and Sarafem for treating depression and perinatal depression, on a developing prefrontal cortex.
Since fluoxetine works by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, the researchers looked at the impact serotonin has on prefrontal ...
First human trial shows ‘wonder’ material can be developed safely
2024-02-16
A revolutionary nanomaterial with huge potential to tackle multiple global challenges could be developed further without acute risk to human health, research suggests.
Carefully controlled inhalation of a specific type of graphene – the world’s thinnest, super strong and super flexible material – has no short-term adverse effects on lung or cardiovascular function, the study shows.
The first controlled exposure clinical trial in people was carried out using thin, ultra-pure ...
Towards more efficient catalysts
2024-02-16
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Harvard Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology, and Utrecht University have reported on a previously elusive way to improve the selectivity of catalytic reactions, adding a new method of increasing the efficacy of catalysts for a potentially wide range of applications in various industries including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and much more.
The research is published in ...
Laboratory study on conditions for spontaneous excitation of "chorus emission," wave of space plasma
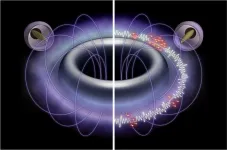
2024-02-16
A dipole magnetic field, created by a ring current, is the most fundamental type of magnetic field that is found both in laboratories and in space. Planetary magnetospheres, such as Jupiter's, effectively confine plasma. The RT-1 project aims to learn from nature and create a magnetosphere-type high-performance plasma to realize advanced fusion energy. Simultaneously, the artificial magnetosphere offers a means to experimentally understand the mechanisms of natural phenomena in a simplified and controlled ...
Advanced artificial photosynthesis catalyst uses CO2 more efficiently to create biodegradable plastics
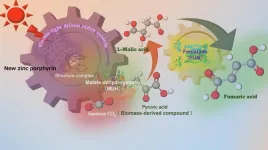
2024-02-16
Amid growing global concern over climate change and plastic pollution, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are making great strides in the sustainable production of fumaric acid – a component of biodegradable plastics such as polybutylene succinate, which is commonly used for food packaging. The researchers have managed to efficiently produce fumaric acid, which is traditionally derived from petroleum, using renewable resources, carbon dioxide, and biomass-derived compounds.
In a previous study, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao of the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at ...
Mystery solved: the oldest fossil reptile from the alps is an historical forgery
2024-02-16
A 280-million-year-old fossil that has baffled researchers for decades has been shown to be, in part, a forgery following new examination of the remnants.
The discovery has led the team led by Dr Valentina Rossi of University College Cork, Ireland (UCC) to urge caution in how the fossil is used in future research.
Tridentinosaurus antiquus was discovered in the Italian alps in 1931 and was thought to be an important specimen for understanding early reptile evolution.
Its body outline, appearing dark against the surrounding rock, was initially interpreted ...
The ties that bind
2024-02-15
Trace metals are nutrient elements, like zinc, that animals and plants need in small amounts to function properly. Animals generally get trace metals in their diets or through environmental exposures, while plants take their trace minerals up from soil. If we get too little, we may experience a deficiency, but the opposite can also be true: too much of a trace metal can be toxic.
Scientists believe that up to 50% of the trace metals in soils and urban environments may be bound to the surfaces of mineral grains — rendering the trace metals ...
New GSA publication addresses dementia care in adults with I/DD
2024-02-15
Addressing Brain Health in Adults With Intellectual Disabilities and Developmental Disabilities: A Companion to the KAER Toolkit for Primary Care Providers is a new publication from the Gerontological Society of America (GSA) designed to address the needs of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD) who develop dementia.
Freely available at geron.org/brainhealth, this companion document:
Raises awareness of unique needs of adults living with I/DD.
Equips and encourages caregivers and health care teams to engage in ...
Inequities in HIV testing, diagnosis and care for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities
2024-02-15
People with disabilities are often at higher risk for exposure to HIV due to barriers in engaging healthcare and other systemic factors and are thus considered a priority for prevention and testing efforts. However, these efforts don’t always extend to people with intellectual disabilities due to the perception that people with intellectual disabilities are mostly asexual.
Researchers at University of Michigan Health conducted one of the largest epidemiological studies of individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities to closely examine where the gaps in HIV care lie and found large disparities in care for Black patients as well as for patients ...
Earthquake fatality measure offers new way to estimate impact on countries
2024-02-15
A new measure that compares earthquake-related fatalities to a country’s population size concludes that Ecuador, Lebanon, Haiti, Turkmenistan, Iran and Portugal have experienced the greatest impact from fatalities in the past five centuries.
The new impact measure, introduced in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America by Max Wyss and colleagues at International Centre for Earth Simulation Foundation, is called the earthquake fatality load or EQFL. The EQFL of a particular earthquake is the ratio of earthquake fatalities to the population estimate for the country in the year of the earthquake.
In their study, Wyss, Michel Speiser ...