(Press-News.org) In this winter of heavy snows--with more on the way this week--nature's bull's-eye might be Oswego, N.Y., and the nearby Tug Hill Plateau.
There the proximity of the Great Lakes whips wind and snow into high gear. Old Man Winter then blows across New York state, burying cities and towns in snowdrifts several feet high. This season, however, something is standing in his way.
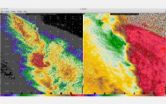
The Doppler-on-Wheels (DOW), a data-collecting radar dish, is waiting. This month and next, scientists inside the DOW are tracking snowstorms in and around Oswego to learn what drives lake-effect snowstorms that form parallel to the long axis of a Great Lake and produce enormous snowfall rates.
These long lake-axis-parallel (LLAP) bands of snow are more intense than those of other snow squalls and produce some of the highest snowfall rates and amounts in the world, say atmospheric scientists Scott Steiger of the State University of New York (SUNY)-Oswego, Jeffrey Frame of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Alfred Stamm of SUNY-Oswego.
"The mobility of a DOW," Steiger says, "is ideal for following lake-effect storms. The DOW will allow us to witness them as they form and cross lakes, which other weather radars can't do."
The DOW, or more properly "DOWs" as there are three, is a National Science Foundation (NSF) atmospheric science facility.
A DOW looks more like the dish of a radio telescope than a sophisticated weather instrument. It's mounted on the back of a flat-bed truck. With a DOW on board, the truck becomes an odd configuration of generator, equipment and operator cabin.
Ungainly as it may appear, it's ideally suited to provide detailed information on the inner workings of snow and other storms, says Josh Wurman, director of the Center for Severe Weather Research (CSWR) in Boulder, Colo.
Wurman should know. He and colleagues developed the first DOW in 1995.
The DOW uses Doppler radar to produce velocity data about severe storms at a distance.
When a DOW is deployed, it collects fine-scale data from within a snowstorm and displays features that can't be seen with more distant radars.
The DOW radars are dual polarization, says Wurman, which means that they send out both horizontally- and vertically-oriented energy. By looking at differences in the energy bounced back from these horizontal and vertical beams, scientists can learn more about the snowflakes, ice, rain and snow pellets in snowbands.
"NSF's dual-polarization DOW radars offer an important new avenue toward better understanding this intense winter weather phenomenon affecting the Great Lakes region," says Brad Smull, program director in NSF's Division of Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences, which funds the DOWs and the LLAP project.
The DOWs measure Doppler winds, snow intensity, and properties related to whether snow is dense, comprised of pellets, or formed from loose collections of traditional six-sided snowflakes. A storm's snow crystal type plays a major role in whether lake-effect snowbands drop a few inches of snow--or more than two feet.
"Understanding snow type is critically important," says Wurman.
The DOWs collect data that will be used to determine how LLAP snowbands intensify and weaken, and move across a region. The scientists are right behind.
"Instead of waiting for snowbands to come to us," says Wurman, "we and the DOWs are going to them."
After forecasting likely snowband events, Steiger, Wurman and colleagues and the DOW drive to one of more than 30 sites near Lake Ontario, Lake Erie, and the Tug Hill Plateau to monitor LLAP snowbands.
During the past week, scientists deployed the DOW to four locations near Oswego and Rochester to study intense snowbands. The bands dropped snow at up to four inches per hour, with final totals of more than two feet.
Initial findings are that intense storm circulations were observed in the bands, and that the snow type changed during the passage of the storm.
More lake effect snows are forecast for this weekend. DOWs and scientists are again heading to New York hilltops to peer inside.
Old Man Winter may have no choice but to give up his secrets.
INFORMATION:
Inside a snowstorm: Scientists obtain close-up look at Old Man Winter
Doppler-on-wheels gives new view of lake-effect snows
2011-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCSD engineers give solar power a boost
2011-01-12
The growing popularity of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems across the United States has made it more important to maximize their power input. That's why UC San Diego environmental engineering professor Jan Kleissl is working on technologies and methods that will better predict how much power we can actually harness from the sun.
In a paper recently published in the journal Renewable Energy (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/09601481), "Optimum fixed orientations and benefits of tracking for capturing solar radiation in the continental United States," Kleissl ...
Researchers show environmental changes may affect vital cooperate bird behaviors
2011-01-12
New York, Jan. 11, 2011 -- While scientists believe that climate change and related extreme weather events such as drought and flooding will likely affect the earth's flora and fauna, just how much is not known. A new study by researchers Walter Jetz from Yale University and Dustin Rubenstein from Columbia University however shows an important link between the natural variation in climate conditions and complex behaviors among birds.
The study, which appears in print in Current Biology on Jan. 11, 2011, has implications for understanding how organisms may respond behaviorally ...
Feast or famine: Researchers identify leptin receptor's sidekick as a target for appetite regulation
2011-01-12
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — A study by researchers at Mayo Clinic's campus in Florida and Washington University School of Medicine adds a new twist to the body of evidence suggesting human obesity is due in part to genetic factors. While studying hormone receptors in laboratory mice, neuroscientists identified a new molecular player responsible for the regulation of appetite and metabolism.
In the Jan. 11 online issue of PLoS Biology, the authors report that mice engineered not to express the lipoprotein receptor LRP1, in the brain's hypothalamus, began to eat uncontrollably, ...
Winter temperatures play complex role in triggering spring budburst
2011-01-12
The opening of buds on Douglas-fir trees each spring is the result of a complex interplay between cold and warm temperatures during the winter, scientists with the U.S. Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Research Station have found.
Their research—which is featured in the December issue of Science Findings, a monthly publication of the station—led to the development of a novel model to help managers predict budburst under different scenarios of future climate.
"We take it for granted that buds will open each spring, but, in spite of a lot of research on winter dormancy ...
10-year roadmap for reaching public health education goals
2011-01-12
San Diego, CA, January 11, 2011 – Launched on December 2, 2010, Healthy People 2020 is an ambitious, science-based, 10-year agenda for improving the health of all Americans. A key component, Education for Health, is an educational roadmap to achieve the Healthy People 2020 goals. Formulated by the Healthy People Curriculum Task Force, this set of new and revised educational objectives provides a vehicle for promoting the discussion and progress that will be needed to achieve an integrated, seamless approach to education for health for the American public as well as for ...
Technique allows researchers to identify key maize genes for increased yield
2011-01-12
ITHACA, N.Y. — Scientists have identified the genes related to leaf angle in corn (maize) – a key trait for planting crops closer together, which has led to an eight-fold increase in yield since the early 1900s. (Nature Genetics, Jan. 9, 2011.)
The study, led by researchers from Cornell and the U.S. Department of Agriculture – Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS) at Cornell and North Carolina State University, is the first to relate genetic variation across the entire maize genome to traits in a genomewide association study. The researchers have so far located 1.6 ...
Link between fracture prevention and treatment adherence not fully understood by patients
2011-01-12
Newly released findings of a multinational survey conducted on behalf of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) show clear disparities between patients' and doctors' perceptions of osteoporosis and its management.
The 13-country survey of 844 postmenopausal patients over 55 years of age and 837 doctors investigated gaps between patient and doctor understanding of the emotional and physical impact of osteoporosis; identified barriers to patient adherence; and sought to understand the ways in which osteoporotic patients can better share and obtain information about ...
Biomedical breakthrough: Blood vessels for lab-grown tissues
2011-01-12
Researchers from Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) have broken one of the major roadblocks on the path to growing transplantable tissue in the lab: They've found a way to grow the blood vessels and capillaries needed to keep tissues alive.
The new research is available online and due to appear in the January issue of the journal Acta Biomaterialia.
"The inability to grow blood-vessel networks -- or vasculature -- in lab-grown tissues is the leading problem in regenerative medicine today," said lead co-author Jennifer West, department chair and the ...
Virus killer gets supercharged
2011-01-12
A simple technique to make a common virus-killing material significantly more effective is a breakthrough from the Rice University labs of Andrew Barron and Qilin Li.
Rather than trying to turn the process into profit, the researchers have put it into the public domain. They hope wide adoption will save time, money and perhaps even lives.
The Rice professors and their team reported in Environmental Science and Technology, an American Chemical Society journal, that adding silicone to titanium dioxide, a common disinfectant, dramatically increases its ability to degrade ...
MapsofIndia Unveils Online Quiz Game For Android Devices
2011-01-12
MapsofIndia, a Compare Infobase website and a industry leader in thematic mapping solutions, announced the launch of its fully-featured online India Quiz Game in the Android market, marking its continued commitment and expansion into the burgeoning mobile platform.
MapsofIndia's first of its kind game is developed to reside on Android based computing platforms. The online India Quiz Game offers the large fraternity of mobile and internet users, an unmatched opportunity to tease their brains and pit their wits against thousands of their peers and win exciting prizes. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
[Press-News.org] Inside a snowstorm: Scientists obtain close-up look at Old Man WinterDoppler-on-wheels gives new view of lake-effect snows