(Press-News.org) New research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research suggests that the physical postures, breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices of yoga may benefit individuals with back pain.
In the study, 10 women with and 11 without chronic low back pain underwent an 8‐session yoga program over 4 weeks, with the first session conducted in a clinic and the rest delivered with a tele‐approach. Women with chronic low back pain experienced a significant decrease in pain intensity, as assessed through a 10-point visual analog scale (an average pain of 6.80 at the start, dropped to 3.30 after the sessions) and through a spine-related measure called the flexion–relaxation phenomenon, which is often absent or disrupted in people with low back pain (5.12 at the start versus 9.49 after the sessions).
The findings suggest yoga can positively impact the neuromuscular response during trunk flexion and pain perception in individuals with chronic low back pain.
“It was interesting to show the role that yoga might play in the management of chronic back pain,” said corresponding author Prof. Alessandro de Sire, MD, of the University of Catanzaro “Magna Graecia” and University Hospital “Renato Dulbecco,” in Italy.
The authors noted that further research is warranted to assess yoga’s long‐term effects.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jor.25790
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Orthopaedic Research, a publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, is the forum for the rapid publication of high quality reports of new information on the full spectrum of orthopaedic research, including life sciences, engineering, translational, and clinical studies.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Can yoga effectively treat chronic back pain?
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do immigrant deaths at the border influence white and Latinx Americans’ belief in the American dream?
2024-02-21
The American dream narrative posits that anyone who works hard can become successful in the US, whereas the systemic racism narrative argues that the US is a racist country where minorities are systemically held back.
A survey-based study in Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy found that these narratives predict individuals’ support for the presidential candidacy of Donald Trump or Joe Biden, above and beyond more traditional political ideologies.
In a follow-up experiment in which participants were confronted with news clips of immigrant deaths at the border, white individuals decreased their ...
How do renewable energy and innovation impact environmental quality in different countries?
2024-02-21
Renewable energy production leads to reduced carbon dioxide emissions in countries that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) but increased emissions in emerging economies, according to the results of a study published in the Natural Resources Forum. A similar disparity was seen when considering the environmental impacts of innovation. (The OECD is an international organization that works to build better policies for better lives. Thirty-eight countries around the world are currently members.)
Regarding ...
Does watching TV or videos during the day affect nighttime urination?
2024-02-21
In a study published in Neurourology and Urodynamics, adults who spent 5 or more hours a day watching TV and/or videos were more likely to develop nocturia, or the need to urinate multiple times during the night.
The study drew from 2011–2016 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Among 13,294 US individuals aged 20 and older, 4,236 (31.86%) reported experiencing nocturia, while 9,058 (68.14%) did not. Participants with 5 or more hours of TV and/or video viewing time per day had a 48% higher risk of experiencing nocturia compared with those with less than 1 hour of daily TV and/or video viewing time.
“As ...
How do chronic inflammation and physical inactivity affect age-related changes in gene and protein expression in skeletal muscle?
2024-02-21
New research indicates that some age-related changes in gene and protein expression in the skeletal muscles of older individuals may be affected more by physical inactivity and chronic inflammation than primary aging, or intrinsic maturational processes.
Physical inactivity and chronic inflammation are the most important drivers of secondary aging, or changes over time that are caused by extrinsic factors such as diseases or poor health practices.
In the Aging Cell study that included 15 young healthy people and 8 young and 37 older patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis (who suffered from long-term inactivity ...
Study finds menthol cigarette ban would lead a lot of people to quit smoking
2024-02-21
A new paper in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, published by Oxford University Press, finds that banning the sale of menthol cigarettes would likely lead to a meaningful reduction in smoking rates.
Menthol cigarettes are of particular public health concern because studies have found that the cooling effects of menthol mask the harshness of cigarettes, making it easier for young people to start smoking. Prior research has also found that menthol in cigarettes makes it easier for smokers to absorb nicotine, which results in ...
New cloud model could help with climate research
2024-02-21
When clouds meet clear skies, cloud droplets evaporate as they mix with dry air. A new study involving researchers from the University of Gothenburg has succeeded in capturing what happens in a model. Ultimately, this could lead to more accurate climate modeling in the future.
The clouds in the sky have a significant impact on our climate. Not only do they produce precipitation and provide shade from the sun, they also act as large reflectors that prevent the radiation of heat from the Earth – commonly known as the greenhouse effect.
“Although clouds have been studied for a long time, they are one of the biggest sources of uncertainty in climate models,” ...
Unravelling the genetic and environmental influences on trust
2024-02-21
Trust, a cornerstone of human interaction, has a significant genetic component, with around 33% of the variation between individuals attributed to our genes, according to new Australian research using data from twins and a meta-analysis of previous studies on the heritability of trust.
Successful relationships, economic transactions and social cohesion are all a matter of trust. Without trust, businesses collapse, political parties fail, and conflicts erupt, whether on a personal or international scale, resulting in broken hearts and lives lost.
“Higher levels of trust are associated with a range of social and economic benefits, ...
People who a eat healthy, plant-based diet are less likely to suffer with dangerous snoring
2024-02-21
People who eat a healthy, plant-based diet that is high in vegetables, fruit, whole grains and nuts are less likely to suffer with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, people eating an unhealthy plant-based diet, high in refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, high-sugar and high-salt foods, are at a higher risk of OSA.
People with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Not only does this cause tiredness, but it can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The new study ...
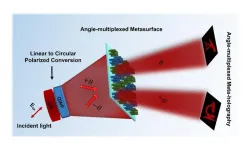
Angle-dependent holograms made possible by metasurfaces
2024-02-21
The expression "flawless from every angle" is commonly used to characterize a celebrity's appearance. This doesn't simply imply that they appear attractive from a specific viewpoint, but rather that their appeal remains consistent and appealing from various angles and perspectives. Recently, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has employed metasurface to fabricate angle-dependent holograms with multiple functions, capturing significant interest within ...
These tiny power converters run on vibrational energy
2024-02-21
University of California San Diego and CEA-Leti scientists have developed a ground-breaking piezoelectric-based DC-DC converter that unifies all power switches onto a single chip to increase power density. This new power topology, which extends beyond existing topologies, blends the advantages of piezoelectric converters with capacitive-based DC-DC converters.
The power converters the team developed are much smaller than the huge, bulky inductors currently used for this role. The devices could eventually be used for any type of DC-DC conversation, ...